Sample cloud-init file: https://cloudinit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/examples.html#including-users-and-groups
multipass launch --name k8s-master{Node.ID} --memory 2G --cloud-init cloud-init.yml --disk=15G
multipass launch --name k8s-node{Node.ID} --memory 1536M --cloud-init cloud-init.yml --disk=15G
[k8s-master]
k8s-master1 ansible_host=10.57.172.124
k8s-master2 ansible_host=10.57.172.117
k8s-master3 ansible_host=10.57.172.216
[k8s-worker]
k8s-worker1 ansible_host=10.57.172.213
k8s-worker2 ansible_host=10.57.172.221
k8s-worker3 ansible_host=10.57.172.145
[k8s-cluster:children]
k8s-master
k8s-workerAnd test connection with default ansible ping command
ansible --inventory ~/cloud-init/ansible/inventory/cluster.ini k8s-cluster -m pingClone repo
git clone git@github.com:kubernetes-sigs/kubespray.gitInstall python requirements
pip install -r requirements.txt Make copy of dir
cp -R ./kubespray/inventory/sample ./kubespray/inventory/clusterEdit cluster nodes for ansible
[all]
master1 ansible_host=10.57.172.124
master2 ansible_host=10.57.172.117
master3 ansible_host=10.57.172.216
worker1 ansible_host=10.57.172.213
worker2 ansible_host=10.57.172.221
worker3 ansible_host=10.57.172.145
# ## configure a bastion host if your nodes are not directly reachable
# [bastion]
# bastion ansible_host=x.x.x.x ansible_user=some_user
[kube_control_plane:children]
kube_master
[kube_master]
master1
master2
master3
[etcd:children]
kube_master
[kube_node]
worker1
worker2
worker3
[calico_rr]
[k8s_cluster:children]
kube_master
kube_node
calico_rrEdit cluster configuration in group_vars/k8s_cluster/k8s-cluster.yaml (For expert)
ansible-playbook --inventory=./inventory/cluster/inventory.ini ./cluster.yml --becomeFor test cluster, connect to master-node and test cluster:
kubectl cluster-infoIf we have error by 8080 port, move kube config only on master-nodes
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config# download file
curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/`curl -s https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/stable.txt`/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl
# set as executable
chmod +x ./kubectl
# move to /usr/local/bin folder for access from any place in terminal
sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
# test them
kubectl version --clientFor establish connection from local kubectl to k8s master node we can get configuration file from master-node
# download file from remote host
scp 10.57.172.124:/etc/kubernetes/admin.conf ~/cloud-init/admin.conf
# update ENV variable
echo "export KUBECONFIG=~/cloud-init/admin.conf" >> ~/.bash_profile
# apply changes
source ~/.bash_profileNow, we need test connection to cluster;
kubectl versionIf we see message "connection refused", change IP-address from localhost in config-file to master-node address and test connection
Get k8s nodes
kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
master1 Ready control-plane 10h v1.25.6 10.57.172.124 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS 5.15.0-58-generic containerd://1.6.15
master2 Ready control-plane 144m v1.25.6 10.57.172.117 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS 5.15.0-58-generic containerd://1.6.15
master3 Ready control-plane 143m v1.25.6 10.57.172.216 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS 5.15.0-58-generic containerd://1.6.15
worker1 Ready <none> 142m v1.25.6 10.57.172.213 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS 5.15.0-58-generic containerd://1.6.15
