A python library for teaching TensorFlow neural networks to play Blackjack and count cards.
Blackjack.py is used to generate data sets about hands of blackjack via Monte Carlo simulations. This is done by generating random hands, letting the computer make random moves, and storing representations of the hands tagged with the eventual outcome of the decision.
git clone https://github.com/justinbodnar/Artificial-Intelligence-in-BlackJack-Card-Counting.git pip install -r requirements.txt
To generate a data set of Blackjack hands using Monte Carlo simulations use:
import Blackjack as blackjack blackjack.gen_data_set( 100, "test", 1 )
The first parameter is how many hands to play (note the data set may be larger as each 'hit' will generate another data point). The second parameter is the name of the file to save to in the '/data_sets' directory. the example code will create two files '/data_sets/test.data' and '/data_sets/test.tags' If the data set already exists the new data points will be appended. The third paramter is the level of information to put in the dataset.
Level 1 stores only information about the players hand value. Level 2 stores level 1 plus the dealers face-up card. Level 3 stores level 2 plus a record of all cards seen.
For the purpose of training a nuerel network to play blackjack, we want to represent a hand in a way that tells us whether we should 'hit' or 'stay.' Luckily we only need to store a few integers. We then tag the data as either 'h' or 's' for 'hit' or 'stay.'
How we determine whether the hand warrants a 'h' or 's' is a matter of opinion. The current iteration will simply append in the following manner:
if user hits and busts: tag = 's' elif user hits and doesn't bust: tag = 'h' elif user stays and wins hand: tag = 's' elif user stays and loses hand: tag = 'h'
Example scenarios and expected data:
Example 1 player hand: ( 3-s, 4-c ) player hits player hand: ( 3-s, 4-c, 12-d ) player stays dealer busts generated data and tags: (because we won the game, we assume every move was a good move) 7, h # hit on 7 19, s # stay on 19 Example 2 player hand: ( 2-d, 10-c ) player hits player hand: ( 2-d, 10-c, 2-s ) player hits player hand: ( 2-d, 10-c, 2-s, 9-c ) player busts generated data and tag 12, h 14, s
The first model teaches a neural net to play based soley on the value of the current hand. A data set for this task was produced with 3,959 monte carlo simulations generated with Blackjack.py. The data set is located at /data_sets/blackjack.data.1 and /data_sets/blackjack.tags.1.
code to create this data set
import Blackjack as bj bj.gen_data_set( 3000, "blackjack1", 1 ) # this was renamed later
code for preprocessing the level 1 data set
# get the data set
data = open( "data_sets/blackjack2-2-out.data").readlines()
tags = open( "data_sets/blackjack2-2-out.tags").readlines()
data_clean = []
tags_clean = []
#strip whitespaces and such
first = True
i = 0
for datum in data:
# skip empty line first
if first:
first = False
continue
clean_datum = datum[:datum.index('\n')].strip()
data_clean = data_clean + [ int(clean_datum) ]
first = True
for tag in tags:
if first:
first = False
continue
tag = tag[:tag.index('\n')]
if tag is "h":
tags_clean = tags_clean + [ 1.0 ]
else:
tags_clean = tags_clean + [ 0.0 ]
size = int( len(data)*(0.75) )
train_data = np.array( data_clean[1:size] )
train_tags = np.array( tags_clean[1:size] )
test_data = np.array( data_clean[size:] )
test_tags = np.array( tags_clean[size:] )
The model in this example a dense 2-layer neurel network. The first layer contained 4096 neurons, while the second only had two, for 'hit' or 'stay.' The 'adam' optimizer was used, with a loss of 'sparse_categorical_crossentropy.' Training and testing data was split 50/50 randomly. There are 10 epochs.
