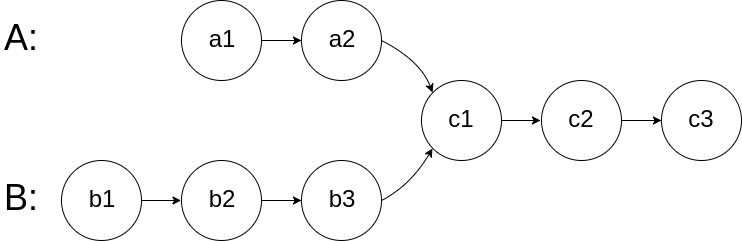
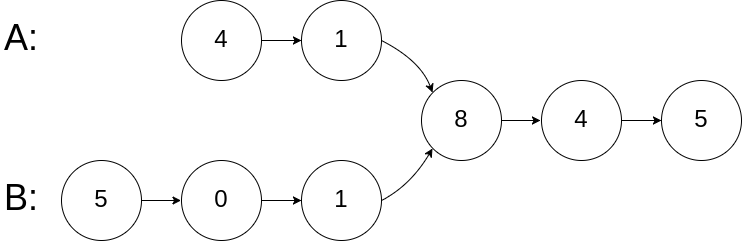
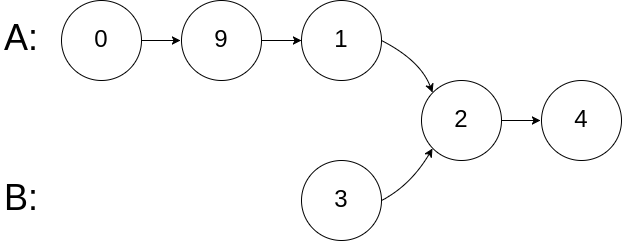
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.Example 3:
思路和代码 (reference: Cracking the Coding Interview):
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public class Result {
public ListNode tail;
public int size;
public Result(ListNode tail, int size){
this.tail = tail;
this.size = size;
}
}
Result getTailAndSize(ListNode list){
if (list == null) return null;
int size = 1;
ListNode current = list;
while(current.next != null){
size++;
current = current.next;
}
return new Result(current,size);
}
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) return null;
Result resA = getTailAndSize(headA);
Result resB = getTailAndSize(headB);
// if different tail nodes, then there's no intersection
if (resA.tail != resB.tail) return null;
// set pointer to the start of each linked list
ListNode shorter = resA.size < resB.size ? headA : headB;
ListNode longer = resA.size < resB.size ? headB : headA;
// Advance the pointer for the longer linked list by difference in lengths
longer = getKthNode(longer, Math.abs(resA.size - resB.size));
// move both pointers until you have a collision
while (shorter != longer){
shorter = shorter.next;
longer = longer.next;
}
return longer;
}
public ListNode getKthNode(ListNode head, int k){
ListNode current = head;
while (k>0 && current != null){
current = current.next;
k--;
}
return current;
}
}核心思想(One-pass一趟完成):
用快慢指针,将fast指针先移动到第n+1个位置。例如1-2-3-4-5,n = 2, 则将fast移动到“3”的位置上。
然后,开始移动slow, 并且继续移动fast,直到fast == None,即移动到空value为止。
此时只需要将slow.next给跳过,即slow.next = slow.next.next
最终返回start.next。
# one-pass
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
start = ListNode(-1)
fast = start
slow = start
slow.next = head
for i in range(1,n+2):
fast = fast.next
while fast != None:
# let fast keep moving, till it ends
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
# just skip the slow.next to .next.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return start.next 1. 用快慢指针,slower = faster = head
2. while (faster.next != None and faster.next.next != None):
slower = slower.next
faster = faster.next.next
if (slower == faster):
return True
3. return False input : 1-2-3-4
output: 2-1-4-3
********************
dummy.next = head
current = dummy
[d-1-2-3-4]
1) current = dummy, first = 1, second = 2
first.next = second.next
1 - 3
current.next = second
head = 2
current.next.next = first
(head.next = first)
2 - 1 - 3
current = current.next.next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
current = dummy
while current.next != None and current.next.next != None:
first = current.next
second = current.next.next
first.next = second.next
current.next = second
current.next.next = first
current = current.next.next
return dummy.nextExample:
Given this linked list:
1->2->3->4->5For k = 2, you should return:
2->1->4->3->5For k = 3, you should return:
3->2->1->4->5
/*
dm - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5
| | | | |
prev tail curr next last
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null) return null;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
while (prev != null)
prev = reverse(prev, k); // return tail, each k times move, let prev = tail
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverse(ListNode prev, int k) {
ListNode last = prev;
for (int i = 0; i < k + 1; i++) {
last = last.next;
if (i != k && last == null)
// k=3, dm-1-2-3-4-5, 4和5来说,长度不满足3, 无法反转
return null;
}
/*
dm - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5
| | | | |
prev tail curr next last
*/
ListNode tail = prev.next; // tail is "1"
ListNode curr = prev.next.next; // curr is "2"
while (curr != last) {
ListNode next = curr.next; // next is "3"
curr.next = prev.next; // 2 -> 1
prev.next = curr; // dm -> 2
tail.next = next; // 1 -> 3
curr = next; // move curr to next
}
return tail;
}
}Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4 Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
-
dm - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 | | | | | prev tail curr next last -
模板题,要反转“2 -> 3 -> 4”,依次将3接上2,4接上3,即可。
-
与上一题相似,也是属于反转链表的题目,要在[m, n]区间反转:
- 关键:明确五个指针的含义(以Example为例):
prev: 区间的前一个node,“1”last: 区间的后一个node,“5“tail: 左区间node,“2”。因为反转后会跑到区间尾部,顾名思义为 tailcurr: 区间的第二个node,“3”。因为定义了last表示区间的下一个点,如果循环curr到 last 则表明不再执行 reverse 操作。next:curr的下一个,next = curr.next
- 关键:明确五个指针的含义(以Example为例):
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (head == null)
return null;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode prev = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) { // 通过(m - 1)步找到prev
prev = prev.next;
}
reverse(prev, n - m + 1); // 区间长度
return dummy.next;
}
private void reverse(ListNode prev, int k) {
ListNode last = prev;
for (int i = 0; i < k + 1; i++) {
last = last.next; // 区间右边界
}
/*
dm - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 5 - null
| | | |
prev tail curr next
*/
ListNode tail = prev.next;
ListNode curr = prev.next.next;
while (curr != last) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev.next;
prev.next = curr;
tail.next = next;
curr = next;
}
}
}class Solution(object):
def minDepth(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: int
"""
if not root: return 0
