| title | date | order | categories | tags | permalink | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Java 缓存中间件 |
2022-02-17 14:34:30 -0800 |
2 |
|
|
/pages/85460d/ |
关键词:Spring Cache、J2Cache、JetCache
JSR107 中制订了 Java 缓存的规范。
因此,在很多缓存框架、缓存库中,其 API 都参考了 JSR 107 规范。
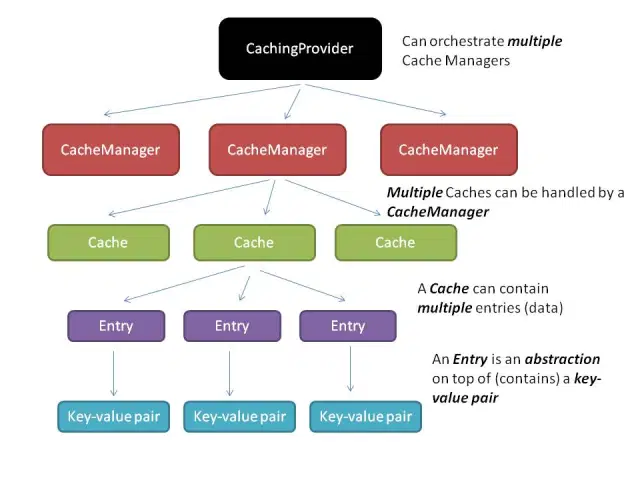
Java Caching 定义了 5 个核心接口
- CachingProvider - 定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个
CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。 - CacheManager - 定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的 Cache,这些 Cache 存在于 CacheManager 的上下文中。一个 CacheManager 仅被一个 CachingProvider 所拥有。
- Cache - 是一个类似 Map 的数据结构并临时存储以 Key 为索引的值。一个 Cache 仅被一个 CacheManager 所拥有。
- Entry - 是一个存储在 Cache 中的 key-value 对。
- Expiry - 每一个存储在 Cache 中的条目有一个定义的有效期,即 Expiry Duration。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过 ExpiryPolicy 设置。
Spring 作为 Java 开发最著名的框架,也提供了缓存功能的框架—— Spring Cache。
Spring 支持基于注释(annotation)的缓存(cache)技术,它本质上不是一个具体的缓存实现方案(例如:EHCache 或 OSCache),而是一个对缓存使用的抽象,通过在既有代码中添加少量它定义的各种 annotation,即能够达到缓存方法的返回对象的效果。
Spring Cache 的特点:
- 通过缓存注解即可支持缓存功能
- 支持 Spring EL 表达式
- 支持 AspectJ
- 支持自定义 key 和缓存管理
Spring 为缓存功能提供了注解功能,但是你必须启动注解。
有两种方式:
(一)使用标记注解 @EnableCaching
这种方式对于 Spring 或 Spring Boot 项目都适用。
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class AppConfig {
}(二)在 xml 中声明
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager"/>Spring 对缓存的支持类似于对事务的支持。
首先使用注解标记方法,相当于定义了切点,然后使用 Aop 技术在这个方法的调用前、调用后获取方法的入参和返回值,进而实现了缓存的逻辑。
@Cacheable 用于触发缓存。
表明所修饰的方法是可以缓存的:当第一次调用这个方法时,它的结果会被缓存下来,在缓存的有效时间内,以后访问这个方法都直接返回缓存结果,不再执行方法中的代码段。
这个注解可以用condition属性来设置条件,如果不满足条件,就不使用缓存能力,直接执行方法。
可以使用key属性来指定 key 的生成规则。
@CachePut 用于更新缓存。
与@Cacheable不同,@CachePut不仅会缓存方法的结果,还会执行方法的代码段。
它支持的属性和用法都与@Cacheable一致。
@CacheEvict 用于清除缓存。
与@Cacheable功能相反,@CacheEvict表明所修饰的方法是用来删除失效或无用的缓存数据。
下面是@Cacheable、@CacheEvict和@CachePut基本使用方法的一个集中展示:
@Service
public class UserService {
// @Cacheable可以设置多个缓存,形式如:@Cacheable({"books", "isbns"})
@Cacheable(value={"users"}, key="#user.id")
public User findUser(User user) {
return findUserInDB(user.getId());
}
@Cacheable(value = "users", condition = "#user.getId() <= 2")
public User findUserInLimit(User user) {
return findUserInDB(user.getId());
}
@CachePut(value = "users", key = "#user.getId()")
public void updateUser(User user) {
updateUserInDB(user);
}
@CacheEvict(value = "users")
public void removeUser(User user) {
removeUserInDB(user.getId());
}
@CacheEvict(value = "users", allEntries = true)
public void clear() {
removeAllInDB();
}
}@Caching 用于组合定义多种缓存功能。
如果需要使用同一个缓存注解(@Cacheable、@CacheEvict或@CachePut)多次修饰一个方法,就需要用到@Caching。
@Caching(evict = { @CacheEvict("primary"), @CacheEvict(cacheNames="secondary", key="#p0") })
public Book importBooks(String deposit, Date date)@CacheConfig 用于定义公共缓存配置。
与前面的缓存注解不同,这是一个类级别的注解。
如果类的所有操作都是缓存操作,你可以使用@CacheConfig来指定类,省去一些配置。
@CacheConfig("books")
public class BookRepositoryImpl implements BookRepository {
@Cacheable
public Book findBook(ISBN isbn) {...}
}Spring Boot Cache 是在 Spring Cache 的基础上做了封装,使得使用更为便捷。
(1)引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 按序引入需要的缓存库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>(2)缓存配置
例如,选用缓存为 redis,则需要配置 redis 相关的配置项(如:数据源、连接池等配置信息)
# 缓存类型,支持类型:GENERIC、JCACHE、EHCACHE、HAZELCAST、INFINISPAN、COUCHBASE、REDIS、CAFFEINE、SIMPLE
spring.cache.type = redis
# 全局缓存时间
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live = 60s
# Redis 配置
spring.redis.database = 0
spring.redis.host = localhost
spring.redis.port = 6379
spring.redis.password =(3)使用 @EnableCaching 开启缓存
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
// ...
