npm install colors
- black
- red
- green
- yellow
- blue
- magenta
- cyan
- white
- gray
- grey
- bgBlack
- bgRed
- bgGreen
- bgYellow
- bgBlue
- bgMagenta
- bgCyan
- bgWhite
- reset
- bold
- dim
- italic
- underline
- inverse
- hidden
- strikethrough
- rainbow
- zebra
- america
- trap
- random
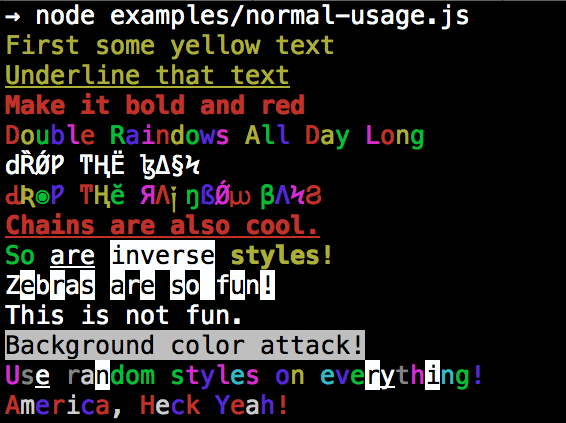
By popular demand, colors now ships with two types of usages!
The super nifty way
var colors = require('colors');
console.log('hello'.green); // outputs green text
console.log('i like cake and pies'.underline.red) // outputs red underlined text
console.log('inverse the color'.inverse); // inverses the color
console.log('OMG Rainbows!'.rainbow); // rainbow
console.log('Run the trap'.trap); // Drops the bassor a slightly less nifty way which doesn't extend String.prototype
var colors = require('colors/safe');
console.log(colors.green('hello')); // outputs green text
console.log(colors.red.underline('i like cake and pies')) // outputs red underlined text
console.log(colors.inverse('inverse the color')); // inverses the color
console.log(colors.rainbow('OMG Rainbows!')); // rainbow
console.log(colors.trap('Run the trap')); // Drops the bassI prefer the first way. Some people seem to be afraid of extending String.prototype and prefer the second way.
If you are writing good code you will never have an issue with the first approach. If you really don't want to touch String.prototype, the second usage will not touch String native object.
To disable colors you can pass the following arguments in the command line to your application:
node myapp.js --no-colorConsole.log string substitution
var name = 'Marak';
console.log(colors.green('Hello %s'), name);
// outputs -> 'Hello Marak'var colors = require('colors');
colors.setTheme({
silly: 'rainbow',
input: 'grey',
verbose: 'cyan',
prompt: 'grey',
info: 'green',
data: 'grey',
help: 'cyan',
warn: 'yellow',
debug: 'blue',
error: 'red'
});
// outputs red text
console.log("this is an error".error);
// outputs yellow text
console.log("this is a warning".warn);var colors = require('colors/safe');
// set single property
var error = colors.red;
error('this is red');
// set theme
colors.setTheme({
silly: 'rainbow',
input: 'grey',
verbose: 'cyan',
prompt: 'grey',
info: 'green',
data: 'grey',
help: 'cyan',
warn: 'yellow',
debug: 'blue',
error: 'red'
});
// outputs red text
console.log(colors.error("this is an error"));
// outputs yellow text
console.log(colors.warn("this is a warning"));You can also combine them:
var colors = require('colors');
colors.setTheme({
custom: ['red', 'underline']
});
console.log('test'.custom);Protip: There is a secret undocumented style in colors. If you find the style you can summon him.