tools is a collection of scripts for testing and configuration of Cyphal/CAN and DroneCAN nodes.
This package is under development.
1. Install the package from pypi, test.pypi or from sources
pip install raccoonlab-toolspip install -i https://test.pypi.org/simple/ raccoonlab-toolsgit clone https://github.com/PonomarevDA/tools.git
cd tools
pip install .2. Install dependencies
If you already have a Cyphal in your system, you probably don't need to install anything additional and have your own way of handling the environment variables and DSDL. Just check scripts/ubuntu.sh script in case if you miss something.
But if you use Cyphal for the first time or deploy a project in a new system, consider to run scripts/ubuntu.sh script. This script:
- Install all recommended dependencies,
- Clone recommended DSDL to
~/.cyphaldirectory, - Create in
~/.cyphaldirectory asetup.shscript that configure cyphal related environment variables and appendsource $HOME/cyphal/setup.shto the end of your.bashrcfile, so your shell will automatically setup the environment variables.
# By default, it installs both Cyphal and DroneCAN dependencies:
./scripts/ubuntu.sh
# Try --help option to get usage details. It allows to perform more precise installation:
./scripts/ubuntu.sh --helpClick here for details about which environment variables are required for a Cyphal application
To start with Cyphal/CAN (pycyphal, yakut, yukon) the following environment variables should be configured:
| Environment variable | Meaning |
|---|---|
| CYPHAL_PATH | Path to DSDL. Let's use the default:$HOME/.cyphal |
| UAVCAN__NODE__ID | The application node identifier |
| UAVCAN__CAN__IFACE | CAN iface name |
| UAVCAN__CAN__BITRATE | Arbitration/data segment bits per second |
| UAVCAN__CAN__MTU | Maximum transmission unit: 8 for classic CAN |
Check pycyphal/yakut/yukon docs for additional details
By default, DroneCAN and Cyphal/CAN uses cross-platform transport interface Python-CAN CAN over Serial / SLCAN.
On Linux, the socketcan interface is recommended. Unlike SLCAN, socketcan interface allows to share the same CAN interface with multiple processes, so you can run a few pycyphal scripts, yukon, yakut simultaniously.
You can run the following script:
./scripts/socketcan.shIf you don't have a real CAN device, you can create a virtual CAN interface:
./scripts/socketcan.sh --virtual-canTry --help option for more details.
