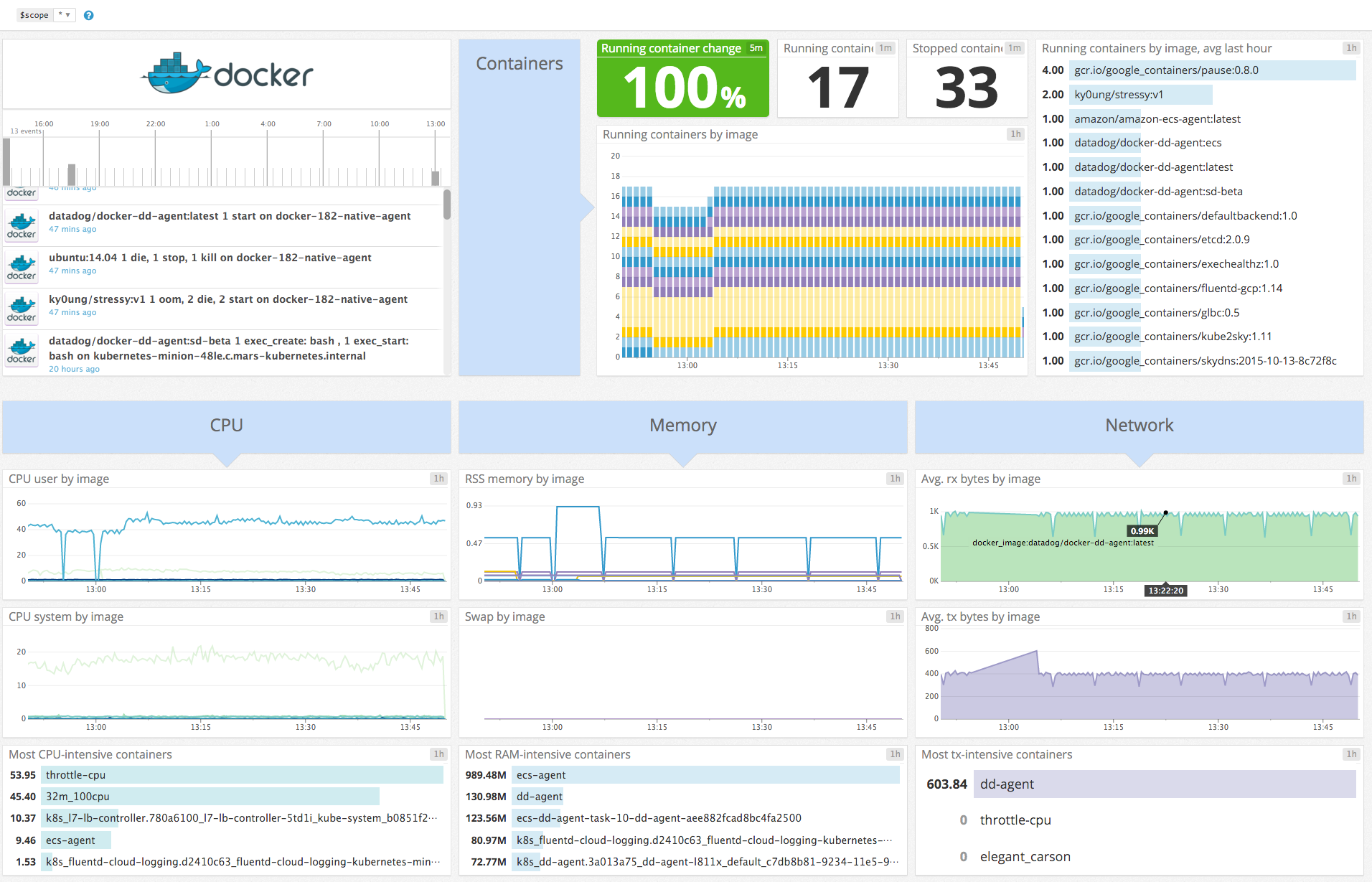
Configure this Agent check to get metrics from docker_daemon service in real time to:
- Visualize and monitor docker_daemon states
- Be notified about docker_daemon failovers and events.