h = map(self.minDepth, [root.left, root.right]) if root else [-1]
return 1 + (min(h) or max(h))res, queue = [], []
queue.append(root)
while len(queue) != 0:
temp = []
quesize = len(queue)
for i in range(quesize):
node = queue.pop(0)
if node.left is not None:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right is not None:
queue.append(node.right)
temp.append(node.val)
res.append(temp)
return res两种办法:
1. 递归。通过递归在分别对左子树和右子树进行如下检查:
初始状态:(-∞ < root.value < ∞)
对左子树: (-∞ < root.left.value < root.val)
对左子树:保持下界不变,改变上界值为其父节点(它的根节点)的值,判断root.left.val 是否比根节点要小,check(root.left, low, root.val)
对右子树: (root.val < root.right.value < ∞)
对右子树:保持上界不变,改变下界值为父节点(它的根节点)的值,
判断root.right.val 是否比根节点大,check(root.right, root.val, high)
2. 中序遍历,in-order traversal
代码如下:
'''
In-order Traversal
'''
class Solution(object):
def isValidBST(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return True
res = []
res1 = self.in_order_trv(root, res)
for i in range(len(res1)-1):
if res1[i+1] <= res1[i]:
return False
return True
def in_order_trv(self, root, res):
if root:
res = self.in_order_trv(root.left, res)
res.append(root.val)
res = self.in_order_trv(root.right, res)
return resif root:
if target < root and not root.left:
into(root.left)
elif target > root and not root.right:
into(root.right)
else:
if target < root:
root.left = target
else:
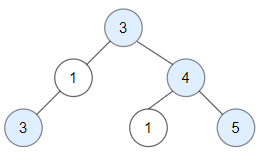
root.right = targetGiven a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and
sum = 22,5 / \ 4 8 / / \ 11 13 4 / \ \ 7 2 1return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path
5->4->11->2which sum is 22.
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, findSum: int) -> bool:
res = []
self.dfs(root,findSum,res)
if True in res:
return True
return False
def dfs(self, root, target, res):
if root:
if not root.left and not root.right:
if root.val == target:
res.append(True)
if root.left:
remain = target - root.val
self.dfs(root.left, remain, res)
if root.right:
remain = target - root.val
self.dfs(root.right, remain, res)
Given a binary tree and a sum, find all root-to-leaf paths where each path's sum equals the given sum.
Note: A leaf is a node with no children.
Example:
Given the below binary tree and
sum = 22,5 / \ 4 8 / / \ 11 13 4 / \ / \ 7 2 5 1Return:
[ [5,4,11,2], [5,8,4,5] ]
三种写法:
- Recursive
- BFS + queue
- DFS + stack
代码:
# 递归 Recursive
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
res = []
self.dfs(root, sum, [], res)
return res
def dfs(self, root, sum, ls, res):
if not root.left and not root.right and sum == root.val:
ls.append(root.val)
res.append(ls)
return res
else:
if root.left:
self.dfs(root.left, sum - root.val, ls + [root.val], res)
if root.right:
self.dfs(root.right, sum - root.val, ls + [root.val], res)
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
# BFS + queue
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
res = []
queue = deque([(root, root.val, [root.val])])
while queue:
node, pop_val, ls = queue.popleft()
if not node.left and not node.right and pop_val == sum:
res.append(ls)
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left, pop_val + node.left.val, ls+[node.left.val]))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right, pop_val + node.right.val, ls+[node.right.val]))
return res
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
# DFS + stack
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
res = []
stack = [(root, sum - root.val, [root.val])]
while stack:
node, pop_val, ls = stack.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right and pop_val == 0:
res.append(ls)
if node.right:
stack.append((node.right, pop_val - node.right.val, ls+[node.right.val]))
if node.left:
stack.append((node.left, pop_val - node.left.val, ls+[node.left.val]))
return resYou are given a binary tree in which each node contains an integer value.
Find the number of paths that sum to a given value.
The path does not need to start or end at the root or a leaf, but it must go downwards (traveling only from parent nodes to child nodes).
The tree has no more than 1,000 nodes and the values are in the range -1,000,000 to 1,000,000.
Example:
root = [10,5,-3,3,2,null,11,3,-2,null,1], sum = 8 10 / \ 5 -3 / \ \ 3 2 11 / \ \ 3 -2 1 Return 3. The paths that sum to 8 are: 1. 5 -> 3 2. 5 -> 2 -> 1 3. -3 -> 11
代码:
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, S: int) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
ans = {"nums":0}
sums = {0:1}
def dfs(node, sums, currSum):
if not node:
return
newSum = node.val + currSum
if newSum - S in sums:
ans['nums'] += sums[newSum - S]
if not node.left and not node.right:
return
sums[newSum] = sums.get(newSum,0)+1
dfs(node.left, sums, newSum)
dfs(node.right, sums, newSum)
sums[newSum] -= 1
dfs(root, sums, 0)
return ans['nums']
public class Solution {
int maxValue;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
maxValue = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
maxPathDown(root);
return maxValue;
}
private int maxPathDown(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
int left = Math.max(0, maxPathDown(node.left));
int right = Math.max(0, maxPathDown(node.right));
maxValue = Math.max(maxValue, left + right + node.val);
return Math.max(left, right) + node.val;
}
}Given preorder and inorder traversal of a tree, construct the binary tree.
