2. 两数相加
61. 旋转链表
141.环形链表
⚡23. 合并K个升序链表 面试遇到
206.反转链表 相关题:92. 反转链表 II、 143. 重排链表、 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 25. K 个一组翻转链表
203. 移除链表元素 相关题:83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素、 82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
21.合并两个有序链表 相关题:148-排序链表
234. 回文链表 递归方法很巧妙
86. 分隔链表
-
链表是一种兼具递归和迭代性质(子问题)的数据结构。很多题用递归写起来非常快
-
哑结点用来避免某些极端情况,比如需要对头结点进行操作。
Difficulty: 简单
请编写一个函数,使其可以删除某个链表中给定的(非末尾)节点。传入函数的唯一参数为 要被删除的节点 。
现有一个链表 -- head = [4,5,1,9],它可以表示为:
示例 1:
输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 5
输出:[4,1,9]
解释:给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
示例 2:
输入:head = [4,5,1,9], node = 1
输出:[4,5,9]
解释:给定你链表中值为 1 的第三个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 5 -> 9.
提示:
- 链表至少包含两个节点。
- 链表中所有节点的值都是唯一的。
- 给定的节点为非末尾节点并且一定是链表中的一个有效节点。
- 不要从你的函数中返回任何结果。
思路:思维很容易被局限住。可以和后面的节点交换一下,然后指向后面的后面。
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}Difficulty: 中等
进阶题:445. 两数相加 II
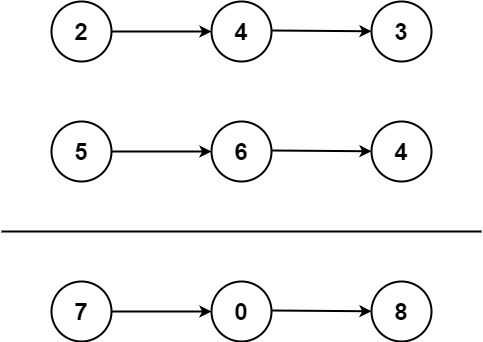
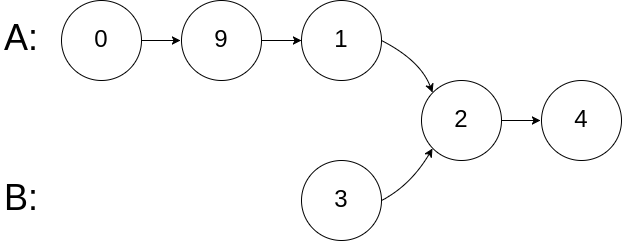
给你两个 非空 的链表,表示两个非负的整数。它们每位数字都是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
请你将两个数相加,并以相同形式返回一个表示和的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
输出:[7,0,8]
解释:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
输出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
提示:
- 每个链表中的节点数在范围
[1, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 9- 题目数据保证列表表示的数字不含前导零
思路:本身就是逆序,直接遍历相加即可。
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) {
return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode head = dummy;
int sum = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || sum != 0) {
if (l1 != null) {
sum += l1.val;
l1 = l1.next;
}
if (l2 != null) {
sum += l2.val;
l2 = l2.next;
}
head.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
head = head.next;
sum = sum / 10;
}
return dummy.next;
}Difficulty: 中等
给你两个 非空 链表来代表两个非负整数。数字最高位位于链表开始位置。它们的每个节点只存储一位数字。将这两数相加会返回一个新的链表。
你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
进阶:
如果输入链表不能修改该如何处理?换句话说,你不能对列表中的节点进行翻转。
示例:
输入:(7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
思路:逆序——用Stack。重新构造一个链表
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
Stack<ListNode> l1Stack = new Stack<>();
while (l1 != null) {
l1Stack.push(l1);
l1 = l1.next;
}
Stack<ListNode> l2Stack = new Stack<>();
while (l2 != null) {
l2Stack.push(l2);
l2 = l2.next;
}
int carry = 0;
ListNode nextNode = null;
while (!l1Stack.isEmpty() || !l2Stack.isEmpty() || carry != 0) {
int n1 = l1Stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : l1Stack.pop().val;
int n2 = l2Stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : l2Stack.pop().val;
int sum = n1 + n2 + carry;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum % 10);
newNode.next = nextNode;
nextNode = newNode;
carry = sum / 10;
}
return nextNode;
}Difficulty: 困难
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。
如果节点总数不是k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
示例:
给你这个链表:1->2->3->4->5
当 k = 2 时,应当返回: 2->1->4->3->5
当 k = 3 时,应当返回: 3->2->1->4->5
说明:
- 你的算法只能使用常数的额外空间。
- 你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode tail = dummy;
while (tail.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k && tail != null; i++) tail = tail.next;