code for training the model
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add( keras.layers.Dense(4096, input_dim=2) )
model.add( keras.layers.Dense(2, activation=tf.nn.softmax) )
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_data, train_tags, epochs=10)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_data, test_tags)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)
The model will output the accuracy of the model, using a random 25% of input as test cases. The model can then be saved via
# save model
# taken from https://machinelearningmastery.com/save-load-keras-deep-learning-models/
model_json = model.to_json()
with open( "models/blackjackmodel.1.json", "w") as json_file:
json_file.write(model_json)
# serialize weights to HDF5
model.save_weights("models/blackjackmodel.1.h5")
print( "Model saved" )
To find a heuristic, hand values from 2-21 were tested on the classifier. To do this we need to first deserialize the model from its file
# open serialized model
# taken from https://machinelearningmastery.com/save-load-keras-deep-learning-models/
json_file = open('models/blackjackmodel.1.json', 'r')
loaded_model_json = json_file.read()
json_file.close()
model = keras.models.model_from_json( loaded_model_json, custom_objects={"GlorotUniform": tf.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform} )
model.load_weights( "models/blackjackmodel.1.h5" )
print( "Model loaded from disk" )
Giving the test cases was done via
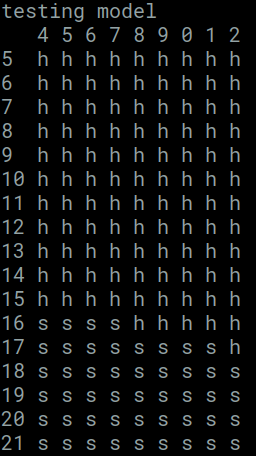
print( "testing model" ) for i in range(21): prediction = model.predict( np.array([ [i,10] ]) ) if prediction[0][0] > prediction[0][1]: print( str(i) + " stay" ) else: print( str(i) + " hit" )
This gave the output
0 hit 1 hit 2 hit 3 hit 4 hit 5 hit 6 hit 7 hit 8 hit 9 hit 10 hit 11 hit 12 hit 13 hit 14 hit 15 hit 16 hit 17 stay 18 stay 19 stay 20 stay
The model learned to hit on any hand value below 17. This happens to be the strategy used by the dealer.
To test the model against a large number of monte carlo simulations, we can use the test_model() function in Blackjack.py. The command is
wins, losses, ties = test_model( "blackjackmodel.1", 10000, True, 1, False ) total = wins + losses + ties win_percentage = (wins/total)*100.0 loss_percentage = (losses/total)*100.0 tie_percentage = (ties/total)*100.0 print( "Percentage won: " + str( win_percentage ) )
The win percentage for 10,000 games for this model is 52.42%.
This model will use all the previous techniques, but the data set will now include the dealer's upward facing card.
So where previously we used the single integer for data, we will now use a tuple of players_hand, and dealers_hand respectively.
Example
[ 18, 13, s ]
The data set for this consists of 5,323 entries, located in data_sets/blackjack.data.2 and data_sets/blackjack.tags.2. Loading the data is done the same as in model 1.
code to generate this data set
import Blackjack as bj bj.gen_data_set( 4000, "test", 2 ) # this was renamed later
Code to grab the data from the data set
# get the data set
data = open( "data_sets/blackjack2-2-out.data").readlines()
tags = open( "data_sets/blackjack2-2-out.tags").readlines()
data_clean = []
tags_clean = []
#strip whitespace
first = True
i = 0
for datum in data:
# skip empty line first
if first:
first = False
continue
clean_datum = datum[:datum.index('\n')].strip()
clean_datum = clean_datum[1:-1].split(',')
clean_datum[0] = int( clean_datum[0] )
clean_datum[1] = int( clean_datum[1][1:] )
print( clean_datum )
data_clean = data_clean + [ clean_datum ]
first = True
for tag in tags:
if first:
first = False
continue
tag = tag[:tag.index('\n')]
if tag is "h":
tags_clean = tags_clean + [ 1.0 ]
else:
tags_clean = tags_clean + [ 0.0 ]
size = int( len(data)*(0.75) )
train_data = np.array( data_clean[1:size] )
train_tags = np.array( tags_clean[1:size] )
test_data = np.array( data_clean[size:] )
test_tags = np.array( tags_clean[size:] )
The neural network used a similar layer scheme as the previous, with an 16-neuron second layer. The optimizer was 'nadam,' and there were 100 epochs.
code for training this network
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add( keras.layers.Dense(16, input_dim=2) )
model.add( keras.layers.Dense(2, activation=tf.nn.softmax) )
model.compile(optimizer='nadam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_data, train_tags, epochs=100)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_data, test_tags)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)
Notice the only difference between the training of model 1 and model 2 is parameters and file names.
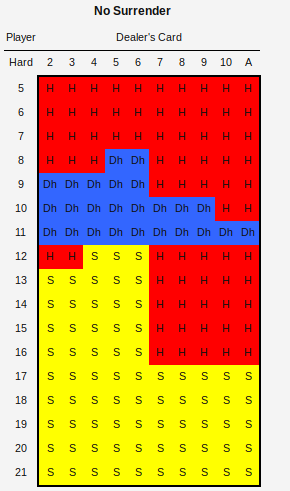
For testing purposes I found this nifty chart for Blackjack strategy at wizardofodds.com/games/blackjack/strategy/calculator/
Generating s imiliar table through the neural entwork can be done via
results = [] for i in range(0,17): results = results + [ "" ] for j in range(0,9): prediction = model.predict( np.array([ [i+5,j+2] ] ) ) if prediction[0][0] > prediction[0][1]: results[i] = results[i] + "s" else: results[i] = results[i] + "h" print( " ", end="" ) for x in range( len(results[0]) ): print( " " + str( (x+4)%10 ), end="" ) print( ) for i in range( len(results) ): print( i+5, end="" ) if i+5 < 10: print( " ", end="" ) else: print( " ", end="" ) for j in range( len(results[i] ) ): print( results[i][j], end=" " ) print( )
This produces the following chart.
