English | 简体中文
Why we create catch-react-error
For errors that occur in the React lifecycle, you only need to use the ErrorBoundary component to wrap components that may have exceptions.
However, this solution is only suitable for client-side rendering, but it is completely helpless for errors in server-side rendering; nowadays, large-scale projects all adopt server-side rendering, so we need to find an easy-to-use application that can be applied to isomorphic applications. React error handling scheme.
catch-react-error is exactly to solve this problem, catch-react-error normally uses ErrorBoundary to wrap components when rendering on the client; when server-side rendering, use try-catch to wrap the render function, so you can Errors in the React lifecycle.
cd example-client
npm run devcd example-server
npm run devnpm install catch-react-error --saveWe use ES7's Decorator syntax to make the code more concise, of course, you can also use the functional style.
npm install --save-dev @ babel / plugin-proposal-decorators
npm install --save-dev @ babel / plugin-proposal-class-propertiesAdd babel plugin
{
"plugins": [
["@ babel / plugin-proposal-decorators", { "legacy": true }],
["@ babel / plugin-proposal-class-properties", { "loose": true }]
]
}import catchreacterror from "catch-react-error";@catchreacterror()
class Count extends React.Component {
render() {
const { count } = this.props;
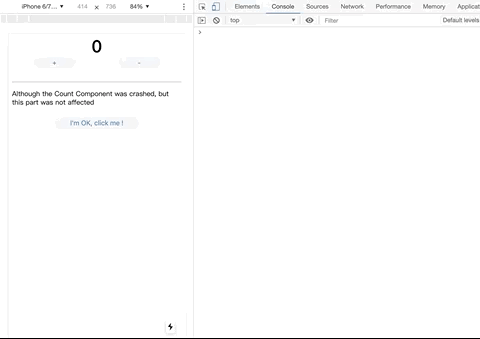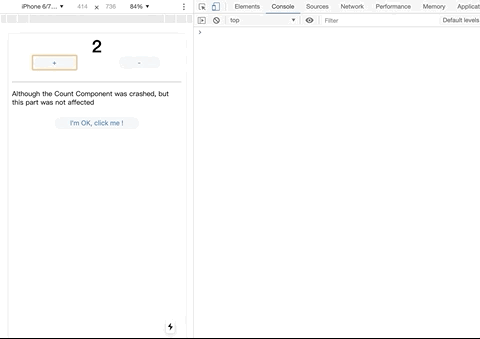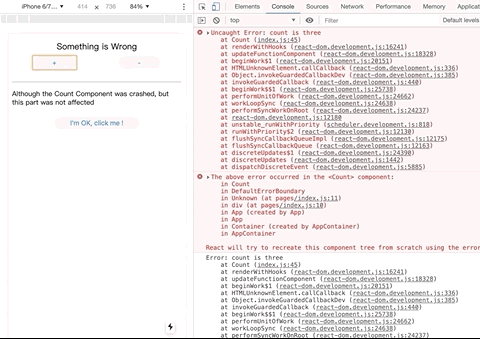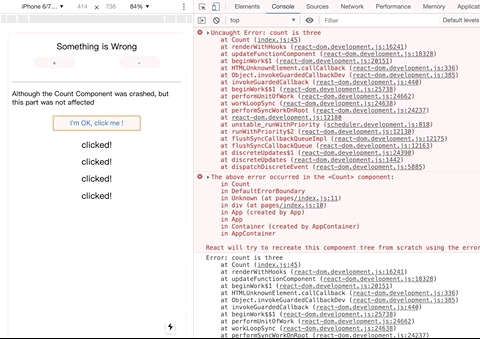
if (count === 3) {
throw new Error("count is three");
}
return <h1>{count}</h1>;
}
}catchreacterror is essentially a curried function with a signature:
catchreacterror :: ErrorBoundary-> Function-> Component
The catchreacterror function accepts one parameter: ErrorBoundary (DefaultErrorBoundary is used by default) and returns a High-Order-Function.
The principle is: client-side rendering will use React 16's Error Boundary related functions to handle errors, and server-side use try catch to catch render errors.
The above is the processing for ClassComponent, but some people like to use function components, here are also provided methods of use, as follows.
// If the Count component is not wrapped with catchreacterror,
// If count is 3, an error will be reported, causing the program to crash
function Count({ count }) {
if (count === 3) {
throw new Error("count is three");
}
return <h1>{count}</h1>;
}
// After being wrapped by catchreacterror, the error will be caught,
// Only cause the current component to be destroyed, and other content is displayed normally
const SaleCount = catchreacterror()(Count);
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<SaleCount count={3} />
<button>I'm OK, click me !</button>
</div>
);
}Copy the examples provided by React below, you can add logs and customize the fallback content
class CustomErrorBoundary extends React. Component {
constructor (props) {
super (props);
this.state = {hasError: false};
}
static getDerivedStateFromError (error) {
// Update state so the next render will show the fallback UI.
return {hasError: true};
}
componentDidCatch (error, errorInfo) {
// You can also log the error to an error reporting service
logErrorToMyService (error, errorInfo);
}
render () {
if (this.state.hasError) {
// You can render any custom fallback UI
return <h1> Something went wrong. </ h1>;
}
}
return this.props.children;
}
}MIT.