We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation.
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
prototype原型对象可以理解为一个共享空间,保存了一些方法和属性,提供给 prototype.constructor 构造函数实例的对象使用,有效节省内容。
prototype.constructor
1、父类新增原型属性/方法,子类都能访问到; 2、实现逻辑简单,易实现;
1、创建子类实例时,无法向父类构造函数传参。 2、父类构造函数中的引用类型(比如数组/对象),会被所有子类实例共享。只要其中一个子类的实例对其进行修改,就会导致所有其他子类实例的这个值都变化。
//父类型 function Person(name, age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; this.setName = function () {}; } Person.prototype.setAge = function () {}; //子类型 function Student(price) { this.price = price; this.setScore = function () {}; } Student.prototype = new Person('G-Dragon', 30); // 子类型的原型为父类型的一个实例对象 var s1 = new Student(15000); var s2 = new Student(14000); console.log(s1, s2); // Person { price: 15000, setScore: [Function] } Person { price: 14000, setScore: [Function] } // 给父类新增属性 方法 Person.prototype.username = '美男子'; Person.prototype.getInfo = function() { return { username: this.username, name: this.name, age: this.age } } console.log(s1.username) //美男子 console.log(s2.getInfo()) //{ username: '美男子', name: 'G-Dragon', age: 30 }
call()
解决了原型链继承中子类实例共享父类引用类型属性的问题。 创建子类实例时,可以向父类传递参数。
只能继承父类的实例属性和方法,不能继承原型属性和方法; 无法实现函数复用,每个子类都有父类实例函数的副本,影响性能; (对比原型链继承的方式,方法直接写在原型上,子类创建时不需要重新创建方法)
// 父类 function Parent(name, age) { this.name = name, this.age = age, this.setName = function() {} } Parent.prototype.setAge = function() {} // 子类 function Child(name, age, score) { Parent.call(this, name, age) // this.name = name, // this.age = age, this.score = score } Child.prototype.haha = function() { return '哈哈哈....' }; let c1 = new Child('高龙', 30, 100) let c2 = new Child('小强🪳', 32, 98) console.log(c1) // Child { // name: '高龙', // age: 30, // play: [ 1, 2, 3 ], // setName: [Function], // score: 100 } console.log(c1.setAge) //undefined, 即表示无法继承父类原型上的属性和方法 console.log(c1.haha()) //哈哈哈.... c1.play = [3, 2, 1] console.log(c2) // Child { // name: '小强🪳', // age: 32, // play: [ 1, 2, 3 ], // setName: [Function], // score: 98 }
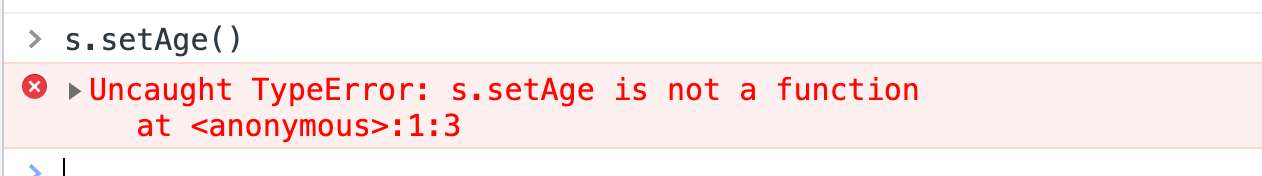
该继承只是部分的继承,原因是父类原型上的属性 or 方法子类并没有继承。如下图所示:
同时结合原型链继承、构造函数继承就是组合继承了。
同时解决了构造函数引用类型的问题,同时避免了方法会被创建多次的问题;
父类构造函数被调用了两次。同时子类实例以及子类原型对象上都会存在 name 属性。虽然根据原型链机制,并不会访问到原型对象上的同名属性,但总归是不美。
name
// 父类型 function Person(name, age) { this.name = name, this.age = age, this.setAge = function () { } } Person.prototype.setAge = function () { console.log("111") return this.age; } // 子类型 function Student(name, age, price) { Person.call(this, name, age) this.price = price this.setScore = function () { } } Student.prototype = new Person() //子类原型 指向父类的一个实例 Student.prototype.constructor = Student //组合继承也是需要修复构造函数指向的 Student.prototype.sayHello = function () { } var s1 = new Student('Tom', 20, 15000) var s2 = new Student('Jack', 22, 14000) var p1 = new Person('Sam', 30) console.log(s1) console.log(s1.constructor) //Student console.log(p1.constructor) //Person
解决了组合继承中的构造函数调用两次、构造函数引用类型共享、以及原型对象上存在多余属性的问题。是推荐的最合理实现方式(除ES6的class extends)。
没有啥特别的缺点
function Parent() { this.name = 'fedaily' } Parent.prototype.getName = function() { return this.name } function Child() { Parent.call(this) this.topic = 'fe' } // 仔细看这个函数的实现 inherit(Child, Parent)
function inherit(child, parent) { var prototype = object(parent.prototype) prototype.constructor = child child.prototype = prototype } // 这个函数的作用可以理解为复制了一份父类的原型对象 // 如果直接将子类的原型对象赋值为父类原型对象 // 那么修改子类原型对象其实就相当于修改了父类的原型对象 function object(o) { function F() {} F.prototype = o; return new F(); }
ES6中引入了class关键字,class可以通过extends关键字实现继承,还可以通过static关键字定义类的静态方法,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多。
ES5 的继承,实质是先创造子类的实例对象this,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上面(Parent.apply(this))。 ES6 的继承机制完全不同,实质是先将父类实例对象的属性和方法,加到this上面(所以必须先调用super方法),然后再用子类的构造函数修改this。
Parent.apply(this)
需要注意的是,class关键字只是原型的语法糖,JavaScript继承仍然是基于原型实现的。
class Person { //调用类的构造方法 constructor(name, age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } //定义一般的方法 showName() { console.log('调用父类的方法'); console.log(this.name, this.age); } } let p1 = new Person('kobe', 39); console.log(p1); //定义一个子类 class Student extends Person { constructor(name, age, salary) { super(name, age); //通过super调用父类的构造方法 this.salary = salary; } showName() { //在子类自身定义方法 console.log('调用子类的方法'); console.log(this.name, this.age, this.salary); } } let s1 = new Student('wade', 38, 1000000000); console.log(s1); s1.showName();
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
No branches or pull requests
prototype原型对象可以理解为一个共享空间,保存了一些方法和属性,提供给
prototype.constructor构造函数实例的对象使用,有效节省内容。1. 原型链继承
2. 借用构造函数继承
call()调用父类构造函数。其实就是修改父类构造函数this实现继承。我们在子类构造函数中执行父类构造函数,同时修改父类构造函数的this为子类的this。该继承只是部分的继承,原因是父类原型上的属性 or 方法子类并没有继承。如下图所示:
3. 组合式继承 (原型链继承 + 构造函数继承)
同时结合原型链继承、构造函数继承就是组合继承了。
4. 原型式继承
5. 寄生式继承
6. 寄生组合继承
7、ES6中Class的继承
ES6中引入了class关键字,class可以通过extends关键字实现继承,还可以通过static关键字定义类的静态方法,这比 ES5 的通过修改原型链实现继承,要清晰和方便很多。
ES5 的继承,实质是先创造子类的实例对象this,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上面(
Parent.apply(this))。ES6 的继承机制完全不同,实质是先将父类实例对象的属性和方法,加到this上面(所以必须先调用super方法),然后再用子类的构造函数修改this。
需要注意的是,class关键字只是原型的语法糖,JavaScript继承仍然是基于原型实现的。
参考阅读
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: