forked from viabtc/viabtc_mining_server
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
/
THONG NGO
196 lines (146 loc) · 6.72 KB
/
THONG NGO
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
# Viabtc Mining Server
ViaBTC Mining Server is a high-performance distributed Bitcoin mining pool server. We have
made a lot of optimizations for Bitcoin blocks and transaction broadcasting, which can
effectively reduce the orphaned block rate of the mining pool.
## Overall Structure
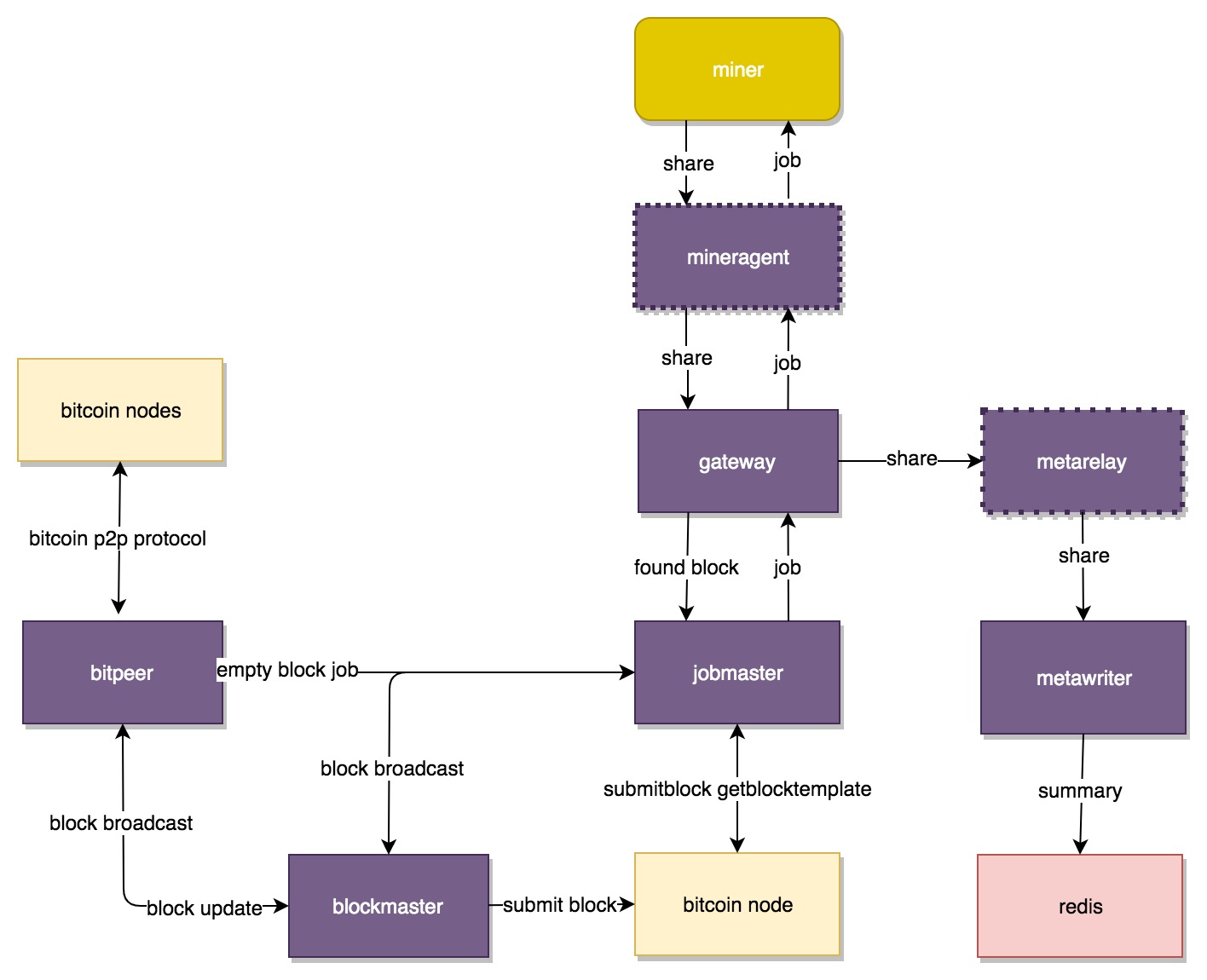
## Code structure
**Required systems**
* Redis: used to save the hashrate data of miners
**Base library**
* network: An event base and high performance network programming library, easily supporting [1000K TCP connections](http://www.kegel.com/c10k.html). Include TCP/UDP/UNIX SOCKET server and client implementation, a simple timer, state machine, thread pool.
* utils: Some basic library, including log, config parse, some data structure and http/websocket/rpc server implementation.
**Modules**
1. Jobmaster, deployed on the mining pool server to connect to the Bitcoin node.
* Jobmaster obtains mining task from the Bitcoin node and the Merged mining node, and sends it to Gateway.
* To accept instructions from Bitpeer and Poolbench, so as to generate empty block task.
* If a new block is successfully mined, it will be submitted to the node and broadcast by Blockmaster at the same time.
2. Gateway, deployed on the mining pool server and can be scaled horizontally.
* Implements the stratum protocol. When jobmaster sends the task, Gateway will forward it to miners, accept and verify the hashrate submitted by miners.
* Implements a custom proxy protocol. When jobmaster sends the task, gateway will forward it to mineragent, accept and verify the hashrate of mineragent.
* Aggregates hashrate and submits it to metawriter or metarelay.
3. Mineragent, mainly used in mining farms with a huge number of mining machines and deployed in the mining farms, which can effectively save bandwidth and improve performance.
* Implements the stratum protocol. It assigns task to miners, receives and verifies the hashrate submitted by miners.
* Implements custom proxy protocol, receives mining task from gateway and submits hashrate to gateway.
4. Blockmaster, connects the bitcoin node and bitpeer
* Implements the thin block function and speeds up the synchronization of nodes and blocks.
* After receiving the newly mined block, jobmaster will broadcast to multiple blockmaster and bitpeer to accelerate the block broadcasting.
5. Bitpeer, can be considered as a special bitcoin node, with any number of deployments.
* Implements the bitcoin p2p protocol and is connectable to multiple bitcoin nodes.
* After accepting blockmaster’s block submission, Bitpeer will broadcast the block to the connected bitcoin node.
* When Bitpeer noticed the block update of the connected node, it will prompt jobmaster to start mining empty blocks.
6. Poolbench
* Monitors the task update status of each mining pool.
* If the height of the tasks of other mining pools is updated, it will prompt jobmaster to start mining empty blocks.
7. Metawriter: Accpets the hashrate data submitted by Gateway or forwarded by Metarelay, and writes to redis after aggregating the data.
8. Metarelay: Accpets the hashrate data submitted by Gateway and forwards it to Metawriter.
9. Alertcenter: A simple server that writes FATAL level log to redis list so we can send alert emails.
## Redis Data Format
There are 3 type of keys.
1. event
* list of keys:
```
newblock
newevent
newworker
```
* example:
```
When new block found
newblock: {"name": "BTC", "hash": "0000000000000000032aee4bb112977ae8f4fb3614e0df196893285aa9c2adc0", "user": "haiyang", "worker": "example"}
list of event: connected, disconnected, When new connection connected or disconnected
newevent: {"user": "haiyang", "worker": "example", "coin": "BTC", "peer": "127.0.0.1", "event": "connected"}
When new worker connected
newworker: {"user": "haiyang", "worker": "example", "coin": "BTC"}
```
* read example: (python code)
```
while True:
try:
r = redis_master.blpop('newblock', 60)
except:
time.sleep(1)
continue
if not r:
continue
try:
data = json.loads(r[1])
except:
continue
```
2. Mining data
* key format:
```
<coin>:<t>:<user>(:<worker>(:reject))
coin: btc
t:
s: share count ( count of submit shares)
p: pow count (pow * 2^32 means how many hash have calculate)
g: pow goal, counts the contribution of user’s hashrate in mining a block. 1 means that the hashrate that can mine a block has been submitted.
1) type: hash
2) key: unix timestamp, integer, multiple of 60, example: 1482252540 , represent the summary 3) of result in that minute.
4) value: integer or float(pow goal)
```
* example:
```
btc:s:haiyang means user haiyang valid submit share count every minute
btc:s:haiyang:reject means user haiyang invalid submit share count every minute
btc:p:haiyang means user haiyang valid work every minute
btc:s:haiyang:example means user haiyang, worker example valid submit share count every minute
btc:s:haiyang:example:reject means user haiyang, worker example invalid submit share count every minute
btc:p:haiyang:example means user haiyang, worker example valid work every minute
```
3. System data
* key format:
```
<coin>:<type>:<key>
coin: btc
type:
m: monitor data
mh: monitor data of spec host
1) type: hash
2) key: unix timestamp, integer
3) value: integer
```
* example:
```
btc:m:pow means the hole mining pool work every minute. use this calculate pool hashrate
btc:mh:127.0.0.1:pow means gateway 127.0.0.1 total work every minute.
```
* important key:
```
btc:m:pow
btc:m:share
btc:m:reject
btc:m:block
btc:m:connections
set key: monitor:keys is a set of all keys
use redis command: SMEMBERS monitor:keys to get all keys
set key: <coin>:mk:<key> is a set of all host of special key,
example: SMEMBERS btc:mk:pow
1) "192.168.2.17"
2) "192.168.2.18"
```
## Compile and Install
**Operating system**
Ubuntu 16.04 or Ubuntu 18.04 or Ubuntu 20.04 or Debian 10. Not yet tested on other systems.
**Requirements**
See [requirements](https://github.com/viabtc/viabtc_mining_server/wiki/requirements). Install the mentioned system or library.
You MUST use the depends/hiredis to install the hiredis library. Or it may not be compatible.
**Compilation**
Compile network and utils first. The rest all are independent.
**Deployment**
Please do not install every instance on the same machine.
Every process runs in deamon and starts with a watchdog process. It will automatically restart within 1s when crashed.
The best practice of deploying the instance is in the following directory structure:
```
gateway
|---bin
| |---gateway.exe
|---log
| |---gateway.log
|---conf
| |---config.json
|---shell
| |---restart.sh
| |---check_alive.sh