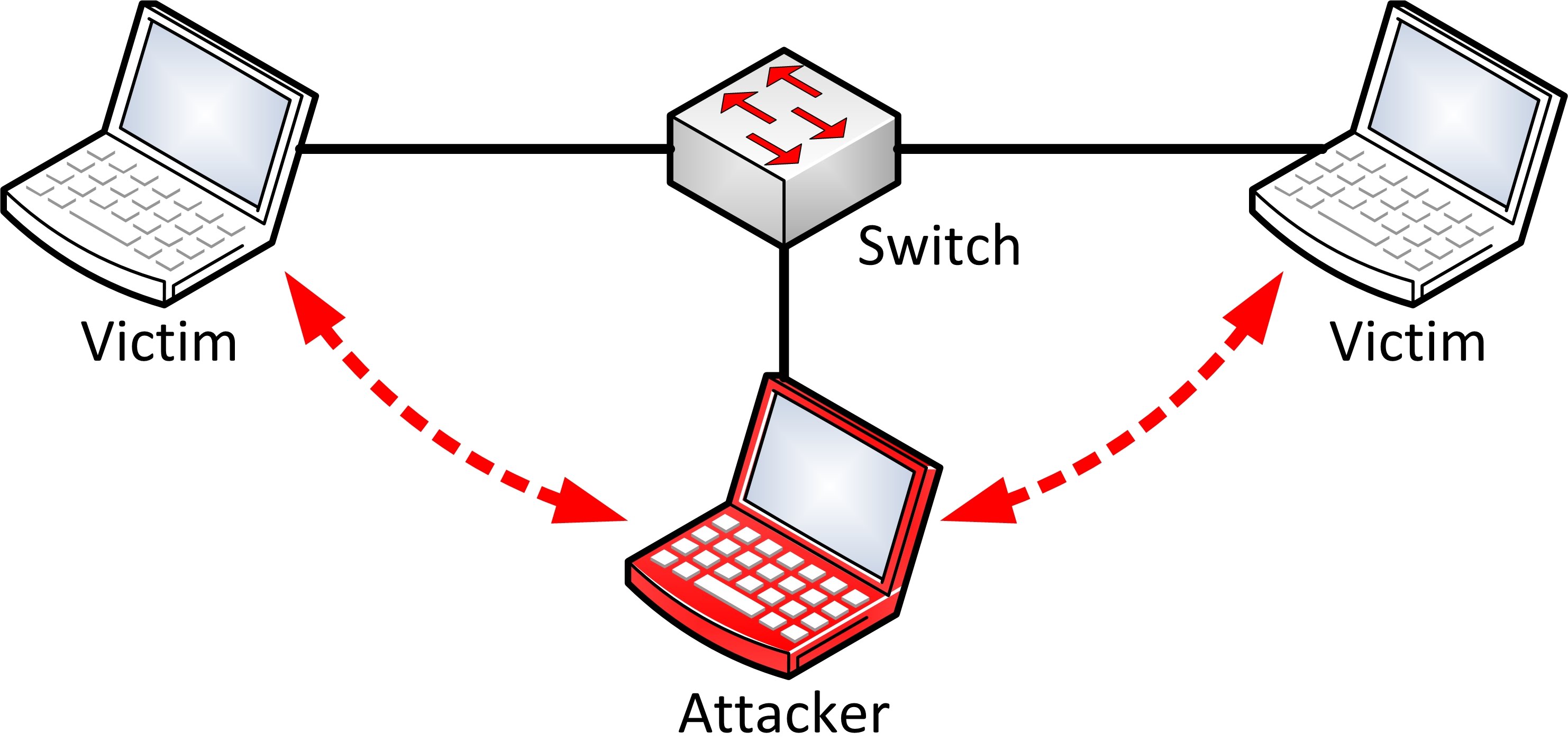
Sniffing is the process of monitoring and capturing all the packets passing through a given network using sniffing tools. It is a form of “tapping phone wires” and get to know about the conversation. It is also called wiretapping applied to the computer networks.
There is so much possibility that if a set of enterprise switch ports is open, then one of their employees can sniff the whole traffic of the network. Anyone in the same physical location can plug into the network using Ethernet cable or connect wirelessly to that network and sniff the total traffic.
- Email traffic
- FTP passwords
- Web traffics
- Telnet passwords
- Router configuration
- Chat sessions
- DNS traffic
Sniffing can be either Active or Passive.
the traffic is locked but it is not altered in any way. Passive sniffing allows listening only. It works with Hub devices. On a hub device, the traffic is sent to all the ports. In a network that uses hubs to connect systems, all hosts on the network can see the traffic. Therefore, an attacker can easily capture traffic going through.
the traffic is not only locked and monitored, but it may also be altered in some way as determined by the attack. Active sniffing is used to sniff a switch-based network. It involves injecting address resolution packets (ARP) into a target network to flood on the switch content addressable memory (CAM) table. CAM keeps track of which host is connected to which port.
Some Active Sniffing techniques:
- MAC Flooding
- DHCP Attacks
- DNS Poisoning
- Spoofing Attacks
- ARP Poisoning
Protocols such as the tried and true TCP/IP were never designed with security in mind and therefore do not offer much resistance to potential intruders. Several rules lend themselves to easy sniffing.
-
HTTP − It is used to send information in the clear text without any encryption and thus a real target.
-
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) − SMTP is basically utilized in the transfer of emails. This protocol is efficient, but it does not include any protection against sniffing.
-
NNTP _(Network News Transfer Protocol)_− It is used for all types of communications, but its main drawback is that data and even passwords are sent over the network as clear text.
-
POP (Post Office Protocol) − POP is strictly used to receive emails from the servers. This protocol does not include protection against sniffing because it can be trapped.
-
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) − FTP is used to send and receive files, but it does not offer any security features. All the data is sent as clear text that can be easily sniffed.
-
IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) − IMAP is same as SMTP in its functions, but it is highly vulnerable to sniffing.
-
Telnet − Telnet sends everything (usernames, passwords, keystrokes) over the network as clear text and hence, it can be easily sniffed.
Source: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/ethical_hacking/ethical_hacking_sniffing.htm