-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1.7k
Description
一、概述
前面我们讲到,JS 中有六种简单数据类型:undefined、null、boolean、string、number、symbol,以及引用类型:object
但是我们在声明的时候只有一种数据类型,只有到运行期间才会确定当前类型
let x = y ? 1 : a;上面代码中,x的值在编译阶段是无法获取的,只有等到程序运行时才能知道
虽然变量的数据类型是不确定的,但是各种运算符对数据类型是有要求的,如果运算子的类型与预期不符合,就会触发类型转换机制
常见的类型转换有:
- 强制转换(显示转换)
- 自动转换(隐式转换)
二、显示转换
显示转换,即我们很清楚可以看到这里发生了类型的转变,常见的方法有:
- Number()
- parseInt()
- String()
- Boolean()
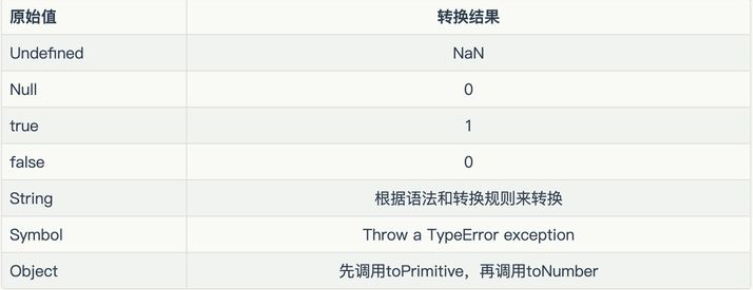
Number()
将任意类型的值转化为数值
先给出类型转换规则:
实践一下:
Number(324) // 324
// 字符串:如果可以被解析为数值,则转换为相应的数值
Number('324') // 324
// 字符串:如果不可以被解析为数值,返回 NaN
Number('324abc') // NaN
// 空字符串转为0
Number('') // 0
// 布尔值:true 转成 1,false 转成 0
Number(true) // 1
Number(false) // 0
// undefined:转成 NaN
Number(undefined) // NaN
// null:转成0
Number(null) // 0
// 对象:通常转换成NaN(除了只包含单个数值的数组)
Number({a: 1}) // NaN
Number([1, 2, 3]) // NaN
Number([5]) // 5从上面可以看到,Number转换的时候是很严格的,只要有一个字符无法转成数值,整个字符串就会被转为NaN
parseInt()
parseInt相比Number,就没那么严格了,parseInt函数逐个解析字符,遇到不能转换的字符就停下来
parseInt('32a3') //32String()
可以将任意类型的值转化成字符串
给出转换规则图:
实践一下:
// 数值:转为相应的字符串
String(1) // "1"
//字符串:转换后还是原来的值
String("a") // "a"
//布尔值:true转为字符串"true",false转为字符串"false"
String(true) // "true"
//undefined:转为字符串"undefined"
String(undefined) // "undefined"
//null:转为字符串"null"
String(null) // "null"
//对象
String({a: 1}) // "[object Object]"
String([1, 2, 3]) // "1,2,3"Boolean()
可以将任意类型的值转为布尔值,转换规则如下:
实践一下:
Boolean(undefined) // false
Boolean(null) // false
Boolean(0) // false
Boolean(NaN) // false
Boolean('') // false
Boolean({}) // true
Boolean([]) // true
Boolean(new Boolean(false)) // true三、隐式转换
在隐式转换中,我们可能最大的疑惑是 :何时发生隐式转换?
我们这里可以归纳为两种情况发生隐式转换的场景:
- 比较运算(
==、!=、>、<)、if、while需要布尔值地方 - 算术运算(
+、-、*、/、%)
除了上面的场景,还要求运算符两边的操作数不是同一类型
自动转换为布尔值
在需要布尔值的地方,就会将非布尔值的参数自动转为布尔值,系统内部会调用Boolean函数
可以得出个小结:
- undefined
- null
- false
- +0
- -0
- NaN
- ""
除了上面几种会被转化成false,其他都换被转化成true
自动转换成字符串
遇到预期为字符串的地方,就会将非字符串的值自动转为字符串
具体规则是:先将复合类型的值转为原始类型的值,再将原始类型的值转为字符串
常发生在+运算中,一旦存在字符串,则会进行字符串拼接操作
'5' + 1 // '51'
'5' + true // "5true"
'5' + false // "5false"
'5' + {} // "5[object Object]"
'5' + [] // "5"
'5' + function (){} // "5function (){}"
'5' + undefined // "5undefined"
'5' + null // "5null"自动转换成数值
除了+有可能把运算子转为字符串,其他运算符都会把运算子自动转成数值
'5' - '2' // 3
'5' * '2' // 10
true - 1 // 0
false - 1 // -1
'1' - 1 // 0
'5' * [] // 0
false / '5' // 0
'abc' - 1 // NaN
null + 1 // 1
undefined + 1 // NaNnull转为数值时,值为0 。undefined转为数值时,值为NaN