if (tail == null) break;
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode nextNode = tail.next;
tail.next = null;
pre.next = reverse(start);
start.next = nextNode;
pre = start;
tail = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = pre;
pre = curr;
curr = next;
}
return pre;
}递归方法更简单:先数出k个来,后面的又是相同的翻转k个链表的问题。
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode cur = head;
int cnt = 0;
while (cur != null && cnt != k) {
cur = cur.next;
cnt++;
}
if (cnt == k) {
cur = reverseKGroup(cur, k);
//只需要把前k个按序连接到cur的前面即可
while (cnt != 0) {
ListNode tmp = head.next;
head.next = cur;
cur = head;
head = tmp;
cnt--;
}
head = cur;
}
return head;
}Difficulty: 简单
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有 6 个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是 1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第 2 个节点是值为 4 的节点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (fast == null) {
return null;
}
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}Difficulty: 中等 偏简单
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
**进阶:**你能尝试使用一趟扫描实现吗?
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中结点的数目为
sz 1 <= sz <= 300 <= Node.val <= 1001 <= n <= sz
思路:快慢双指针,也很简单。涉及到后续的,也应该想到stack——先进后出。
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummy, slow = dummy;
// Advances fast pointer so that the gap between fast and slow is n nodes apart
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
fast = fast.next;
}
// Move fast to the end, maintaining the gap
while (fast != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
slow.next = slow.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}Difficulty: 中等
给定一个链表,旋转链表,将链表每个节点向右移动 _k _个位置,其中 _k _是非负数。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
输出: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
示例 2:
输入: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
输出: 2->0->1->NULL
解释:
向右旋转 1 步: 2->0->1->NULL
向右旋转 2 步: 1->2->0->NULL
向右旋转 3 步: 0->1->2->NULL
向右旋转 4 步: 2->0->1->NULL
思路:先统计链表的长度,再快慢指针找到倒数第k个,断开,连接末尾-快指针与原链表头部。
这里提供另一种思路:先遍历连接链表成环,然后找到断开位置断开环。
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 1. 找尾节点,形成环形链表;统计链表长度
ListNode curr = head;
int len = 1;
while (curr.next != null) {
len++;
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = head;
// 2. 找到断开位置
k = k % len;
for (int i = 0; i < len - k; i++) {
curr = curr.next;
}
head = curr.next;
curr.next = null;
return head;
}Difficulty: 简单
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递,仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
进阶:
你能用 O(1)(即,常量)内存解决此问题吗?
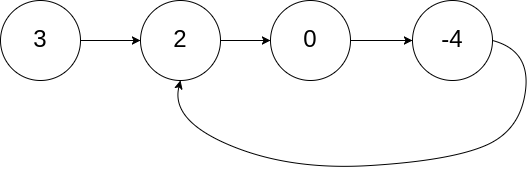
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
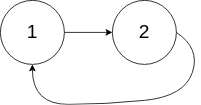
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 104]
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos为-1或者链表中的一个 有效索引 。
思路:快慢指针,若存在环,必相遇。
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) { //这个判断可以删掉
return false;
}
ListNode fast = head, slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}Difficulty: 中等
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。注意,pos 仅仅是用于标识环的情况,并不会作为参数传递到函数中。
**说明:**不允许修改给定的链表。
进阶:
- 你是否可以使用
O(1)空间解决此题?
