Multimedia Generative Script Learning for Task Planning
Accepted by Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023
-
Python 3.8.5
-
Ubuntu 20.04
To set up the environment for this repository, please follow the steps below:
Step 1: Create a Python environment (optional) If you wish to use a specific Python environment, you can create one using the following:
conda create -n pyt1.11 python=3.8.5Step 2: Install PyTorch with CUDA (optional) If you want to use PyTorch with CUDA support, you can install it using the following:
conda install pytorch==1.11 torchvision torchaudio cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorchStep 3: Install Python dependencies To install the required Python dependencies, run the following command:
pip install -r requirements.txtMultimedia Goal-oriented Generative Script Learning Dataset This link contains a dataset consisting of multimedia steps for two categories: gardening and crafts. The dataset consists of a total of 79,089 multimedia steps across 5,652 tasks.
The dataset is split into three sets: training, development, and testing. The gardening category has 20,258 training tasks, 2,428 development tasks, and 2,684 testing tasks. The crafts category has 32,082 training tasks, 4,064 development tasks, and 3,937 testing tasks. Each task is associated with a set of multimedia steps, which include corresponding step images related to the task.
Note that this dataset is specific to the gardening and crafts categories and may not be representative of other categories or domains.
The *_data folder contains the full dataset, which will be released after the paper is published. Each *_data folder includes three files: train.json, valid.json, and test.json. These files are used for training, validation, and testing respectively.
Each file is a JSON file that contains multiple lines. Each line represents an instance and follows the schema described below:
{
"title": # goal of activity
"method": # subgoal of activity
"steps": # list of step text
"captions": # list of corresponding captions of step
"target": # next step text
"img": # last step image id
"target_img": # next step image id
"retrieve": # 20 retrieved historical relevant steps
"retrieve_neg": # list of retrieved top-20 most similar steps with respect to the last step. They will serve as retrieve-negatives
}The img subfolder in the *_data folder contains all images and the corresponding wikihow task json file for the gardening and crafts datasets.
Download and unzip the Wiki_dataset.zip from Multimedia Goal-oriented Generative Script Learning Dataset. Put crafts_data and gardening_data under the main folder.
To train the model on the crafts domain, run the following command:
bash finetune_crafts.sh To train the model on the gardening domain, run the following command:
bash finetune_garden.sh These scripts will run the training process and save the trained model to specified folders.
To test the model on the crafts domain, run the following command:
bash test_crafts.sh To test the model on the gardening domain, run the following command:
bash test_garden.sh These scripts will load the saved trained model and run the testing process.
Note that the training and testing scripts assume that the data is located in the default directory. If you have stored the data in a different directory, you will need to modify the scripts accordingly.
You can also download the gardening checkpoint and the crafts checkpoint from google drive.
@inproceedings{wang-etal-2023-multimedia,
title = "Multimedia Generative Script Learning for Task Planning",
author = "Wang, Qingyun and
Li, Manling and
Chan, Hou Pong and
Huang, Lifu and
Hockenmaier, Julia and
Chowdhary, Girish and
Ji, Heng",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023",
month = jul,
year = "2023",
address = "Toronto, Canada",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2023.findings-acl.63",
pages = "986--1008",
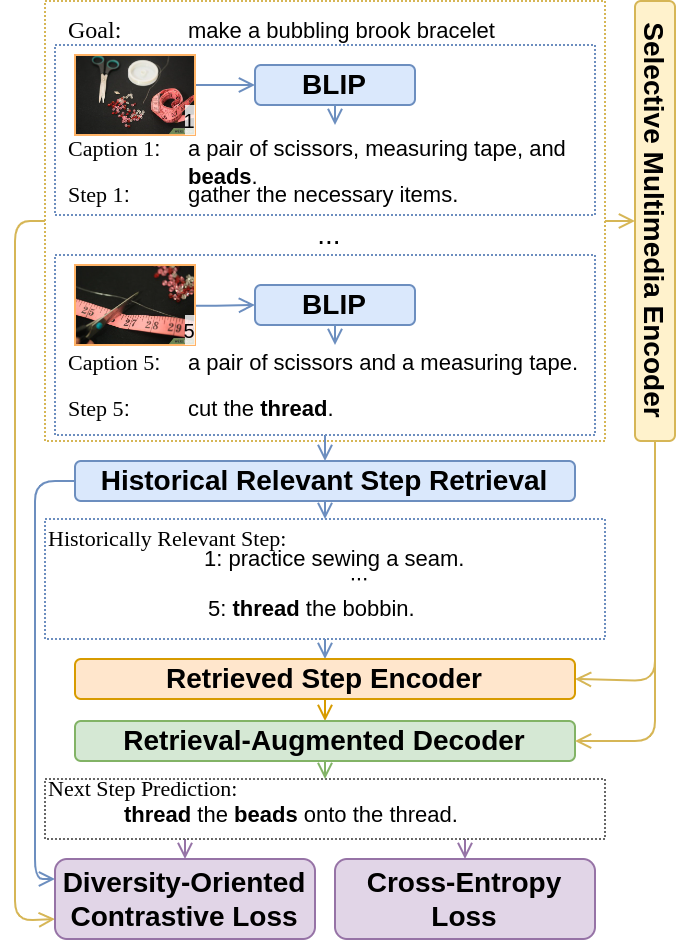
abstract = "Goal-oriented generative script learning aims to generate subsequent steps to reach a particular goal, which is an essential task to assist robots or humans in performing stereotypical activities. An important aspect of this process is the ability to capture historical states visually, which provides detailed information that is not covered by text and will guide subsequent steps. Therefore, we propose a new task, Multimedia Generative Script Learning, to generate subsequent steps by tracking historical states in both text and vision modalities, as well as presenting the first benchmark containing 5,652 tasks and 79,089 multimedia steps. This task is challenging in three aspects: the multimedia challenge of capturing the visual states in images, the induction challenge of performing unseen tasks, and the diversity challenge of covering different information in individual steps. We propose to encode visual state changes through a selective multimedia encoder to address the multimedia challenge, transfer knowledge from previously observed tasks using a retrieval-augmented decoder to overcome the induction challenge, and further present distinct information at each step by optimizing a diversity-oriented contrastive learning objective. We define metrics to evaluate both generation and inductive quality. Experiment results demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms strong baselines.",
}