worker2 Ready <none> 142m v1.25.6 10.57.172.221 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS 5.15.0-58-generic containerd://1.6.15
worker3 Ready <none> 142m v1.25.6 10.57.172.145 <none> Ubuntu 22.04.1 LTS 5.15.0-58-generic containerd://1.6.15All actions deal on local workstation
Create new service with defenition from remote repository
# create service
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.7.0/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml
# run proxy service
kubectl proxyNow we can connect to dashboard from localhost station
First time we should be create service account with name admin-user in namespace kubernetes-dashboard (default created for dashboard)
Create ./manifests/accounting/service-account.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboardApply manifest
kubectl apply -f ~/cloud-init/manifests/accounting/service-account.yamlOutput:
serviceaccount/admin-user created
The most popular tools already have ClusterRole with user cluster-admin in the cluster. We need to link created user to exists admin account manualy Create ./manifests/accounting/cluster-role-binding.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin-user
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin-user
namespace: kubernetes-dashboardApply manifest
kubectl apply -f ~/cloud-init/manifests/accounting/cluster-role-binding.yamlOutput:
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/admin-user created
Create admin token
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard create token admin-userOutput:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6InBDNnhmUWR1VzJ6ZUVKZHdjSmgzdVVXaTA5bkU3cTUxQ1A3WkNNODY2c1EifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiXSwiZXhwIjoxNjc0NTU2MjEzLCJpYXQiOjE2NzQ1NTI2MTMsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZCIsInNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Ijp7Im5hbWUiOiJhZG1pbi11c2VyIiwidWlkIjoiYmE4Y2ZmMjgtOTRjNy00ZWFmLWE2NWUtNzk1ZDI0ZjUyOGZjIn19LCJuYmYiOjE2NzQ1NTI2MTMsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDprdWJlcm5ldGVzLWRhc2hib2FyZDphZG1pbi11c2VyIn0.qUwno1PCTepp4bzqPKyhuAO7B9cd1jg6eLNVTD8P9utr8EToHECpYSs7KnC-dJRo0L8DTydUKoHMSWZLA8SGyO7WZ4UfjeLcXDuU9vWXHOw0SnDA_FjcCP8QQUYejkTzcTGxAt73B9jOG8mm7ZIVYJkowYFotGSoQvtpb_3l0kEi9Hd0SRXh-yhjPI-BtHSBpk9rgYEwwp_sZU0wptbeli7tBNWzyrEK2ZNDKmV7VqWtvkJxaICZRkEz1PyHFcs5juslC5loRd39myaZ6fTshvivgSMPJivrWNGDWi5ycnWhpCbsXhyTDEvs7lTTx79v8eugD2m7eVX7dvLzlyLZtg
Paste output token into form and u are connected to dashboard
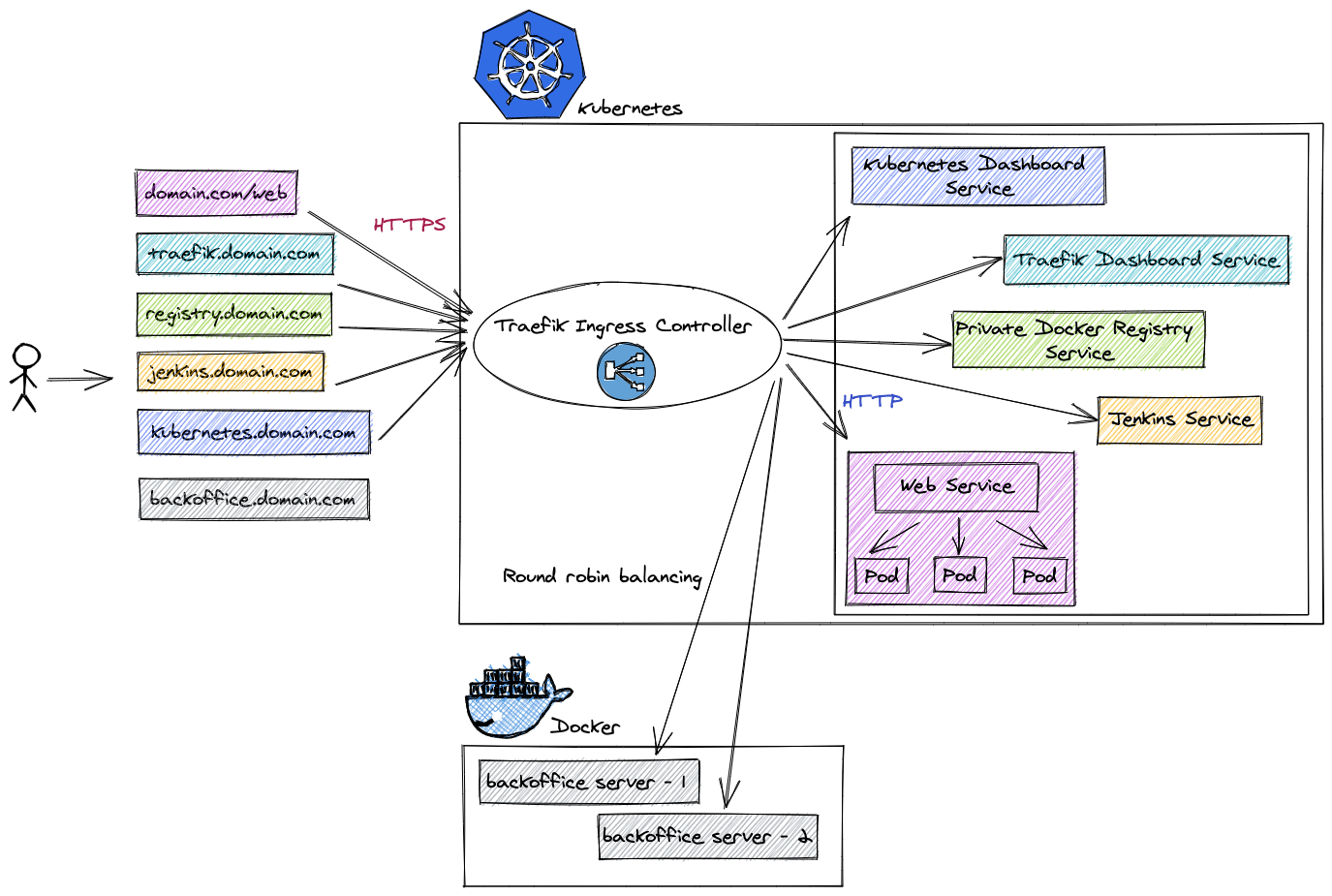
So. We can choose between 3 most popular Ingress controllers and one default k8s controller:
- K8s default controller
- NGINX Ingress controller
- HAProxy Ingress controller
- Traefik Ingress controller
Default k8s and NGINX controllers are very slow that Traefik and HAProxy.
HAProxy faster that Traefik in ops on one CPU, Traefik faster that HAProxy on latency between controller and services.
I choose Traefik Ingress Controller on my learning.
# Deal all actions on local workstation
# create helm dir
mkdir ~/cloud-init/helm
# get latest release from git repo and save into helm installation dir
wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.11.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz -O ~/cloud-init/helm/helm-v3.11.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
# unpack archive
tar -zxvf ~/cloud-init/helm/helm-v3.11.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz -c ~/cloud-init/helm
# move binary
sudo mv ~/cloud-init/helm/linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
# remove temporary files
rm -rf ~/cloud-init/helm
# test them
helm helpInstructions: