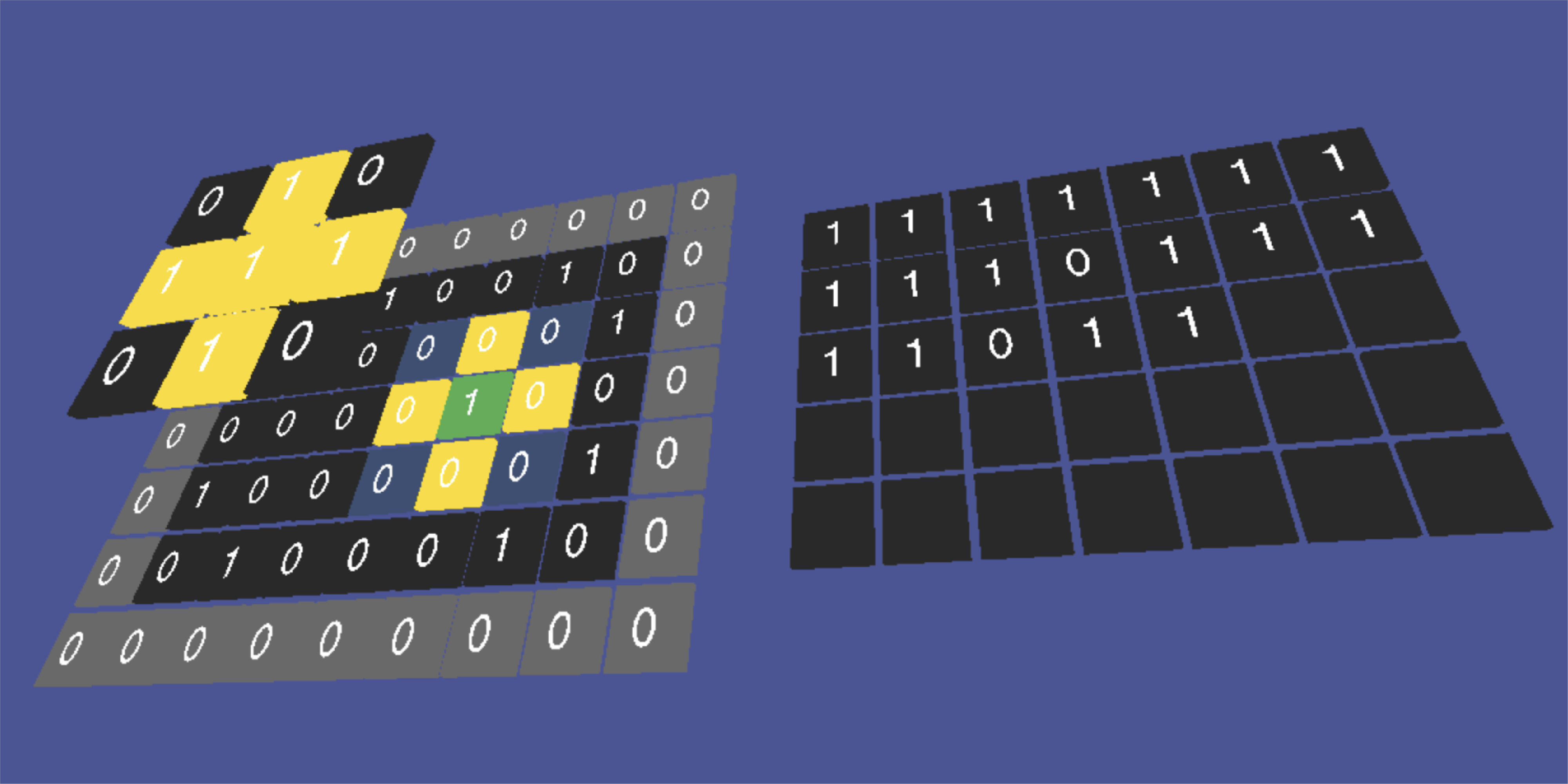
The project is a part of the Series Visualizing the Code with Geekosophers which is designed to give users the ability to visualize different morphological operations which includes- Dilation, Erosion, Opening and Closing.
Brief about the series- It is an initiative taken by us to bring the world of algorithms closer to the tech enthusiasts by helping them visualise the algorithms. Join us in this journey where we will be covering a wide range of algorithms from Simple Binary search to complex Data Structure and Algorithms. Learn more about the series by clicking here.
Dilation is one of the most common morphological operation along with Erosion. Dilation is used to add pixels to the boundary of the input image making the object more visible and fill small voids in the image. Dilation operator takes two inputs, one is the image and the other one is the structuring element. The structuring element determines the effect of dilation on the input image.
- Dilation is the dual of erosion.
- Size of input and output image is same.
- It grows the object and fill any voids in the input image.
- The nature of thickening is determined by the structuring element.
- Dilation can be performed on Binary images as well as Grayscale images.
Read more about Dilation in the blog.
The interactive animation can be viewed here.
Erosion is one of the most common morphological operation along with Dilation. Erosion is used to remove pixels from the boundary of the input image shrinking the object. Erosion operator takes two inputs, one is the image and the other one is the structuring element. The structuring element determines the effect of erosion on the input image.
- Erosion is the dual of dilation.
- Size of input and output image is same.
- It shrinks the object in the input image.
- The nature of thinning(shrinking) is determined by the structuring element.
- Erosion can be performed on Binary images as well as Grayscale images.
Read more about the Erosion in the blog.
The interactive animation can be viewed here.
Opening is Erosion followed by Dilation. The fundamental of opening process has similar effect as erosion which is to remove pixels from the boundary of the input image shrinking the object. Although, it is less destructive than erosion in nature.
- Opening is the dual of closing.
- Size of input and output image is same.
- It shrinks the object in the input image, same as erosion.
- The nature of thinning(shrinking) is determined by the structuring element.
- Opening can be performed on Binary images as well as Grayscale images.
Read more about the Opening in the blog.
The interactive animation can be viewed here.
Closing is Dilation followed by Erosion. The fundamental of closing process has similar effect as dilation which is to add pixels to the boundary of the input image making the object more visible and fill small voids in the image. Although, it is less destructive than dilation in nature.
- Closing is the dual of opening.
- Size of input and output image is same.
- It grows the object and fill any voids in the input image, same as dilation.
- The nature of thickening is determined by the structuring element.
- Closing can be performed on Binary images as well as Grayscale images.
Read more about the Closing in the blog.
The interactive animation can be viewed here.