-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 8k
Home
As distributed systems becoming increasingly popular, the stability between services is becoming more important than ever before. Sentinel is a library that takes "flow" as breakthrough point, works on multiple fields including flow control, concurrency, circuit breaking, load protection, to protect service stability.
- 2012, Sentinel was first used in Alibaba's application. Its main purpose is for flow control.
- 2013-2017, Sentinel was growing fast, and became a basic component for all applications in Alibaba. It has been used in more than 4000 applications, and covers almost all core e-commerce scenarios.
- 2018,Sentinel is ready for opensource。
Resource is a key concept of Sentinel. It can be anything, such as a service, a method, or even a code snippet.
Once it is wrapped by Sentinel API, it is a resource, and can apply for protections provided by sentinel.
How sentinel can protect resource is defined by rules, such as flow control,concurrency, circuit breaking etc. Rules can be dynamic changed, and take effect in real-time.
Sentinel can make the application to handle random incoming requests to the appropriate shape as needed.
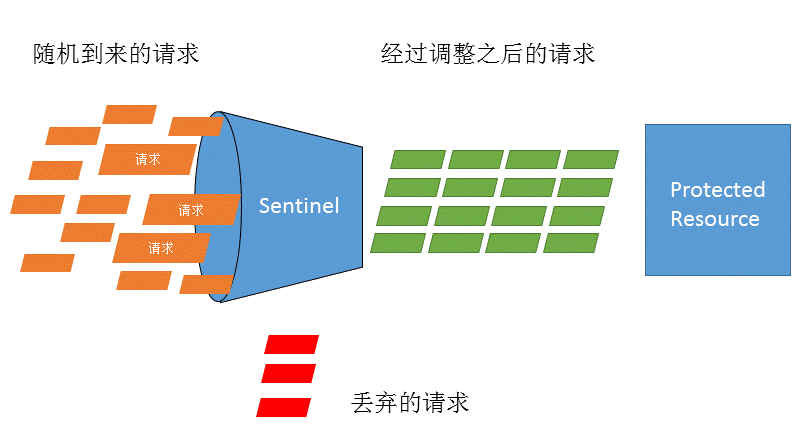
Flow control is based on following statistics:
- Calling path between resources
- Runtime metrics such as QPS, thread pool, system load, etc.
- Desired actions to take, such as reject, queue, etc.
Sentinel allow applications combine all these statistics flexibly.
Circuit breaking is used to detect failures and encapsulates the logic of preventing a failure from constantly recurring, during maintenance, temporary external system failure or unexpected system difficulties.
Netflix chose the use of threads and thread-pools to achieve isolation. The main benefit of thread pools is that the isolation is clean.
However, Sentinel uses following principles to implement circuit breaking:
Unlike using thread pools, Sentinel reduces the impact of unstable resources by restricting the number of concurrent threads.
When response time of a resource becomes longer, threads will start to occupy. When the number of threads accumulates to a certain amount, new incoming requests will be rejected. Vice versa, when the resource restores and become stable, the occupied thread will be reduced as well, and new requests will be accepted.
Using restricting concurrent threads instead of thread pool can avoid pre-allocating the size of thread pool and avoid the computational overhead such as the queueing, scheduling, and context switching.
Besides restricting the concurrent threads, downgrade unstable resources by response time is also an effective way to do circuit breaking. When the response time of resource is too long, all access to the resource will be rejected in the specified time window.
Sentinel can be used to protect your server in case system load goes too high.It can achieve a good balance between system load and incoming requests and restore very quickly.
- Provides APIs and adaptations to the popular frameworks to define resources
- Collects run time information and call path of resources
- Define rules in real time
- Provide real time monitor and extension rules configuration
-
文档
-
Documents
- Read Me
- Introduction
- How to Use
- How it Works
- Flow Control
- Parameter Flow Control
- Cluster Flow Control
- API Gateway Flow Control
- Circuit Breaking
- Adaptive System Protection
- Metrics
- General Configuration
- Dynamic Rule Configuration
- Dashboard
- Integrations with open-source frameworks
- Contribution Guideline