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:返回索引为 0 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:返回 null
解释:链表中没有环。
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目范围在范围 [0, 104] 内
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
pos的值为-1或者链表中的一个有效索引
思路:判断是否存在,最直接的方法是Set,空间复杂度是O(N)。O(1)方法需要利用141.环形链表快慢双指针方法,这种方法需要数学证明,第一次做其实很难想到。
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
} else {
return null;
}
if (fast == slow) {
fast = head;
while (fast != slow) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return null;
}Difficulty: 简单
**相关题目:[92. 反转链表 II](#92-反转链表 II) 143. 重排链表 24. 两两交换链表中的节点 [25. K 个一组翻转链表](#25-K 个一组翻转链表) **
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
进阶: 你可以迭代或递归地反转链表。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
//1. 递归方法
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head; //下一节点指向当前节点
head.next = null; //当前节点指向空 返回上一层递归后当前节点又会作为下一节点继续往前指
return newHead;
}
//2. 迭代方法
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode nextNode = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = nextNode;
}
return pre;
}Difficulty: 简单
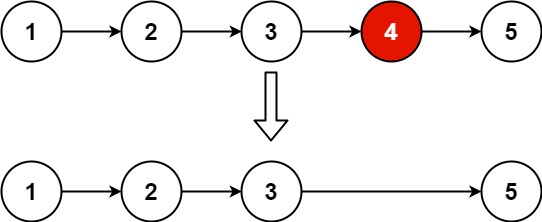
删除链表中等于给定值 **_val _**的所有节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->6->3->4->5->6, val = 6
输出: 1->2->3->4->5
//1. 递归
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
if (head.val == val) {
return head.next;
} else {
return head;
}
}
//2. 迭代
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode curr = dummy;
while(curr != null && curr.next != null){
if(curr.next.val == val){
curr.next = curr.next.next;
}else {
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
}Difficulty: 简单
给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
示例 1:
输入: 1->1->2
输出: 1->2
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->2->3->3
输出: 1->2->3
//1. 递归
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
if (head.val == head.next.val) {
return head.next;
} else {
return head;
}
}
//2. 迭代
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null && cur.next != null) {
if(cur.val == cur.next.val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}Difficulty: 简单
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例 1:
输入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
输出:[0]
提示:
- 两个链表的节点数目范围是
[0, 50] -100 <= Node.val <= 100l1和l2均按 非递减顺序 排列
//1. 递归方法
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
//2. 迭代方法 用头节点
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 合并后 l1 和 l2 最多只有一个还未被合并完,直接将链表末尾指向未合并完的链表即可
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return dummy.next;
}Difficulty: 简单
请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: 1->2->2->1
输出: true
进阶:
你能否用 O(n) 时间复杂度和 O(1) 空间复杂度解决此题?
思路:用快慢指针遍历的同时翻转前半部分,然后与后半部分比较。
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
ListNode temp = slow.next;
if (pre != null) {
slow.next = pre;
}
pre = slow;
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = temp;
}
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while (slow != null) {
if (slow.val != pre.val) {
return false;
}
slow = slow.next;
pre = pre.next;
}
return true;
}更巧妙的解法:递归
class Solution {
private ListNode frontPointer;
private boolean recursivelyCheck(ListNode currentNode) {
if (currentNode != null) {
if (!recursivelyCheck(currentNode.next)) {
return false;
}
if (currentNode.val != frontPointer.val) {
return false;
}
frontPointer = frontPointer.next;
}
return true;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
frontPointer = head;
return recursivelyCheck(head);
}
}
作者:LeetCode-Solution
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/solution/hui-wen-lian-biao-by-leetcode-solution/
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。相关高频题:9. 回文数
Difficulty: 中等
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
pre = pre.next;
}
ListNode start = pre.next;
ListNode then = start.next;
// 1 - 2 -3 - 4 - 5 ; m=2; n =4 ---> pre = 1, start = 2, then = 3
// dummy-> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
