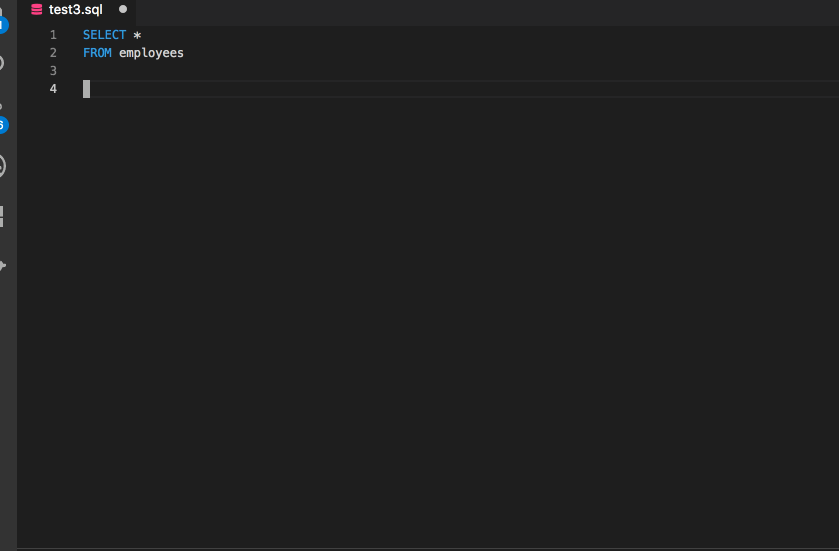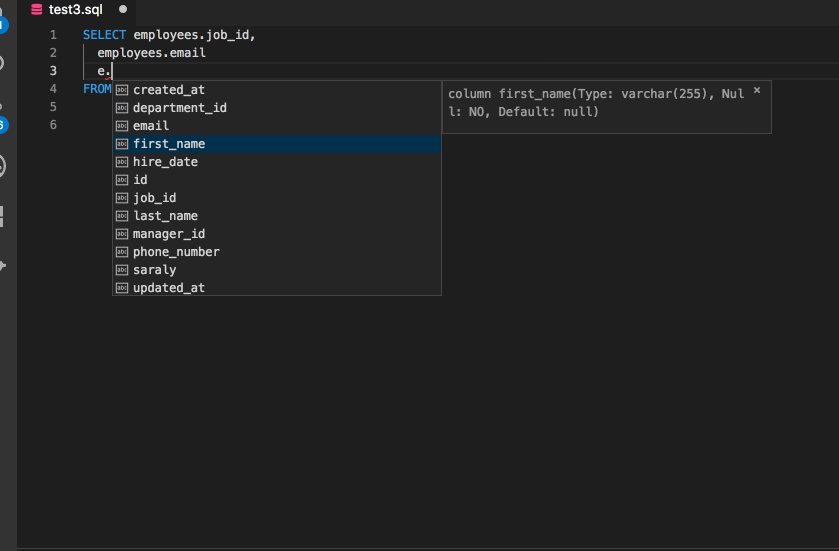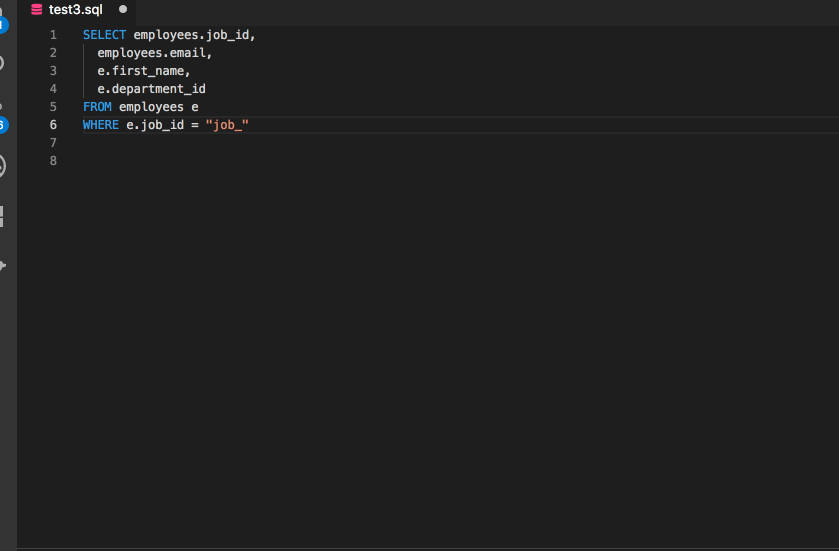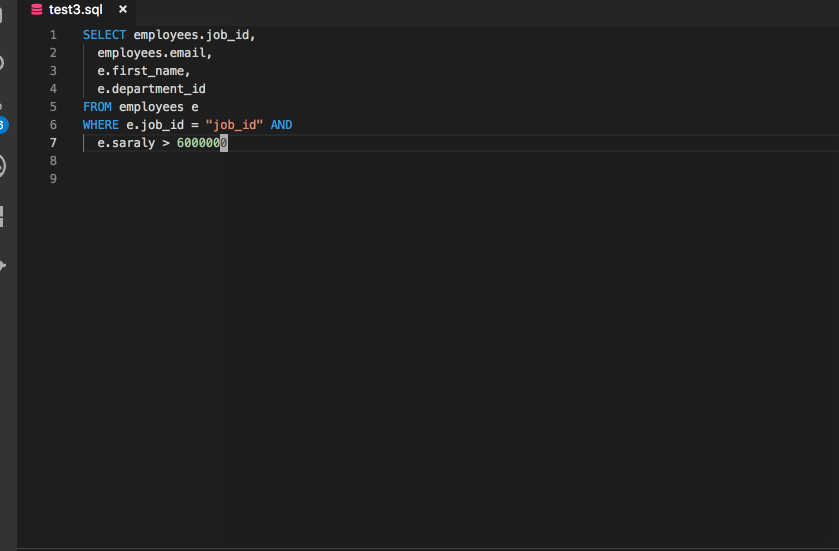
SQL Language Server
Install vsc extension.
npm i -g sql-language-server
Neovim example(LanguageClient-neovim)
- .vimrc
let g:LanguageClient_serverCommands = {
\ 'sql': ['sql-language-server', 'up', '--method', 'stdio'],
\ }
$ sql-language-server up [options] run sql-language-server
--version Show version number [boolean]
--help Show help [boolean]
--method, -m What use to communicate with sql language server
[string] [choices: "stdio", "node-ipc"] [default: "node-ipc"]
--debug, -d Enable debug logging [boolean] [default: false]
- Example
$ sql-language-server up --method stdio
There are two ways to use configuration files.
- Set personal configuration file(~/.config/sql-language-server/sqllsrc.json)
- Set project configuration file on your project root(${YOUR_PROJECT/.sqllsrc.json})
- Examples
{
"connections": [
{
"name": "sql-language-server",
"adapter": "mysql",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 3307,
"user": "username",
"password": "password",
"database": "mysql-development",
"projectPaths": ["/Users/joe-re/src/sql-language-server"],
"ssh": {
"user": "ubuntu",
"remoteHost": "ec2-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx.ap-southeast-1.compute.amazonaws.com",
"dbHost": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3306,
"identityFile": "~/.ssh/id_rsa",
"passphrase": "123456"
}
},
{
"name": "postgres-project",
"adapter": "prostgres",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 5432,
"user": "postgres",
"password": "pg_pass",