For example, given
preorder = [3,9,20,15,7]
inorder = [9,3,15,20,7]
Return the following binary tree:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
核心思路:
通过前序遍历,找到根节点,然后在中序遍历中把该根节点的下标找到,以root为中心,依次对中序遍历的左半部分和右半部分分别进行左子树和右子树的构建。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def buildTree(self, preorder, inorder):
"""
:type preorder: List[int]
:type inorder: List[int]
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
def build(preorder, inorder, pre_start, in_start, in_end, mp):
# corner case
if pre_start >= len(preorder) or in_start > in_end:
return None
root = TreeNode(preorder[pre_start])
root_index = mp[preorder[pre_start]]
# build left and right subtree
root.left = build(preorder, inorder, pre_start+1, in_start, root_index-1, mp)
root.right = build(preorder, inorder, pre_start + root_index - in_start+1,
root_index+1, in_end, mp)
return root
mp = {}
for i, num in enumerate(inorder):
mp[num] = i
return build(preorder, inorder, 0, 0, len(inorder)-1, mp)Given a binary tree, collect a tree's nodes as if you were doing this: Collect and remove all leaves, repeat until the tree is empty.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5] 1 / \ 2 3 / \ 4 5 Output: [[4,5,3],[2],[1]]
class Solution():
def findLeaves(self, root):
if root == None:
return []
def removeLeaves(root, lst):
if root == None:
return True
if root.left == None and root.right==None:
lst.append(root.val)
return True
if root.left and removeLeaves(root.left,lst):
root.left = None
if root.right and removeLeaves(root.right, lst):
root.right = None
return False
res = []
while root:
lst = []
if (removeLeaves(root,lst)):
root = None
res.append(lst)
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1:
Input: 1 1 / \ / \ 2 3 2 3 [1,2,3], [1,2,3] Output: trueExample 2:
Input: 1 1 / \ 2 2 [1,2], [1,null,2] Output: falseExample 3:
Input: 1 1 / \ / \ 2 1 1 2 [1,2,1], [1,1,2] Output: false
代码:
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// 递归终止,左右子树均为空,则返回true
if (p==null && q==null)
return true;
// 一边为空,一边不为空,说明不是same tree,返回false
if (p==null || q==null)
return false;
// 比较值不同,返回false
if (p.val != q.val)
return false;
// 递归调用左子树(p.left, q.left) 和 右子树(p.right, q.right)
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
}Given a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (ie, symmetric around its center).
For example, this binary tree
[1,2,2,3,4,4,3]is symmetric:1 / \ 2 2 / \ / \ 3 4 4 3But the following
[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]is not:1 / \ 2 2 \ \ 3 3
判断条件:
- 两个值相同,
t1.val == t2.val - 左=右,右=左,
isMirror(t1.right, t2.left) && isMirror(t1.left, t2.right);
代码:
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return isMirror(root, root);
}
public boolean isMirror(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return false;
return (t1.val == t2.val)
&& isMirror(t1.right, t2.left)
&& isMirror(t1.left, t2.right);
}
}Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted array: [-10,-3,0,5,9], One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST: 0 / \ -3 9 / / -10 5
思路:
- 因为数组已经排好序,且BST是左 < 中 < 右,则只需要将数组中位数
arr[mid]作为root,分别对数组左半部分和右半部分进行递归。
代码:
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0)
return null;
int mid = nums.length / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = sortedArrayToBST(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, mid));
root.right = sortedArrayToBST(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, mid + 1, nums.length));
return root;
}
}class Solution:
def sortedArrayToBST(self, arr: List[int]) -> TreeNode:
if not arr:
return None
mid = len(arr) // 2
root = TreeNode(arr[mid])
root.left = self.sortedArrayToBST(arr[:mid])
root.right = self.sortedArrayToBST(arr[mid+1:])
return rootGiven an integer n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1 ... n.
Example:
Input: 3 Output: [ [1,null,3,2], [3,2,null,1], [3,1,null,null,2], [2,1,3], [1,null,2,null,3] ] Explanation: The above output corresponds to the 5 unique BST's shown below: 1 3 3 2 1 \ / / / \ \ 3 2 1 1 3 2 / / \ \ 2 1 2 3
思路:
- 对于1...n 中每个值 i ,都可以作为树根,那么左子树范围 [1... i-1] 和右子树范围 [i+1 ... n]分别通过相同的递归添加到
root{i}.left和root{i}.right中。 - 递归终止1:当上述范围出现区间的边界值都相等,比如[3, 3],这时直接把“3”加到result列表中,并返回
- 递归终止2:当区间 [l, r] 出现 l > r, 则说明构不成BST,直接返回
null
代码:
class Solution {
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) {
if (n == 0)
return new ArrayList<TreeNode>();
return gen(1, n);
}
private List<TreeNode> gen(int l, int r) {
List<TreeNode> ans = new ArrayList<>();
if (l > r) {
ans.add(null);
return ans;
}
if (l == r) {
ans.add(new TreeNode(l));
return ans;
}
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
// 对每个值都当做根节点root,找到左子树和右子树递归。
List<TreeNode> sub_left = gen(l, i - 1);
List<TreeNode> sub_right = gen(i + 1, r);
for (TreeNode left : sub_left)
for (TreeNode right : sub_right) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
node.left = left;
node.right = right;
ans.add(node);
}
}
return ans;
}
}Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1 ... n?
代码:
class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
dp[i] += dp[j] * dp[i - j - 1];
return dp[n];
}
}Given a binary tree
root, a node X in the tree is named good if in the path from root to X there are no nodes with a value greater than X.Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5] Output: 4 Explanation: Nodes in blue are good. Root Node (3) is always a good node. Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root. Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
思路:
- 从根节点开始递归,因为要找至少大于等于root的值,所以在dfs的时候要先判断当前最大值MAX和当前节点的值,也就是说,找到比max更大的节点值后,需要把MAX更新为 max(MAX, node.val),再进行递归。
代码:
class Solution {
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
return helper(root, -10000); // 讲MAX初始化成一个最小值
}
private int helper(TreeNode root, int MAX) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int count = root.val >= MAX ? 1 : 0; // 找到一个节点大于等于MAX
count += helper(root.left, Math.max(MAX, root.val));
count += helper(root.right, Math.max(MAX, root.val));
return count;
}
}核心思想:
class Solution:
def rob(self, A: List[int]) -> int:
money = [-1]*len(A)
if not A:
return 0
if len(A) == 1:
return A[0]
if len(A) == 2:
return max(A[0],A[1])
money[0] = A[0]
money[1] = max(A[:2])
for i in range(2, len(A)):
money[i] = max(money[i-2]+A[i], money[i-1])
return max(money)class Solution:
def rob_subtree(self, root, Hashmap):
if not root:
return 0
if root in Hashmap:
return Hashmap.get(root)
val = 0
if root.left != None:
val += self.rob_subtree(root.left.left, Hashmap) + self.rob_subtree(root.left.right, Hashmap)
if root.right != None:
val += self.rob_subtree(root.right.left, Hashmap) + self.rob_subtree(root.right.right, Hashmap)
val = max(val + root.val, self.rob_subtree(root.left,Hashmap)
+self.rob_subtree(root.right,Hashmap))
Hashmap[root] = val
return val
def rob(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
Hashmap = {}
return self.rob_subtree(root, {})题目描述详见 issue
直接在costs修改
costs[i][j]
costs[n][0] = min(costs[n-1][1], costs[n-1][2]) + costs[n][0]
costs[n][1] = min(costs[n-1][0], costs[n-1][2]) + costs[n][1]
costs[n][2] = min(costs[n-1][0], costs[n-1][1]) + costs[n][2]返回costs最后一间房子的最小值,
min(costs[-1])
class Solution:
def minCost(self, costs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not costs:
return 0
if len(costs) == 1:
return min(costs[0])
for n in range(1, len(costs)):
costs[n][0] = min(costs[n-1][1], costs[n-1][2]) + costs[n][0]
costs[n][1] = min(costs[n-1][0], costs[n-1][2]) + costs[n][1]
costs[n][2] = min(costs[n-1][0], costs[n-1][1]) + costs[n][2]
return min(costs[-1])NOTE: n houses, k colors, costs: n * k matrix
class Solution:
def minCostII(self, costs: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not costs:
return 0
if len(costs) == 1:
return min(costs[0])
for i_house in range(1, len(costs)):
for j_color in range(len(costs[0])):
costs[i_house][j_color] = min(costs[i_house-1][:j_color]+costs[i_house-1][j_color+1:]) + costs[i_house][j_color]
print(costs)
return min(costs[-1])思路1 (不降维):
参考代码:
class Solution:
def maximalSquare(self, m: List[List[str]]) -> int:
if len(m) == 0:
return 0
rows = len(m)
cols = len(m[0]) if rows > 0 else 0
dp = [[0]*(cols+1) for _ in range(rows+2)]
MAX_LEN = 0
for i in range(1, rows+1):
for j in range(1, cols+1):
if m[i-1][j-1] == "1":
dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j-1], dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1]) + 1
MAX_LEN = max(MAX_LEN, dp[i][j])
return MAX_LEN * MAX_LENYou are given a list of non-negative integers, a1, a2, ..., an, and a target, S. Now you have 2 symbols + and -. For each integer, you should choose one from + and - as its new symbol.
Find out how many ways to assign symbols to make sum of integers equal to target S.
核心思路:
https://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/?s=494
// Java
// Runtime: 7 ms (83%)
class Solution {
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int S) {
int sum = 0;
for (final int num : nums)
sum += num;
if (sum < S) return 0;
final int kOffset = sum;
final int kMaxN = sum * 2 + 1;
int[] ways = new int[kMaxN];
ways[kOffset] = 1;
for (final int num : nums) {
int[] tmp = new int[kMaxN];
for (int i = num; i < kMaxN - num; ++i) {
// 以当前数字为中心,分别找加上或减去num刚好在kMaxN范围内,从上一层的计算得到的ways[i].
// ways[i] means the total ways to sum up N (-kMaxN ~ kMaxN)
tmp[i + num] += ways[i];
tmp[i - num] += ways[i];
}
// update ways
ways = tmp;
}
return ways[S + kOffset];
}
}// DP rules := dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i-2] + cost[i-2], dp[i-1] + cost[i-1])
// dp[i] means the min cost before climbing the "i"th stairs, two ways.
class Solution {
public int minCostClimbingStairs(int[] cost) {
int dp[] = new int[cost.length + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, 0);
for (int i = 2; i<=cost.length; i++){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i-2] + cost[i-2], dp[i-1] + cost[i-1]);
}
return dp[cost.length];
}
}class Solution {
public int numSquares(int n) {
int dp[] = new int[n+1];
Arrays.fill(dp, n+1);
dp[0] = 0;
int top = (int)Math.sqrt(n);
int squares[] = new int[top];
for (int i = 0; i < top; i++){
squares[i] = (i+1) * (i+1);
}
for (int number : squares){
for (int i = number; i <= n; i++){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i-number]+1);
}
}
return dp[n];
}
} 方法1:动态规划问题,从下至上递推求解
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
if (m<=0||n<=0){
return 0;
}
int [][]dp = new int[m][n];
for (int row = 0; row < m ; row++){
dp[row][0] = 1;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++){
dp[0][col] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m ; i++){
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
} 方法2: 记忆化递归求解,耗时较长
public:
int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
if (m<0 || n<0)
return 0;
if (m==1 && n==1)
return 1;
if (memo[m][n] > 0)
return memo[m][n];
int left_path = uniquePaths(m-1, n);
int up_path = uniquePaths(m, n-1);
memo[m][n] = left_path + up_path;
return memo[m][n];
}
private:
unordered_map<int, unordered_map<int, int>> memo;
总结:基本思路一致,就是若要求得走到(m,n)的位置,即f[m][n],只有从left和up两个方向进行考虑
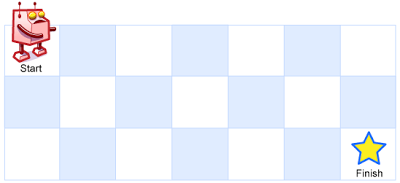
即f[m][n] = f[m-1][n] + f[m][n-1],直到终止条件为起点。A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as 1 and 0 respectively in the grid.
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
与上一题的基本思路相似,可以采用记忆化递归求解,在这里需要注意的是:
- 在递归的时候,需要处理
grid[i-1][j-1] == 1的情况,即碰到障碍物时,将dp[i][j] = 0. - 边界条件,
return 0- 另外,当
r==1 and c==1: return 1-grid[0][0]的意思是,此时已经从右下追溯到起点了,那么对于起点的值,即grid[0][0]来说,如果为0,这说明此路有一种方法可达,即把dp[1][1]设为1,return 1 - 0 = 1,反之,如果在起点的值是1,这说明起点就有障碍物,返回1 - 1 = 0.
