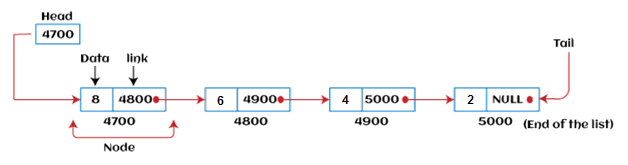
A linked list is a sequence of data structures, which are connected together via links. A linked list is a linear data structure that includes a series of connected nodes. Here, each node stores the data and the address of the next node. For example :
Linked list can be visualized as a chain of nodes, where every node points to the next node.

-
Linked list is a data structure that overcomes the limitations of arrays. Let's first see some of the limitations of arrays -
- The size of the array must be known in advance before using it in the program.
- Increasing the size of the array is a time taking process. It is almost impossible to expand the size of the array at run time.
- All the elements in the array need to be contiguously stored in the memory. Inserting an element in the array needs shifting of all its predecessors.
-
Linked list is useful because -
- It allocates the memory dynamically. All the nodes of the linked list are non-contiguously stored in the memory and linked together with the help of pointers.
- In linked list, size is no longer a problem since we do not need to define its size at the time of declaration. List grows as per the program's demand and limited to the available memory space.
struct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
};
Linked list is classified into the following types :
-
Singly Linked List - Singly linked list can be defined as the collection of an ordered set of elements. A node in the singly linked list consists of two parts: data part and link part. Data part of the node stores actual information that is to be represented by the node, while the link part of the node stores the address of its immediate successor.
-
Doubly Linked List - Doubly linked list is a complex type of linked list in which a node contains a pointer to the previous as well as the next node in the sequence. Therefore, in a doubly-linked list, a node consists of three parts: node data, pointer to the next node in sequence (next pointer), and pointer to the previous node (previous pointer).
-
Circular Singly Linked List - In a circular singly linked list, the last node of the list contains a pointer to the first node of the list. We can have circular singly linked list as well as circular doubly linked list.
-
Circular Doubly Linked List - Circular doubly linked list is a more complex type of data structure in which a node contains pointers to its previous node as well as the next node. Circular doubly linked list doesn't contain NULL in any of the nodes. The last node of the list contains the address of the first node of the list. The first node of the list also contains the address of the last node in its previous pointer.
Following are the basic operations supported by a list.
- Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
- Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
- Display − Displays the complete list.
- Search − Searches an element using the given key.
- Delete − Deletes an element using the given key.
For a complete Linked List program in C programming language. Please check out above code files.