"database": "pg_test",
"projectPaths": ["/Users/joe-re/src/postgres_ptoject"]
}
]
}Please restart sql-language-server process after create .sqlrc.json.
| Key | Description | value | required | default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | Connection name(free-form text) | true | ||
| adapter | Database type | "mysql" #124; "postgres" | true | |
| host | Database host | string | true | |
| port | Database port | string | false | mysql:3306, postgres:5432 |
| user | Database user | string | true | mysql:"root", postgres:"postgres" |
| password | Database password | string | false | |
| database | Database name | string | false | |
| projectPaths | Project path that you want to apply(if you don't set it configuration will not apply automatically when lsp's started up) | string[] | false | [] |
| ssh | Settings for port fowarding | *see below SSH section | false |
| Key | Description | value | required | default |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| remoteHost | The host address you want to connect to | string | true | |
| remotePort | Port number of the server for ssh | number | false | 22 |
| user | User name on the server | string | false | |
| dbHost | Database host on the server | string | false | 127.0.0.1 |
| dbPort | Databse port on the server | number | false | mysql:3306, postgres:5432 |
| identitiFile | Identity file for ssh | string | false | ~/.ssh/config/id_rsa |
| passphrase | Passphrase to allow to use identity file | string | false |
Personal configuration file is located on ~/.config/sql-language-server/.sqllsrc.json.
sql-language-server will try to read when it's started.