}(4)缓存注解(@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvit 等)使用方式与 Spring Cache 完全一样
JetCache 是一个基于 Java 的缓存系统封装,提供统一的 API 和注解来简化缓存的使用。 JetCache 提供了比 SpringCache 更加强大的注解,可以原生的支持 TTL、两级缓存、分布式自动刷新,还提供了
Cache接口用于手工缓存操作。 当前有四个实现,RedisCache、TairCache(此部分未在 github 开源)、CaffeineCache(in memory)和一个简易的LinkedHashMapCache(in memory),要添加新的实现也是非常简单的。
如果使用 Spring Boot,可以按如下的方式配置(这里使用了 jedis 客户端连接 redis,如果需要集群、读写分离、异步等特性支持请使用lettuce客户端)。
(1)引入 POM
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alicp.jetcache</groupId>
<artifactId>jetcache-starter-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.5.14</version>
</dependency>(2)配置
配置一个 spring boot 风格的 application.yml 文件,把他放到资源目录中
jetcache:
statIntervalMinutes: 15
areaInCacheName: false
local:
default:
type: linkedhashmap
keyConvertor: fastjson
remote:
default:
type: redis
keyConvertor: fastjson
valueEncoder: java
valueDecoder: java
poolConfig:
minIdle: 5
maxIdle: 20
maxTotal: 50
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379(3)开启缓存
然后创建一个 App 类放在业务包的根下,EnableMethodCache,EnableCreateCacheAnnotation 这两个注解分别激活 Cached 和 CreateCache 注解,其他和标准的 Spring Boot 程序是一样的。这个类可以直接 main 方法运行。
package com.company.mypackage;
import com.alicp.jetcache.anno.config.EnableCreateCacheAnnotation;
import com.alicp.jetcache.anno.config.EnableMethodCache;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableMethodCache(basePackages = "com.company.mypackage")
@EnableCreateCacheAnnotation
public class MySpringBootApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MySpringBootApp.class);
}
}(4)API 基本使用
创建缓存实例
通过 @CreateCache 注解创建一个缓存实例,默认超时时间是 100 秒
@CreateCache(expire = 100)
private Cache<Long, UserDO> userCache;用起来就像 map 一样
UserDO user = userCache.get(123L);
userCache.put(123L, user);
userCache.remove(123L);创建一个两级(内存+远程)的缓存,内存中的元素个数限制在 50 个。
@CreateCache(name = "UserService.userCache", expire = 100, cacheType = CacheType.BOTH, localLimit = 50)
private Cache<Long, UserDO> userCache;name 属性不是必须的,但是起个名字是个好习惯,展示统计数据的使用,会使用这个名字。如果同一个 area 两个 @CreateCache 的 name 配置一样,它们生成的 Cache 将指向同一个实例。
创建方法缓存
使用 @Cached 方法可以为一个方法添加上缓存。JetCache 通过 Spring AOP 生成代理,来支持缓存功能。注解可以加在接口方法上也可以加在类方法上,但需要保证是个 Spring bean。
public interface UserService {
@Cached(name="UserService.getUserById", expire = 3600)
User getUserById(long userId);
}使用缓存框架,使得开发缓存功能非常便捷。
如果你的系统只需要使用一种缓存,那么推荐使用 Spring Boot Cache。Spring Boot Cache 在 Spring Cache 基础上做了封装,使用更简单、方便。
如果你的系统需要使用多级缓存,那么推荐使用 jetcache。