For a Cyphal application after creating socketcan interface, you need to update UAVCAN__CAN__IFACE environment variable. Just call source ~/.bashrc.
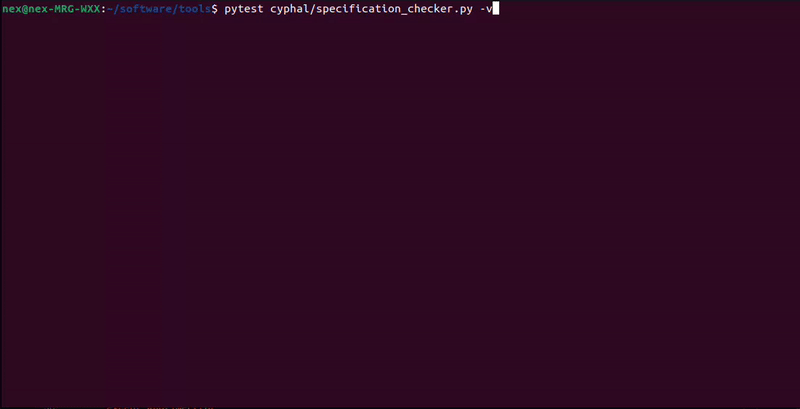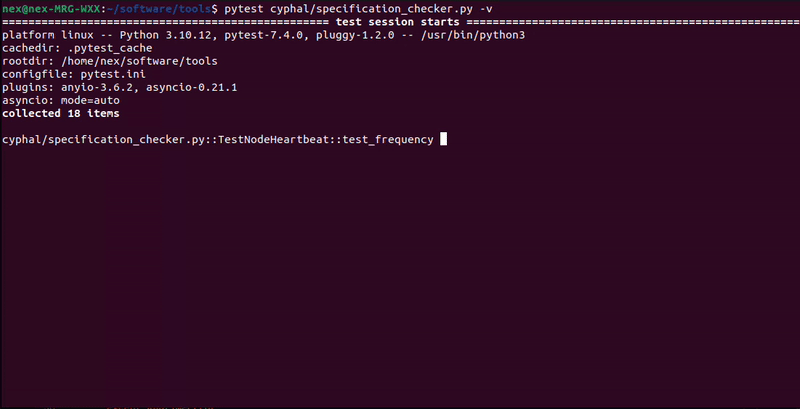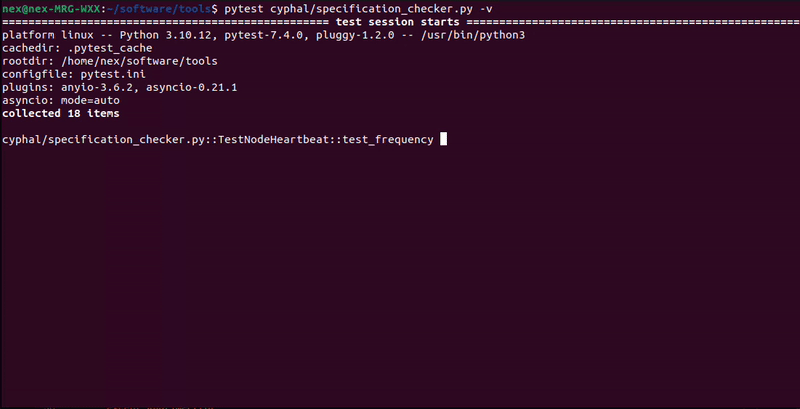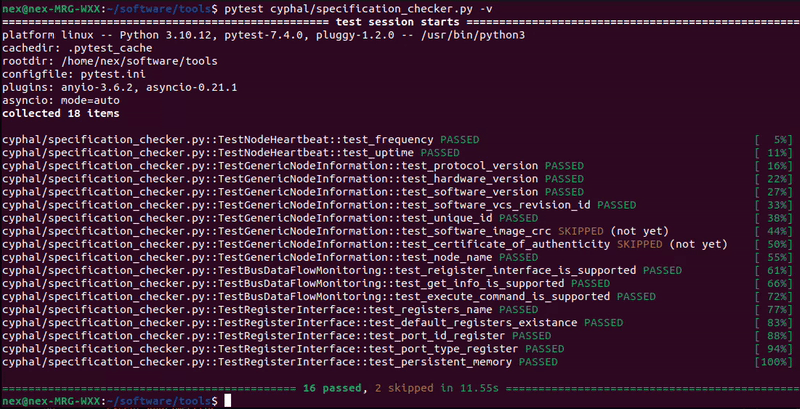
rl-test-cyphal-specificationrl-test-dronecan-specificationrl-test-dronecan-gps-mag-barorl-get-infoReturn:
- Online CAN-sniffers
- Detect protocol if any CAN-node is avaliable: cyphal | dronecan | none
- Show node info of Cyphal/CAN or DroneCAN node if it is avaliable
rl-upload-firmware --config PATH_TO_YAML_CONFIGrl-upload-firmware --binary PATH_TO_BIN_FILEThere are a few ways how you can specify the path to the binary:
- (recommended) Using a GitHub Repository. It will always download the latest released firmware.
# config.yaml
metadata:
link: RaccoonlabDev/mini_v2_node- Direct Link to the Firmware File
# config.yaml
metadata:
link: https://github.com/RaccoonlabDev/docs/releases/download/v1.6.5/gnss_v2_cyphal_v1.6.5_c78d47c3.bin- Using a Local Path
# config.yaml
metadata:
link: /user/home/firmwares/node.bin- Direct .bin path with
--binaryoption
rl-config --config PATHExample of yaml config file:
# config.yaml
params:
uavcan.node_id: 31
uavcan.node.name: co.rl.minirl-monitorThis script is used for automated node analysis. Within a single command:
- detect the protocol (Cyphal or DroneCAN),
- detect the node type,
- check the software version and highlight if it is not the latest,
- configure it if it has not been configured yet,
- subscribes on all possible topics,
- provide basic tests and diagnostics, highlight issues,
- publish some test commands if possible,
- print all data in real time.
An example of rl-monitor with gnss node:
rl-ublox-centerFor RL GNSS it is possible to run u-center over Cyphal via gps.ubx_tx and gps.ubx_rx topics.
- Download u-center (tested with u-center 23.08)
- Run the u-center. On ubuntu you can use wine (
wine64 u-centersetup_v23.08/u-center_v23.08.exe) - Configure the Cyphal environment
- Run the script
rl-ublox-center - Press Receiver - > Connection -> Network connection
- Add new connection
tcp://127.0.0.1:2001
An illustration:
Deploy to TestPyPI:
./scripts/deploy.shDeploy to PyPI:
./scripts/deploy.sh --pypiThe scripts are distributed under MIT license. In general, you can do with them whatever you want. If you find a bug, please suggest a PR or an issue.