Project configuration file is located on ${YOUR_PROJECT_ROOT}/.sqllsrc.json.
All setting items are similarly to personal configuration file, with some exceptions:
- Specify under
connectionproperty element directly(you don't need to set array) - You don't need to set project path.(if you set it it will be ignored)
- It's merged to personal configuration if you have it.
Example:
{
"name": "postgres-project",
"adapter": "prostgres",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 5432,
"user": "postgres",
"database": "pg_test"
}And also if you have set personal configuration and both of them's names are matched, it's merged automatically.
Personal configuration example:
{
"connections": [{
"name": "postgres-project",
"password": "password",
"ssh": {
"user": "ubuntu",
"remoteHost": "ec2-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx.ap-southeast-1.compute.amazonaws.com",
"dbHost": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 5432,
"identityFile": "~/.ssh/id_rsa",
"passphrase": "123456"
}
}]
}It will merge them as following:
{
"name": "postgres-project",
"adapter": "prostgres",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 5432,
"user": "postgres",
"database": "pg_test",
"password": "password",
"ssh": {
"user": "ubuntu",
"remoteHost": "ec2-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx.ap-southeast-1.compute.amazonaws.com",
"dbHost": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 5432,
"identityFile": "~/.ssh/id_rsa",
"passphrase": "123456"
}
}${env:VARIABLE_NAME} syntax allows you to replace configuration value with enviroment variable. This is useful when you don't write actual value on configuration file.
{
"adapter": "mysql",
"host": "localhost",
"port": 3307,
"user": "username",
"password": "${env:DB_PASSWORD}",
"database": "mysql-development",
"ssh": {
"user": "ubuntu",
"remoteHost": "ec2-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx.ap-southeast-1.compute.amazonaws.com",
"dbHost": "127.0.0.1",
"port": 3306,
"identityFile": "~/.ssh/id_rsa",