// dummy->1 - 3 - 2 - 4 - 5; pre = 1, start = 2, then = 4
// dummy->1 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 5; pre = 1, start = 2, then = 5
for (int i = 0; i < n - m; i++) {
start.next = then.next;
then.next = pre.next;
pre.next = then;
then = start.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}也可以用递归方法:todo
Difficulty: 中等
给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 _没有重复出现 _的数字。
示例 1:
输入: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5
输出: 1->2->5
示例 2:
输入: 1->1->1->2->3
输出: 2->3
//1. 递归
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
if (head.next.val == head.val) {
while (head.next != null && head.next.val == head.val) {
head = head.next;
}
return deleteDuplicates(head.next);
} else {
head.next = deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head;
}
}
//2. 迭代,用哑节点
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
while (temp.next != null && temp.val == temp.next.val) {
temp = temp.next;
}
cur.next = temp.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummy.next;
} Difficulty: 中等
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
进阶:
- 你可以在
O(n log n)时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
示例 1:
输入:head = [4,2,1,3]
输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 5 * 104] 内
- -105 <= Node.val <= 105
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// 1、递归结束条件
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 2、找到链表中间节点并断开链表
ListNode midNode = middleNode(head);
ListNode rightHead = midNode.next;
midNode.next = null;
ListNode left = sortList(head);
ListNode right = sortList(rightHead);
// 3、合并有序链表
return mergeTwoLists(left, right);
}
// 找到链表中间节点(876. 链表的中间结点)
private ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next.next;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow;
}
// 合并两个有序链表(21. 合并两个有序链表)
private ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode curr = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
curr.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
curr.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
curr = curr.next;
}
curr.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
return dummy.next;
}常数级空间复杂度的方法:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
int length = getLength(head);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
for(int step = 1; step < length; step*=2){ //依次将链表分成1块,2块,4块...
//每次变换步长,pre指针和cur指针都初始化在链表头
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = dummy.next;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode h1 = cur; //第一部分头 (第二次循环之后,cur为剩余部分头,不断往后把链表按照步长step分成一块一块...)
ListNode h2 = split(h1,step); //第二部分头
cur = split(h2,step); //剩余部分的头
ListNode temp = merge(h1,h2); //将一二部分排序合并
pre.next = temp; //将前面的部分与排序好的部分连接
while(pre.next!=null){
pre = pre.next; //把pre指针移动到排序好的部分的末尾
}
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
public int getLength(ListNode head){
//获取链表长度
int count = 0;
while(head!=null){
count++;
head=head.next;
}
return count;
}
public ListNode split(ListNode head,int step){
//断链操作 返回第二部分链表头
if(head==null) return null;
ListNode cur = head;
for(int i=1; i<step && cur.next!=null; i++){
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode right = cur.next;
cur.next = null; //切断连接
return right;
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode h1, ListNode h2){
//合并两个有序链表
ListNode head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p = head;
while(h1!=null && h2!=null){
if(h1.val < h2.val){
p.next = h1;
h1 = h1.next;
}
else{
p.next = h2;
h2 = h2.next;
}
p = p.next;
}
if(h1!=null) p.next = h1;
if(h2!=null) p.next = h2;
return head.next;
}
}
作者:cherry-n1
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/solution/pai-xu-lian-biao-di-gui-die-dai-xiang-jie-by-cherr/Difficulty: 中等
给定一个单链表 L:L0→_L_1→…→_L_n-1→_L_n ,
将其重新排列后变为: L0→_L_n→_L_1→_L_n-1→_L_2→_L_n-2→…
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
给定链表 1->2->3->4, 重新排列为 1->4->2->3.