- 另外,当
- 记忆化处理:
if dp[i][j] != INT_MIN, 直接返回求过的dp值,return dp[i][j]
代码:
class Solution(object):
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, grid):
row = len(grid)
if row == 0: return 0
col = len(grid[0])
# dp[i][j] = path(i,j), INT_MIN: not solved yet, unknown solution
dp = [[-2**31]*(col+1) for _ in range(row+2)]
def paths(dp,r,c,grid):
if r<=0 or c<=0: return 0
# if r,c=1, reach the start point
if r==1 and c==1: return 1-grid[0][0]
# if already solved, just return the answer.
if dp[r][c] != -2**31: return dp[r][c]
# if there's an obstacle, set path to 0.
if grid[r-1][c-1] == 1:
dp[r][c] = 0
else:
dp[r][c] = paths(dp,r,c-1,grid)+paths(dp,r-1,c,grid)
return dp[r][c]
return paths(dp,row,col,grid)与这题相似的解法题为 [DP-8] Perfect Squares
我们定义dp[i]时,dp长度为amount+1, 初始化dp[0] = 0, 其余dp[1...N]为amount+1 (或者integer最大值)。
class Solution {
public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
int []dp = new int[amount+1];
Arrays.fill(dp, amount+1);
dp[0] = 0;
for (int coinType : coins)
for (int i = coinType; i<= amount; i++){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i], dp[i - coinType]+1);
}
return dp[amount] < amount+1 ? dp[amount] : -1;
}
}与上一题不同,在coin change 2当中,我们定义dp[i]时,dp长度为amount+1, 初始化dp[0] = 1, 其余dp[1...N]为0。
因为这题求的是一共有多少种累加到amount的方法,所以dp[i]应该叠加。
与上一题不同,在每次更新dp[i]时,应该累加之前的结果,转换方程为: dp[i] += dp[i - coin],意思就是每次遇到新的钱币类型($1, $2, $5),时,都要叠加之前算过的结果,和上一题不同的是,上一题的dp[i]代表每次循环新的钱币类型时,都要先比较出一个最小值,再更新dp[i]
python代码:
class Solution(object):
def change(self, amount, coins):
"""
:type amount: int
:type coins: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [0]* (amount + 1)
dp[0] = 1
for coin in coins:
for i in range(coin, amount+1):
dp[i] += dp[i - coin]
return dp[amount] if dp[amount] != 0 else 0Given an array of scores that are non-negative integers. Player 1 picks one of the numbers from either end of the array followed by the player 2 and then player 1 and so on. Each time a player picks a number, that number will not be available for the next player. This continues until all the scores have been chosen. The player with the maximum score wins.
Given an array of scores, predict whether player 1 is the winner. You can assume each player plays to maximize his score.
Example 1:
Input: [1, 5, 2] Output: False Explanation: Initially, player 1 can choose between 1 and 2. If he chooses 2 (or 1), then player 2 can choose from 1 (or 2) and 5. If player 2 chooses 5, then player 1 will be left with 1 (or 2). So, final score of player 1 is 1 + 2 = 3, and player 2 is 5. Hence, player 1 will never be the winner and you need to return False.Example 2:
Input: [1, 5, 233, 7] Output: True Explanation: Player 1 first chooses 1. Then player 2 have to choose between 5 and 7. No matter which number player 2 choose, player 1 can choose 233.Finally, player 1 has more score (234) than player 2 (12), so you need to return True representing player1 can win.Note:
- 1 <= length of the array <= 20.
- Any scores in the given array are non-negative integers and will not exceed 10,000,000.
- If the scores of both players are equal, then player 1 is still the winner.
方法一:递归所有子序列的所有可能,非常慢
# Python
class Solution(object):
def PredictTheWinner(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
def getScore(nums, le, ri):
if le == ri:
return nums[le]
return max(nums[le] - getScore(nums, le+1, ri),
nums[ri] - getScore(nums, le, ri-1))
return getScore(nums, 0, len(nums)-1) >= 0// Java
class Solution {
private int[] m;
public boolean PredictTheWinner(int[] A) {
m = new int[A.length * A.length];
Arrays.fill(m, 0);
return getscore(A, 0, A.length - 1) >= 0;
}
public int getscore(int[] A, int left, int right) {
if (left == right) return A[left];
int pos = left * A.length + right;
if (m[pos] > 0) {
// 记忆化递归
return m[pos];
}
m[pos] = Math.max(A[left] - getscore(A, left + 1, right) ,
A[right] - getscore(A, left, right - 1));
return m[pos];
}
}方法二:记忆化递归,高效(推荐)
class Solution(object):
def PredictTheWinner(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: bool
"""
def getScore(nums, le, ri, m):
if le == ri:
return nums[le]
m_pos = le * len(nums) + ri
if m[m_pos] > 0:
return m[m_pos]
m[m_pos] = max(nums[le] - getScore(nums, le+1, ri, m),
nums[ri] - getScore(nums, le, ri-1, m))
return m[m_pos]
m = [0]*(len(nums)**2)
return getScore(nums, 0, len(nums)-1, m) >= 0方法三:
设定两个函数,
f(x)和s(x)分别表示先手和后手两种情况:如果先发,那么应该返回的是拿走前面的数字或者拿走后面的数字能拿到的结果的最大值。但是如果后发,那么应该返回的是前面不拿和后面不拿的最小值。
class Solution(object):
def PredictTheWinner(self, nums):
_sum = sum(nums)
self.f_map, self.s_map = dict(), dict()
player1 = self.f(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
return player1 >= _sum / 2.0
def f(self, nums, start, end): # 先
if start == end:
return nums[start]
if (start, end) not in self.f_map:
# 先发,取最大值
f_val = max(nums[start] + self.s(nums, start+1, end), nums[end] + self.s(nums, start, end-1))
self.f_map[(start, end)] = f_val
return self.f_map[(start, end)]
def s(self, nums, start, end): # 后
if start == end:
return 0
if (start, end) not in self.s_map:
# 后发,取最小值
s_val = min(self.f(nums, start+1, end), self.f(nums, start, end-1))
self.s_map[(start, end)] = s_val
return self.s_map[(start, end)]Given an integer array with all positive numbers and no duplicates, find the number of possible combinations that add up to a positive integer target.
Example:
nums = [1, 2, 3]
target = 4
The possible combination ways are:
(1, 1, 1, 1)
(1, 1, 2)
(1, 2, 1)
(1, 3)
(2, 1, 1)
(2, 2)
(3, 1)
Note that different sequences are counted as different combinations.
Therefore the output is 7.
class Solution:
def combinationSum4(self, nums, target):
dp = [0] * (target+1)
dp[0] = 1
for i in range(1,target+1):
for num in nums:
if i - num>=0:
dp[i] += dp[i-num]
return dp[target]Given a set of distinct integers, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[3],
[1],
[2],
[1,2,3],
[1,3],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[]
]
class Solution():
def subset(self, nums):
res = [[]]
if not nums:
return res
for num in nums:
for le in range(len(res)):
res.append(res[le] + [num])
return res-
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
-
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Input: [1,2,2]
Output:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
class Solution(object):
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
nums, result, pos = sorted(nums), [[]], {}
for n in nums:
start, len_ = pos.get(n, 0), len(result)
# start: if current num is new, then start = 0
# if not, then start = len_
for r in result[start:]:
result += [r + [n]]
pos[n] = len_
return resultGiven a 2D board and a word, find if the word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cell, where "adjacent" cells are those horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example:
board =
[
['A','B','C','E'],
['S','F','C','S'],
['A','D','E','E']
]
Given word = "ABCCED", return true.
Given word = "SEE", return true.
Given word = "ABCB", return false.
代码:
class Solution {
private int w;
private int h;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
if (board.length == 0)
return false;
h = board.length;
w = board[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
if (search(board, word, 0, i, j))
return true;
return false;
}
public boolean search(char[][] board, String word, int pos, int x, int y){
if (x<0 || x==w || y<0 || y==h || word.charAt(pos) != board[y][x])
return false;
if (pos == word.length() -1)
return true;
char cur = board[y][x];
board[y][x] = 0;
boolean find_every_dir =
search(board, word, pos+1, x+1, y)
|| search(board, word, pos+1, x-1, y)
|| search(board, word, pos+1, x, y+1)
|| search(board, word, pos+1, x, y-1);
board[y][x] = cur;
return find_every_dir;
}
}Given a 2D board containing
'X'and'O'(the letter O), capture all regions surrounded by'X'.A region is captured by flipping all
'O's into'X's in that surrounded region.Example:
X X X X X O O X X X O X X O X XAfter running your function, the board should be:
X X X X X X X X X X X X X O X XExplanation:
Surrounded regions shouldn’t be on the border, which means that any
'O'on the border of the board are not flipped to'X'. Any'O'that is not on the border and it is not connected to an'O'on the border will be flipped to'X'. Two cells are connected if they are adjacent cells connected horizontally or vertically.
基本思路:
- 先处理边界条件,对第一行、最后一行、第一列、最后一列进行遍历,找到为'O'的岛屿进行DFS,标记visited, 对这些岛屿不进行反转。
- 然后,遍历边界内部的区域,找到为'O'的岛屿进行上下左右的DFS,标记visited, 并且将
boolean change设为true, 在DFS中针对这些值为true的岛屿做反转操作。
代码:
class Solution(object):
def solve(self, board):
if not board or len(board) == 0:
return
row, col = len(board), len(board[0])
visited = [[False]*col for _ in range(row)]
# 先处理四条边的情况
for j in range(col):
# 第一行
if board[0][j] == 'O':
self.dfs(board, 0, j, visited, False)
# 最后一行
if board[row-1][j] == 'O':
self.dfs(board, row-1, j, visited, False)
for i in range(row):
# 第一列
if board[i][0] == 'O':
self.dfs(board, i, 0, visited, False)
# 最后一列
if board[i][col-1] == 'O':
self.dfs(board, i, col-1, visited, False)
# 其余情况,对边界内部的岛屿进行dfs和反转操作
for i in range(1,row-1):
for j in range(1, col-1):
if board[i][j] == 'O':
self.dfs(board, i, j, visited, True)
def dfs(self, board, row, col, visited, change):
# 越界情况,return
if row<0 or row>len(board)-1 or col<0 or col>len(board[0])-1:
return
if board[row][col] == 'X':
return
if visited[row][col] == True:
return
if change == True:
board[row][col] = 'X'
visited[row][col] = True
self.dfs(board, row+1, col, visited, change)
self.dfs(board, row-1, col, visited, change)
self.dfs(board, row, col+1, visited, change)
self.dfs(board, row, col-1, visited, change)Given a 2d grid map of
'1's (land) and'0's (water), count the number of islands. An island is surrounded by water and is formed by connecting adjacent lands horizontally or vertically. You may assume all four edges of the grid are all surrounded by water.Example 1:
Input: 11110 11010 11000 00000 Output: 1Example 2:
Input: 11000 11000 00100 00011 Output: 3
三种方法:
- DFS
- BFS + queue
- 并查集 (Union Find)
DFS:
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] board) {
if (board == null || board.length == 0) return 0;
int row = board.length, col = board[0].length;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++){
count += board[i][j] - '0';
dfs(board, i, j);
}
}
return count;
}
private void dfs(char[][] board, int i, int j){
if (i < 0 || j < 0 || i >= board.length || j >= board[0].length || board[i][j] == '0')
return;
board[i][j] = '0';
dfs(board, i, j+1);
dfs(board, i, j-1);
dfs(board, i+1, j);
dfs(board, i-1, j);
}
}BFS + queue:
# BFS
import collections
class Solution(object):
def __init__(self):
self.dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
self.dy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
def numIslands(self, grid): # main
if not grid or not grid[0]: return 0
self.max_x = len(grid); self.max_y = len(grid[0]); self.grid = grid;
self.visited = set()
count = 0
for i in range(self.max_x):
for j in range(self.max_y):
if self.isValid(i, j):
self.floodfill(i, j)
count += 1
return count
def floodfill(self, x, y):
if not self.isValid(x, y):
return
self.visited.add((x, y))
queue = collections.deque()
queue.append((x, y))
while queue:
cur_x, cur_y = queue.popleft()
for i in range(4):
next_x, next_y = cur_x + self.dx[i], cur_y + self.dy[i]
if self.isValid(next_x, next_y):
self.visited.add((next_x, next_y))
queue.append((next_x, next_y))
def isValid(self, x, y):
if x < 0 or x >= self.max_x or y < 0 or y >= self.max_y:
return False
if self.grid[x][y] == '0' or ((x, y) in self.visited):
return False
return True并查集 Union Find:
# numbers of island - union find
class UnionFind(object):
def __init__(self, grid):
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
self.count = 0;
self.parent = [-1] * (m * n) # size = m * n
self.rank = [0] * (m * n) # size = m * n
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == '1':
self.parent[i * n + j] = i * n + j
self.count += 1 # count nums of 1
def find(self, i):
if self.parent[i] != i:
self.parent[i] = self.find(self.parent[i])
return self.parent[i]
def union(self, x, y):
rootx = self.find(x)
rooty = self.find(y)
if rootx != rooty:
if self.rank[rootx] > self.rank[rooty]:
self.parent[rooty] = rootx
elif self.rank[rooty] > self.rank[rootx]:
self.parent[rootx] = rooty
else:
self.parent[rooty] = rootx
self.rank[rootx] += 1
self.count -= 1 # every time find its root
###########################################################################
class Solution(object):
def numIslands(self, grid):
if not grid or not grid[0]:
return 0
uf = UnionFind(grid)
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
dirs = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (1, 0), (-1, 0)]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if grid[i][j] == '0':
continue
for d in dirs:
nr, nc = i + d[0], j + d[1]
if (nr >= 0 and nr < m and nc >=0 and nc < n and grid[nr][nc] == '1'):
uf.union(i * n + j, nr * n + nc)
return uf.countGiven a non-empty 2D array
gridof 0's and 1's, an island is a group of1's (representing land) connected 4-directionally (horizontal or vertical.) You may assume all four edges of the grid are surrounded by water.Find the maximum area of an island in the given 2D array. (If there is no island, the maximum area is 0.)
Example 1:
[[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0], [0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0], [0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0], [0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0], [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]Given the above grid, return
6. Note the answer is not 11, because the island must be connected 4-directionally.Example 2:
[[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]Given the above grid, return
0.
代码:
// return max area of island
class Solution {
private int h;
private int w;
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
if (grid.length == 0) return 0;
h = grid.length;
w = grid[0].length;
int max_area = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
max_area = Math.max(max_area, getArea(grid, j, i));
return max_area;
}
private int getArea(int[][] grid, int x, int y) {
// stop condition, [border or water area]
if (x < 0 || x >= w || y < 0 || y >= h || grid[y][x] == 0)
return 0;
// 排除“0”之后,对于“1”的点,这里作置0处理,即将其岛屿沉没,避免重复计算岛屿数量
grid[y][x] = 0;
int ans = getArea(grid, x + 1, y)
+ getArea(grid, x - 1, y)
+ getArea(grid, x, y + 1)
+ getArea(grid, x, y - 1)
+ 1;
return ans;
}
}There are N students in a class. Some of them are friends, while some are not. Their friendship is transitive in nature. For example, if A is a direct friend of B, and B is a direct friend of C, then A is an indirect friend of C. And we defined a friend circle is a group of students who are direct or indirect friends.
Given a N*N matrix M representing the friend relationship between students in the class. If M[i][j] = 1, then the ith and jth students are direct friends with each other, otherwise not. And you have to output the total number of friend circles among all the students.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,1,0], [1,1,0], [0,0,1]] Output: 2 Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, so they are in a friend circle. The 2nd student himself is in a friend circle. So return 2.Example 2:
Input: [[1,1,0], [1,1,1], [0,1,1]] Output: 1 Explanation:The 0th and 1st students are direct friends, the 1st and 2nd students are direct friends, so the 0th and 2nd students are indirect friends. All of them are in the same friend circle, so return 1.Note:
- N is in range [1,200].
- M[i][i] = 1 for all students.
- If M[i][j] = 1, then M[j][i] = 1.
代码:
class Solution:
def findCircleNum(self, M: List[List[int]]) -> int:
def dfs(M, curr, n):
for i in range(n):
if M[curr][i] == 1:
M[curr][i] = M[i][curr] = 0
# i是curr找到的朋友,因此处理完curr之后,继续对curr的朋友i进行dfs
dfs(M, i, n)
n = len(M)
ans = 0
for i in range(n):
if M[i][i] == 1:
ans += 1
dfs(M, i, n)
return ansAn
imageis represented by a 2-D array of integers, each integer representing the pixel value of the image (from 0 to 65535).Given a coordinate
(sr, sc)representing the starting pixel (row and column) of the flood fill, and a pixel valuenewColor, "flood fill" the image.To perform a "flood fill", consider the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to the starting pixel of the same color as the starting pixel, plus any pixels connected 4-directionally to those pixels (also with the same color as the starting pixel), and so on. Replace the color of all of the aforementioned pixels with the newColor.
At the end, return the modified image.
Example 1:
Input: image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]] sr = 1, sc = 1, newColor = 2 Output: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]] Explanation: From the center of the image (with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1)), all pixels connected by a path of the same color as the starting pixel are colored with the new color. Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not 4-directionally connected to the starting pixel.Note:
The length of
imageandimage[0]will be in the range[1, 50].The given starting pixel will satisfy
0 <= sr < image.lengthand0 <= sc < image[0].length.The value of each color in
image[i][j]andnewColorwill be an integer in[0, 65535].
代码:
class Solution {
private int h;
private int w;
public int[][] floodFill(int[][] image, int sr, int sc, int newColor) {
if (image.length == 0) return null;
if (image[sr][sc] == newColor) return image;
h = image.length;
w = image[0].length;
dfs(image, sc, sr, image[sr][sc], newColor);
return image;
}
private void dfs(int[][] image, int x, int y, int oldColor, int newColor){
if (x < 0 || x >= w || y < 0 || y >= h)
return;
if (image[y][x] != oldColor)
return;
image[y][x] = newColor;
dfs(image, x + 1, y, oldColor, newColor);
dfs(image, x - 1, y, oldColor, newColor);
dfs(image, x, y + 1, oldColor, newColor);
dfs(image, x, y - 1, oldColor, newColor);
}
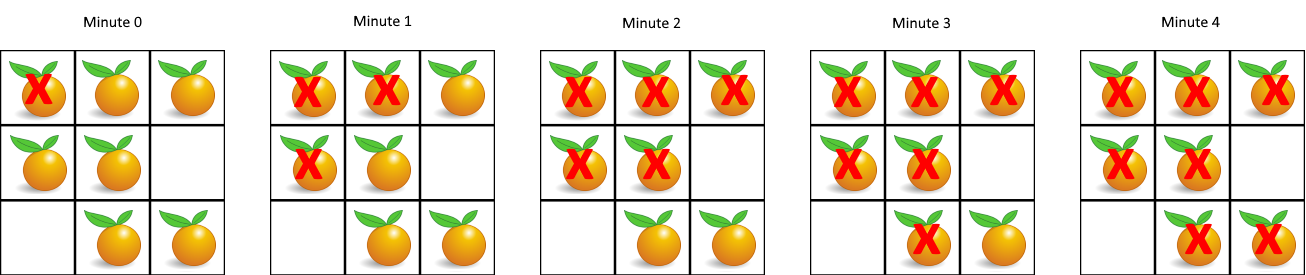
}In a given grid, each cell can have one of three values:
- the value
0representing an empty cell;- the value
1representing a fresh orange;- the value
2representing a rotten orange.Every minute, any fresh orange that is adjacent (4-directionally) to a rotten orange becomes rotten.
Return the minimum number of minutes that must elapse until no cell has a fresh orange. If this is impossible, return
-1instead.Example 1:
Input: [[2,1,1],[1,1,0],[0,1,1]] Output: 4Example 2:
Input: [[2,1,1],[0,1,1],[1,0,1]] Output: -1 Explanation: The orange in the bottom left corner (row 2, column 0) is never rotten, because rotting only happens 4-directionally.Example 3:
Input: [[0,2]] Output: 0 Explanation: Since there are already no fresh oranges at minute 0, the answer is just 0.
代码 (用set处理):
class Solution:
def orangesRotting(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
row, col = len(grid), len(grid[0])
rotting = {(i, j) for i in range(row) for j in range(col) if grid[i][j] == 2}
fresh = {(i, j) for i in range(row) for j in range(col) if grid[i][j] == 1}
dir = [(0,1), (1,0), (0,-1), (-1,0)]
time = 0
while fresh:
if not rotting:
return -1
rotting = {(i+di, j+dj) for i, j in rotting for di, dj in dir if (i+di, j+dj) in fresh}
# remove those infected oranges
fresh -= rotting
time += 1
return time input: n = 5
output: [-7, -1, 1, 3, 4]
*******************
n = 1, ans = [0]
n = 2, ans = [-1, 1]
n = 3, ans = [-1, 0, 1]
代码如下:
class Solution:
def sumZero(self, n: int) -> List[int]:
base = [-1,1]
if n == 1:
return [0]
if n == 2:
return base
if n == 3:
base.insert(1,0)
return base
else:
if n % 2 == 0:
ans = [x for x in range(-n//2, n//2 + 1)]
ans.remove(0)
else:
return [x for x in range(-(n//2), n//2 + 1)]
return ans
'''
n = 4, ans = [-2,-1,1,2], [x for x in range(-n//2, n//2 +1)]
ans.remove(0)
n = 5, ans = [-2,-1,0,1,2]
''' 1. HashMap<int, int>;
2. for (i, nums):
sum = sum + nums[i]
if (match) // if (sum == k)
max = idx + 1 // 这一步是求当前match的数(包括自己在内)前面所有数字的长度
// 即nums[:idx+1]
distance = sum - k
if map.containsKey(distance):
更新max = Math.max(max, idx - map.containsKey(distance))
else (!map.containsKey(sum)):
若当前的sum不在map中,则将对应的sum和下标放到map里面
3. return max 1. corner case:
if len(s) < K:
总长度小于目标K, 直接返回0
2. min_freq_char = min(set(s), key = s.count)
// 把string中频率最小的char取出。
if s.count(min_freq_char) > K:
如果最小频率已经大于目标值K, 则将整个string 返回
return s
3. return max(self.函数(sub, K = freq) for sub in s.split(min_freq_char))
递归。对string进行切片,然后将切片后的每个substring进行递归。class Solution:
def minSubArrayLen(self, k: int, nums: List[int]) -> int:
left, total = 0, 0
minlen = len(nums) + 1
for right, num in enumerate(nums):
total += num
while total >= k:
minlen = min(minlen, right - left + 1)
total -= nums[left]
left += 1
return minlen if minlen <= len(nums) else 0Given a positive integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to n2 in spiral order.
Example:
Input: 3 Output: [ [ 1, 2, 3 ], [ 8, 9, 4 ], [ 7, 6, 5 ] ]
class Solution(object):
def generateMatrix(self, nn):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
matrix = []
level = []
res = []
res1 = []
for i in range(1,nn**2+1):
level.append(i)
if i%nn == 0:
matrix.append(level)
level = []
m = len(matrix)
n = m
count, ub1, ub2 = 1, n, m-1
i, j, di, dj = 0, 0, 0, 1
for k in range(m*n):
matrix[i][j] = k+1
if count == ub1:
count, di, dj = 0, dj, -di
ub1, ub2 = ub2, ub1 - 1
count += 1
i += di
j += dj
# print(matrix)
return matrixGiven a m x n matrix, if an element is 0, set its entire row and column to 0. Do it in-place.
Example 1:
Input: [ [1,1,1], [1,0,1], [1,1,1] ] Output: [ [1,0,1], [0,0,0], [1,0,1] ]Example 2:
Input: [ [0,1,2,0], [3,4,5,2], [1,3,1,5] ] Output: [ [0,0,0,0], [0,4,5,0], [0,3,1,0] ]
class Solution:
def setZeroes(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify matrix in-place instead.
"""
flag, m, n = False, len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
# first scan, find "0", if "0" in first col, flag=0
# if "0" in other position(i,j), then set matrix[i][0] = matrix[0][j] = 0
for i in range(m):
if matrix[i][0] == 0: flag = True
for j in range(1, n):
if matrix[i][j] == 0:
matrix[i][0] = matrix[0][j] = 0
# second scan, bottom-up
for i in range(m-1, -1, -1):
for j in range(n-1, 0, -1):
# for each [i][1...j], check the header of col and row
if matrix[i][0] == 0 or matrix[0][j] == 0:
matrix[i][j] = 0
# for each num in header of row, check flag
if flag == True:
matrix[i][0] = 0