"passphrase": "${env:SSH_PASSPHRASE}"
}
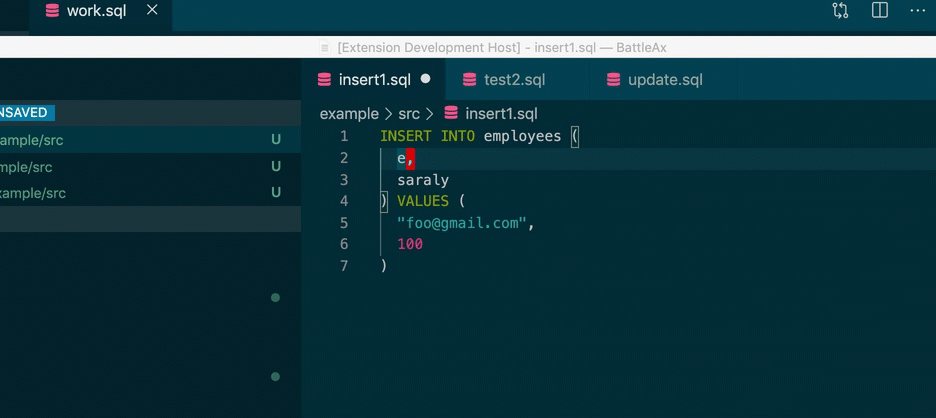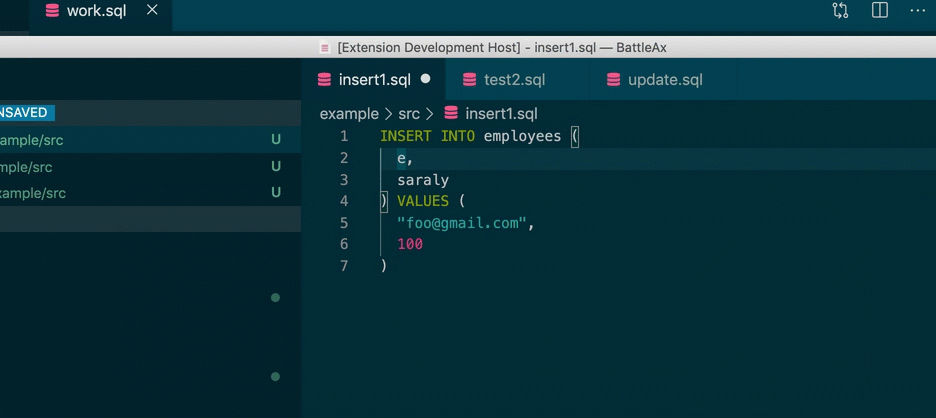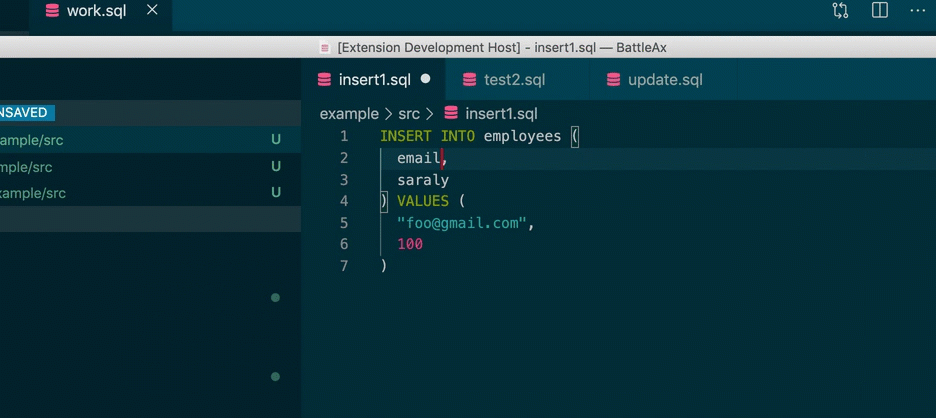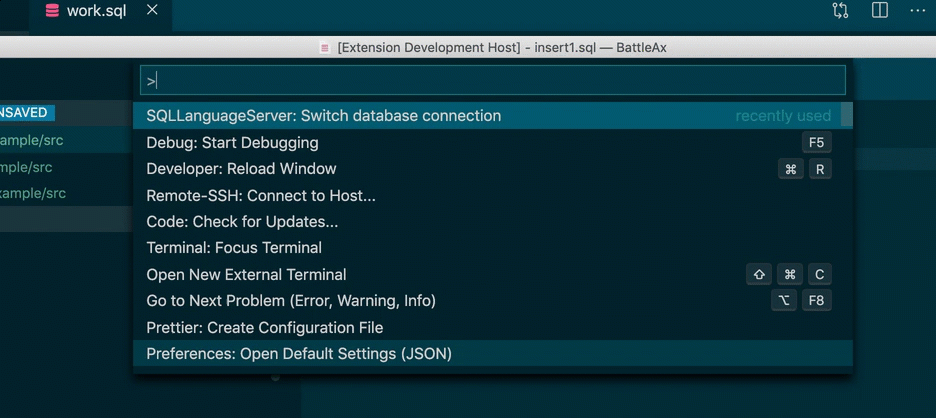
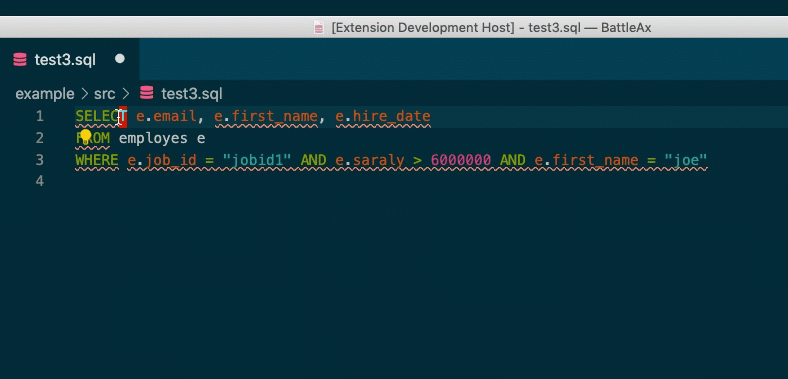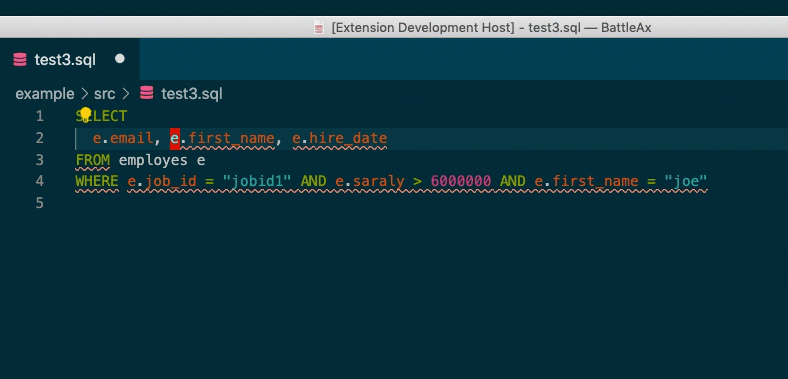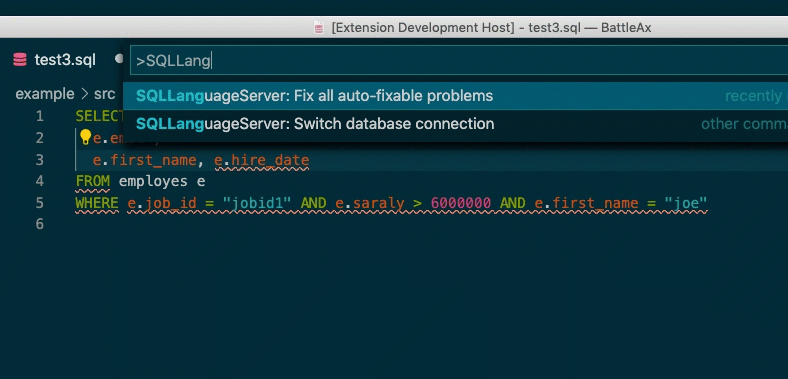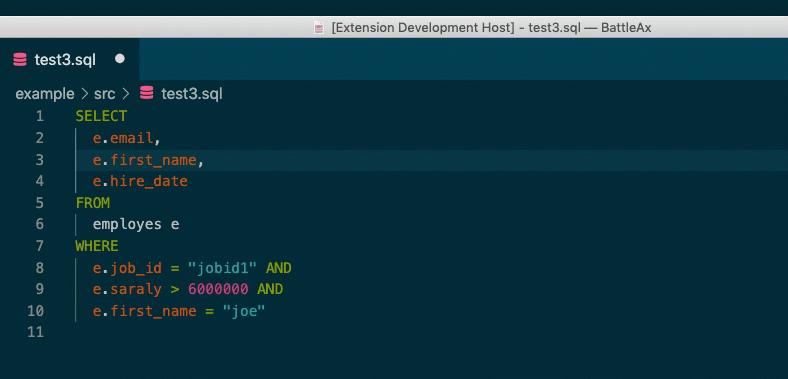
}If you have multiple connection information on personal config file, you can swtich database connection.
VSC extension provides Switch database connection command.
Raw RPC param:
method: workspace/executeCommand
command: switchDataBaseConnection
arguments: string(project name)
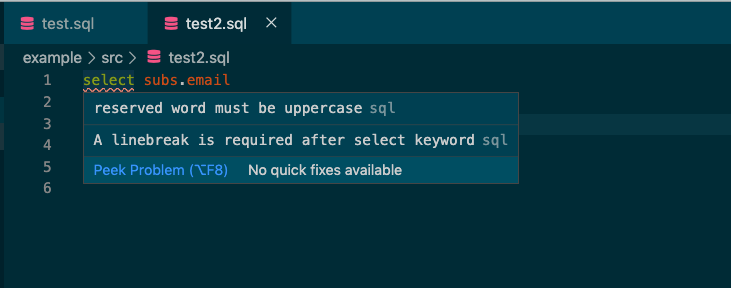
You can use lint rules that are provided sqlint. Please refer this to know how to use and how to configure to make them be matched your case.
Also you can use it to fix your problem if it's possible.
Raw RPC param:
method: workspace/executeCommand
command: fixAllFixableProblems
arguments: string(document uri)