示例 2:
给定链表 1->2->3->4->5, 重新排列为 1->5->2->4->3.思路:先找中点,翻转后半部分,再合并。
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return;
}
ListNode mid = findMiddle(head);
ListNode left = head;
ListNode right = mid.next;
mid.next = null;
right = reverse(right);
mergeList(left, right);
}
//靠右的中点 876. 链表的中间结点
private ListNode findMiddle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
//206. 反转链表
private ListNode reverse(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode newHead = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return newHead;
}
private ListNode mergeList(ListNode left, ListNode right) {
if (left == null || right == null) {
return left == null ? right : left;
}
ListNode merge = mergeList(left.next, right.next);
left.next = right;
right.next = merge;
return left;
}Difficulty: 中等
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1]
输出:[1]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 100]内 0 <= Node.val <= 100
**进阶:**你能在不修改链表节点值的情况下解决这个问题吗?(也就是说,仅修改节点本身。)
//1. 递归
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode res = swapPairs(head.next.next);
ListNode ret = head.next;
ret.next = head;
head.next = res;
return ret;
}
//2. 迭代
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = new ListNode(-1);
pre.next = head;
ListNode temp = pre;
while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {
ListNode first = temp.next;
ListNode second = temp.next.next;
temp.next = second;
first.next = second.next;
second.next = first;
temp = first;
}
return pre.next;
}Difficulty: 中等
给你一个链表的头节点 head 和一个特定值x ,请你对链表进行分隔,使得所有 小于 x 的节点都出现在 大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当 保留 两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,4,3,2,5,2], x = 3
输出:[1,2,2,4,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [2,1], x = 2
输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 链表中节点的数目在范围
[0, 200]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100-200 <= x <= 200
思路:很直接,用两个链表再融合
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
ListNode dummy1 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode dummy2 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode p1 = dummy1, p2 = dummy2;
while (head != null) {
if (head.val < x) {
p1.next = head;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
p2.next = head;
p2 = p2.next;
}
head = head.next;
}
p1.next = dummy2.next;
p2.next = null;
return dummy1.next;
}Difficulty: 困难
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。
1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
示例 2:
输入:lists = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:lists = [[]]
输出:[]
提示:
k == lists.length0 <= k <= 10^40 <= lists[i].length <= 500-10^4 <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4lists[i]按 升序 排列lists[i].length的总和不超过10^4
归并:
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) {
return null;
}
return mergeKLists(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
private ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) {
return lists[left];
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2; //int mid = (left+right)>>>1;
return merge(mergeKLists(lists, left, mid), mergeKLists(lists, mid + 1, right));
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) {
return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = merge(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = merge(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}PQ:
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length, new Comparator<ListNode>() {
@Override
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
return o1.val - o2.val;
}
});
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if (node != null) queue.add(node);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
p.next = queue.poll();
p = p.next;
if (p.next != null) queue.add(p.next);
}
return dummy.next;
}
//或者用lambda表达式
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists == null || lists.length == 0) return null;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length,
(a,b)-> (a.val - b.val)
);
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = dummy;
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if (node != null) queue.add(node);
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
p.next = queue.poll();
p = p.next;
if (p.next != null) queue.add(p.next);
}
return dummy.next;
}Difficulty: 简单
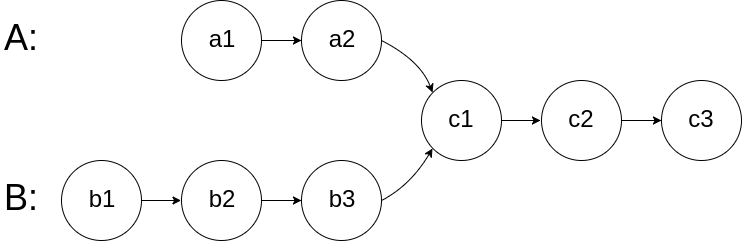
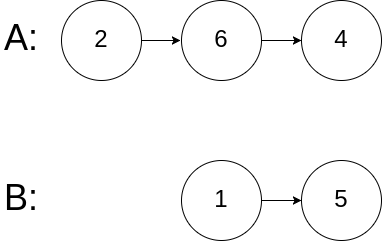
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
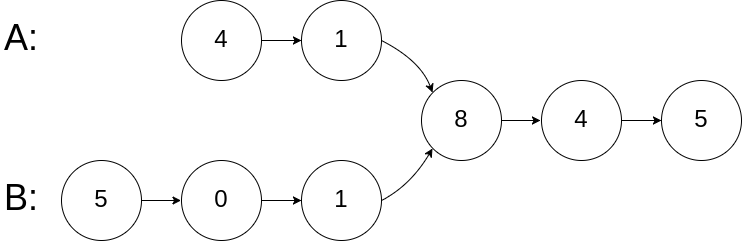
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回
null. - 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
思路:双指针。各自遍历,走到尽头交换到另一个的起点继续遍历,如果有交点,最终会在交点相遇。如果没有,同时变为null。
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
ListNode currA = headA, currB = headB;
while (currA != currB) {
currA = currA == null ? headB : currA.next;
currB = currB == null ? headA : currB.next;
}
return currA;
}2020字节实习二面遇到
Difficulty: 运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制 。
运用你所掌握的数据结构,设计和实现一个 。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以正整数作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字已经存在,则变更其数据值;如果关键字不存在,则插入该组「关键字-值」。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最久未使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
进阶:你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内完成这两种操作?