There is a clear pattern on both. This confirms the neural network has begun to learn the strategy of Blackjack.
To test the model against a large number of monte carlo simulations, we can use the test_model() function in Blackjack.py. The command is
wins, losses, ties = test_model( "blackjackmodel.2", 10000, True, 2, False ) total = wins + losses + ties win_percentage = (wins/total)*100.0 loss_percentage = (losses/total)*100.0 tie_percentage = (ties/total)*100.0 print( "Percentage won: " + str( win_percentage ) ) print( "Percentage lost: " + str( loss_percentage ) ) print( "Percentage tied: " + str( tie_percentage ) )
The win percentage for 10,000 games for this model is 41.49%. Interestingly, this is less accurate than the model that used less information about the game. This implies the data set is incorrect, corrupt, etc. This will be revisited in future revisions.
This model will use the same data as prevous models, but now it will also contain a record of every card so far seen. The simulation implies the dealer is using a single deck until it runs out of cards, and then reshuffles them.
The data set used contains roughyl 16,979 data points and can be found at /data_sets/blackjack.data.3 and /data_sets/blackjack.tags.3.
code to generate the data set
import Blackjack as blackjack blackjack.gen_data_set( 12000, "test", 3 )
code for preprocessing the level 3 data set
# get the data set
data = open( "data_sets/blackjack.data.1").readlines()
tags = open( "data_sets/blackjack.tags.1").readlines()
data_clean = []
tags_clean = []
#strip whitespace
first = True
for datum in data:
# skip empty line first
if first:
first = False
continue
clean_datum = datum[1:datum.index('\n')-1].strip().split(', ')
clean_datum[0] = int( clean_datum[0] )
clean_datum[1] = int( clean_datum[1] )
print( clean_datum )
data_clean = data_clean + [ clean_datum ]
first = True
for tag in tags:
if first:
first = False
continue
tag = tag[:tag.index('\n')]
if tag is "h":
tags_clean = tags_clean + [ 1.0 ]
else:
tags_clean = tags_clean + [ 0.0 ]
size = int( len(data)*(0.75) )
train_data = np.array( data_clean[1:size] )
train_tags = np.array( tags_clean[1:size] )
test_data = np.array( data_clean[size:] )
test_tags = np.array( tags_clean[size:] )
The third model has a two hidden layer of 64 and 128 neurons respectively. The optimizer was 'adam' and there were 50 epochs. The serialized model can be found at /models/blackjackmodel.3.json and /models/blackjackmodel.3.h5.
code used to train the neural net
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add( keras.layers.Dense( 54, input_dim=54 ) )
model.add( keras.layers.Dense( 64, input_dim=26 ) )
model.add( keras.layers.Dense( 128, input_dim=13 ) )
model.add( keras.layers.Dense(2, activation=tf.nn.softmax) )
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(train_data, train_tags, epochs=50)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_data, test_tags)
print('Test accuracy:', test_acc)
The model had an accuracy of 0.73, similiar to the last two models.
To test the model against a large number of monte carlo simulations, we can use the test_model() function in Blackjack.py. The command is
wins, losses, ties = test_model( "blackjackmodel.3", 10000, True, 3, False ) total = wins + losses + ties win_percentage = (wins/total)*100.0 loss_percentage = (losses/total)*100.0 tie_percentage = (ties/total)*100.0 print( "Percentage won: " + str( win_percentage ) ) print( "Percentage lost: " + str( loss_percentage ) ) print( "Percentage tied: " + str( tie_percentage ) )
The win percentage for 10,000 games for this model is 41.33%. This is less accurate than all other models that used less information about the game. This implies the data set is incorrect, corrupt, etc. This will be revisited in future revisions.
The completed table for the tests comes out to:
level 1: 51.82%
level 2: 41.49%
level 3: 41.33%
only hitting: 3.42%
only staying: 41.99%
random moves: 30.67%
Level 1 is the most accurate model, and the model deteriorates as we gain more information about the game. The data sets clearly need some work. The best classifier is only 9.17% better than simply staying for every hand. Levels 2 and 3 are slightly lower than only staying, though the difference is negligible.
Potential issues:
-repeating hands -different conclusions in the same scenario results in opposite tags
In an attempt to rectify these issue a script was written in /data_sets/preproc.py for preprocessing data sets before training models. The script serves 2 functions:
- if opposing data points are found, the one with the lower number of instances is removed
- duplicates are removed
The script cant be run without being modified. TODO includes functionalizing this script and including it in Blackjack.py.