DJL serving is built on top of Deep Java Library. You can visit the DJL github repository to learn more.
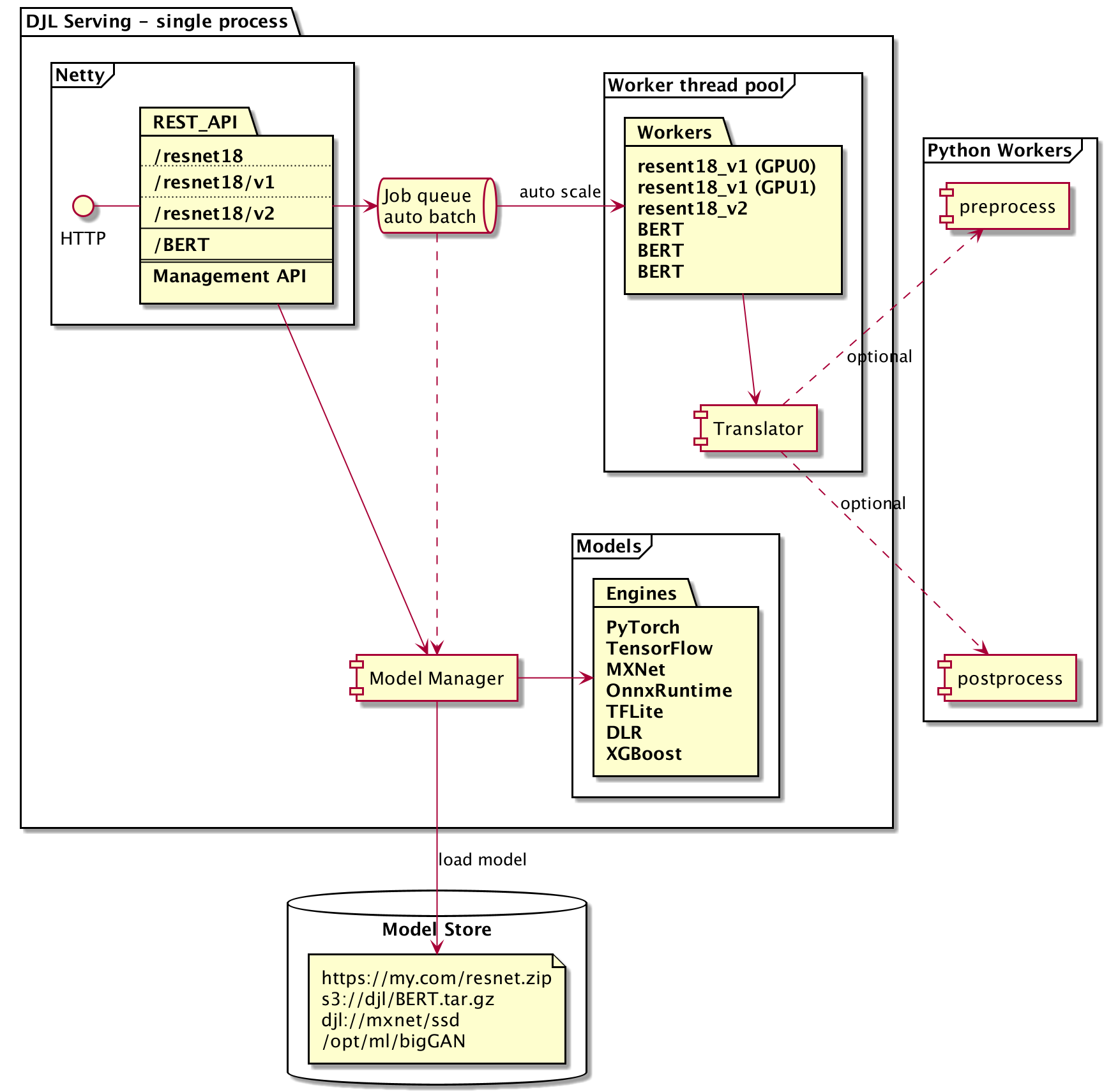
DJL Serving uses a Netty frontend on top of backend worker thread pools. The frontend uses a single Netty setup with multiple HttpRequestHandlers. Different request handlers will provide support for the inference API, Management API, or other APIs available from various plugins.
The backend is based around the WorkLoadManager module.
The WLM takes care of multiple worker threads for each model along with the batching and request routing to them.
It is also available separately and can be utilized through the WLM module (ai.djl.serving:wlm).
Within each worker thread inside the WLM, there is a DJL Predictor. Depending on what Engine the Predictor is, it can run various models such as those from PyTorch, Tensorflow, XGBoost, or any of the other engines supported by DJL. Notably, there is also a Python Engine which can be used to run models, preprocessing, and postprocessing defined in a python script.