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 3000- 0 <= value <= 104
- 最多调用 3 * 104 次
get和put
**思路:**本题的关键是各个方法都要O(1)时间复杂度实现,因此要寻找合适的数据结构。
- 考虑用什么数据结构
- get需要O(1),必须用HashMap
- put需要O(1),当达到capacity之后,要删除最近最少使用的,只用HashMap是无法记录顺序的,需要借助链表。链表要实现O(1)删除指定节点,该节点的前一个结点要指向后一个结点,因此需要双向链表来O(1)获取到该节点的前一个结点pre和后一个结点next。
- HashMap和双向链表分别存什么内容呢?HashMap当然存放key,链表只存放value可以吗?
- 当达到capacity之后,要删除最近最少使用的,也就是链表的末尾(从链表头加入),如果只有value,没办法删除HashMap中的对应key。因此链表需要存key和value。
- 考虑实现顺序
- 建议把问题拆分成子问题。先设计Node结点,包含key和value。再实现双向链表,包含LRUCache依赖的各种方法,最后再实现LRUCache。
- 双向链表需要提供什么方法?
- 至少应该包括:
- 从头结点插入 addFirst(Node node)
- 删除指定结点 remove(Node node)
- 为了兼容删除最后一个结点的特殊情况,可以使用sentinel,首尾各一个sentinel结点,先相互指向,然后在他们之间添加和删除结点。
- 至少应该包括:
public class LRUCache {
static class Node {
private Node pre;
private Node next;
private int key;
private int value;
public Node(int key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
static class DoubleList {
private Node head;
private Node tail;
//为了兼容删除最后一个结点的特殊情况,使用sentinel,首尾相互指向
public DoubleList() {
head = new Node(-1, -1);
tail = new Node(-1, -1);
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
}
private void remove(Node node) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
}
private void addFirst(Node node) {
node.next = head.next;
head.next.pre = node;
node.pre = head;
head.next = node;
}
//把最近刚使用的结点移动到链表的最前面。
private void moveNodeToFirst(Node node) {
remove(node);
addFirst(node);
}
}
private final HashMap<Integer, Node> map;
private DoubleList cache;
private final int capacity;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
map = new HashMap<>();
cache = new DoubleList();
}
public int get(int key) {
Node res = map.get(key);
if (res == null) {
return -1;
} else {
cache.moveNodeToFirst(res);
}
return res.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
Node node = map.get(key);
if (node == null) {
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
//注意:添加的时候Map和DoubleList中都要添加,别忘了
cache.addFirst(newNode);
map.put(key, newNode);
//如果超过capacity,需要删除最近最少使用的结点,也就是队尾的结点。
if (map.size() > capacity) {
Node removeN = cache.tail.pre;
//注意:删除的时候Map和DoubleList中都要删除,别忘了
map.remove(removeN.key);
cache.remove(removeN);
}
} else {
node.value = value;
cache.moveNodeToFirst(node);
}
}
}还可以用LinkedHashMap,题解
相关高频题:
**460. LFU缓存*f