NOTE: The Docker check has been rewritten in Go for Agent v6 to take advantage of the new internal architecture. Hence it is still maintained but only works with Agents prior to major version 6.
To learn how to use the Docker_daemon Integration with the Agent major version 6 Consult our dedicated agent v6 setup.
To collect Docker metrics about all your containers, run one Datadog Agent on every host. There are two ways to run the Agent: directly on each host, or within a docker-dd-agent container. We recommend the latter.
Whichever you choose, your hosts need to have cgroup memory management enabled for the Docker check to succeed. See the docker-dd-agent repository for how to enable it.
- Ensure Docker is running on the host.
- Install the Agent as described in the Agent installation instructions for your host OS.
- Enable the Docker integration tile in the application.
- Add the Agent user to the docker group:
usermod -a -G docker dd-agent - Create a
docker_daemon.yamlfile by copying the example file in the agent conf.d directory. If you have a standard install of Docker on your host, there shouldn't be anything you need to change to get the integration to work. - To enable other integrations, use
docker psto identify the ports used by the corresponding applications.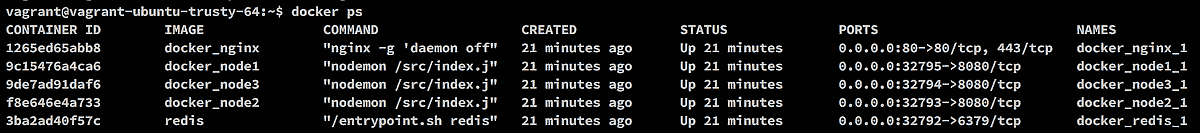
Note: docker_daemon has replaced the older docker integration.
-
Ensure Docker is running on the host.
-
As per the docker container installation instructions, run:
docker run -d --name dd-agent \ -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \ -v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \ -v /sys/fs/cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \ -e API_KEY={YOUR API KEY} \ datadog/docker-dd-agent:latest
Note that in the command above, you are able to pass your API key to the Datadog Agent using Docker's -e environment variable flag. Some other variables you can pass include:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| API_KEY | Sets your Datadog API key. |
| DD_HOSTNAME | Sets the hostname in the Agent container's datadog.conf file. If this variable is not set, the Agent container will default to using the Name field (as reported by the docker info command) as the Agent container hostname. |
| DD_URL | Sets the Datadog intake server URL where the Agent will send data. This is useful when using an agent as a proxy. |
| LOG_LEVEL | Sets logging verbosity (CRITICAL, ERROR, WARNING, INFO, DEBUG). For example, -e LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG will set logging to debug mode. |
| TAGS | Sets host tags as a comma delimited string. You can pass both simple tags and key-value tags. For example, -e TAGS="simple-tag, tag-key:tag-value". |
| EC2_TAGS | Enabling this feature allows the agent to query and capture custom tags set using the EC2 API during startup. To enable, set the value to "yes", for example, -e EC2_TAGS=yes. Note that this feature requires an IAM role associated with the instance. |
| NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC | Enabling this feature will allow statsd reporting from any external IP. For example, -e NON_LOCAL_TRAFFIC=yes. This can be used to report metrics from other containers or systems. See network configuration for more details. |
| PROXY_HOST, PROXY_PORT, PROXY_USER, PROXY_PASSWORD | Sets proxy configuration details. For more information, see the Agent proxy documentation |
| SD_BACKEND, SD_CONFIG_BACKEND, SD_BACKEND_HOST, SD_BACKEND_PORT, SD_TEMPLATE_DIR, SD_CONSUL_TOKEN | Enables and configures Autodiscovery. For more information, please see the Autodiscovery guide. |
Note: Add --restart=unless-stopped if you want your agent to be resistant to restarts.
To run the Datadog Agent container on Amazon Linux, you'll need to make one small change to the cgroup volume mount location:
docker run -d --name dd-agent \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
-v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \
-v /cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \
-e API_KEY={YOUR API KEY} \
datadog/docker-dd-agent:latest
Our standard Docker image is based on Debian Linux, but as of version 5.7 of the Datadog Agent, we also offer an Alpine Linux based image. The Alpine Linux image is considerably smaller in size than the traditional Debian-based image. It also inherits Alpine's security-oriented design.
To use the Alpine Linux image, simply append -alpine to the version tag. For example:
docker run -d --name dd-agent \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
-v /proc/:/host/proc/:ro \
-v /sys/fs/cgroup/:/host/sys/fs/cgroup:ro \
-e API_KEY={YOUR API KEY} \
datadog/docker-dd-agent:latest-alpine
Starting with version 5.5.0 of the Datadog Agent, the docker image follows a new versioning pattern. This allows us to release changes to the Docker image of the Datadog Agent but with the same version of the Agent.
The Docker image version will have the following pattern: X.Y.Z where X is the major version of the Docker Image, Y is the minor version, Z will represent the Agent version.
For example, the first version of the Docker image that will bundle the Datadog Agent 5.5.0 will be: 10.0.550
For more information about building custom Docker containers with the Datadog Agent, the Alpine Linux based image, versioning, and more, please reference our docker-dd-agent project on Github.
Run the Agent's status subcommand and look for docker_daemon under the Checks section.
The new docker check is named docker. Starting from version 6.0, the Agent won't load the docker_daemon check anymore, even if it is still available and maintained for Agent version 5.x. All features are ported on version >6.0 , excepted the following deprecations:
- the
url,api_versionandtags*options are deprecated, direct use of the standard docker environment variables is encouraged. - the
ecs_tags,performance_tagsandcontainer_tagsoptions are deprecated. Every relevant tag is now collected by default. - the
collect_container_countoption to enable thedocker.container.countmetric is not supported.docker.containers.runningand.stoppedare to be used.
Some options have moved from docker_daemon.yaml to the main datadog.yaml:
collect_labels_as_tagshas been renameddocker_labels_as_tagsand now supports high cardinality tags, see the details indatadog.yaml.exampleexcludeandincludelists have been renamedac_includeandac_exclude. In order to make filtering consistent accross all components of the agent, we had to drop filtering on arbitrary tags. The only supported filtering tags areimage(image name) andname(container name). Regexp filtering is still available, seedatadog.yaml.examplefor examplesdocker_rootoption has been split in two optionscontainer_cgroup_rootandcontainer_proc_rootexclude_pause_containerhas been added to exclude pause containers on Kubernetes and Openshift (default to true). This will avoid removing them from the exclude list by error
The import command converts the old docker_daemon.yaml to the new docker.yaml. The command also moves needed settings from docker_daemon.yaml to datadog.yaml.
See metadata.csv for a list of metrics provided by this integration.
The events below will be available:
- Delete Image
- Die
- Error
- Fail
- Kill
- Out of memory (oom)
- Pause
- Restart container
- Restart Daemon
- Update
docker.service_up:
Returns CRITICAL if the Agent is unable to collect the list of containers from the Docker daemon.
Returns OK otherwise.
docker.container_health:
Returns CRITICAL if a container is unhealthy.
Returns UNKNOWN if the health is unknown.
Returns OK otherwise.
docker.exit:
Returns CRITICAL if a container exited with a non-zero exit code.
Returns OK otherwise.
Need help? Contact Datadog Support.
Learn more about how to monitor Docker performance metrics thanks to our series of posts. We detail the challenges when monitoring Docker, its key performance metrics, how to collect them, and lastly how the largest TV and radio outlet in the U.S. monitors Docker using Datadog.
We've also written several other in-depth blog posts to help you get the most out of Datadog and Docker: