|
| 1 | +--- |
| 2 | +Title: 'Normal Distribution' |
| 3 | +Description: 'A kind of continuous probability distribution characterized by a bell-shaped curve that is symmetric around its mean.' |
| 4 | +Subjects: |
| 5 | + - 'Data Science' |
| 6 | + - 'Data Visualization' |
| 7 | + - 'Machine Learning' |
| 8 | +Tags: |
| 9 | + - 'Data Science' |
| 10 | + - 'Deep Learning' |
| 11 | +CatalogContent: |
| 12 | + - 'learn-python-3' |
| 13 | + - 'paths/data-science' |
| 14 | +--- |
| 15 | + |
| 16 | +The **normal distribution**, otherwise known as the Gaussian distribution, is one of the most signifcant probability distributions used for continuous data. It is defined by two parameters: |
| 17 | + |
| 18 | +- **Mean (μ)**: The central value of the distribution. |
| 19 | +- **Standard Deviation (σ)**: Computes the amount of variation or dispersion in the data. |
| 20 | + |
| 21 | +Mathematically, the probability density function (PDF) used for the normal distribution is: |
| 22 | + |
| 23 | +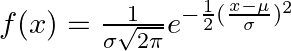 |
| 24 | + |
| 25 | +Where: |
| 26 | + |
| 27 | +- `x` is the random variable |
| 28 | +- `μ` is the mean |
| 29 | +- `σ` is the standard deviation |
| 30 | +- `e` is Euler's number (approximately 2.71828) |
| 31 | +- `π` is Pi (approximately 3.14159) |
| 32 | + |
| 33 | +### Key Properties |
| 34 | + |
| 35 | +1. **Bell-shaped and Symmetric**: The distribution is perfectly symmetrical around its mean. |
| 36 | +2. **Mean, Median, and Mode are Equal**: All three measures of central tendency have the same value. |
| 37 | +3. **Empirical Rule (68-95-99.7 Rule)**: |
| 38 | + - Approximately 68% of the given data falls within 1 standard deviation of the mean |
| 39 | + - Approximately 95% falls within 2 standard deviations |
| 40 | + - Approximately 99.7% falls within 3 standard deviations |
| 41 | +4. **Standardized Form**: Any normal distribution can be converted to a standard normal distribution (`μ=0`, `σ=1`) using the formula `z = (x-μ)/σ`. |
| 42 | + |
| 43 | +### Applications |
| 44 | + |
| 45 | +The normal distribution is broadly used in various fields: |
| 46 | + |
| 47 | +- **Finance**: Modeling stock returns |
| 48 | +- **Natural Sciences**: Measurement errors |
| 49 | +- **Social Sciences**: IQ scores, heights, and other human characteristics |
| 50 | +- **Machine Learning**: Assumptions in many algorithms |
| 51 | +- **Quality Control**: Manufacturing processes |
| 52 | + |
| 53 | +## Example |
| 54 | + |
| 55 | +The following code creates a sample of 1,000 normally distributed data points with a mean of `70` and a standard deviation of `10`, and displays this data in a 2×2 grid of plots for analysis: |
| 56 | + |
| 57 | +```py |
| 58 | +import numpy as np |
| 59 | +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
| 60 | +from scipy import stats |
| 61 | +import seaborn as sns |
| 62 | + |
| 63 | +# Set seed for reproducibility |
| 64 | +np.random.seed(42) |
| 65 | + |
| 66 | +# Generate random data from a normal distribution |
| 67 | +# Parameters: mean=70, standard deviation=10, size=1000 |
| 68 | +data = np.random.normal(70, 10, 1000) |
| 69 | + |
| 70 | +# Create visualizations |
| 71 | +plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8)) |
| 72 | + |
| 73 | +# Histogram with density curve |
| 74 | +plt.subplot(2, 2, 1) |
| 75 | +sns.histplot(data, kde=True, stat="density") |
| 76 | +plt.title('Histogram with Density Curve') |
| 77 | +plt.xlabel('Value') |
| 78 | +plt.ylabel('Density') |
| 79 | + |
| 80 | +# Q-Q plot to check normality |
| 81 | +plt.subplot(2, 2, 2) |
| 82 | +stats.probplot(data, plot=plt) |
| 83 | +plt.title('Q-Q Plot') |
| 84 | + |
| 85 | +# Box plot |
| 86 | +plt.subplot(2, 2, 3) |
| 87 | +sns.boxplot(x=data) |
| 88 | +plt.title('Box Plot') |
| 89 | +plt.xlabel('Value') |
| 90 | + |
| 91 | +# Verify the empirical rule |
| 92 | +plt.subplot(2, 2, 4) |
| 93 | +mean = np.mean(data) |
| 94 | +std = np.std(data) |
| 95 | +within_1_std = np.sum((mean - std <= data) & (data <= mean + std)) / len(data) * 100 |
| 96 | +within_2_std = np.sum((mean - 2*std <= data) & (data <= mean + 2*std)) / len(data) * 100 |
| 97 | +within_3_std = np.sum((mean - 3*std <= data) & (data <= mean + 3*std)) / len(data) * 100 |
| 98 | + |
| 99 | +bars = plt.bar(['1σ', '2σ', '3σ'], [within_1_std, within_2_std, within_3_std]) |
| 100 | +plt.axhline(y=68, color='r', linestyle='-', label='68% (theoretical)') |
| 101 | +plt.axhline(y=95, color='g', linestyle='-', label='95% (theoretical)') |
| 102 | +plt.axhline(y=99.7, color='b', linestyle='-', label='99.7% (theoretical)') |
| 103 | +plt.title('Empirical Rule Verification') |
| 104 | +plt.xlabel('Standard Deviation Range') |
| 105 | +plt.ylabel('Percentage of Data (%)') |
| 106 | +plt.legend() |
| 107 | + |
| 108 | +plt.tight_layout() |
| 109 | +plt.show() |
| 110 | + |
| 111 | +# Statistical summary |
| 112 | +print("Statistical Summary:") |
| 113 | +print(f"Mean: {np.mean(data):.2f}") |
| 114 | +print(f"Median: {np.median(data):.2f}") |
| 115 | +print(f"Standard Deviation: {np.std(data):.2f}") |
| 116 | +print(f"Skewness: {stats.skew(data):.4f}") |
| 117 | +print(f"Kurtosis: {stats.kurtosis(data):.4f}") |
| 118 | +print("\nEmpirical Rule Verification:") |
| 119 | +print(f"Data within 1 standard deviation: {within_1_std:.2f}% (theoretical: 68%)") |
| 120 | +print(f"Data within 2 standard deviations: {within_2_std:.2f}% (theoretical: 95%)") |
| 121 | +print(f"Data within 3 standard deviations: {within_3_std:.2f}% (theoretical: 99.7%)") |
| 122 | +``` |
| 123 | + |
| 124 | +The output of the above code will be: |
| 125 | + |
| 126 | +```shell |
| 127 | +Statistical Summary: |
| 128 | +Mean: 70.19 |
| 129 | +Median: 70.25 |
| 130 | +Standard Deviation: 9.79 |
| 131 | +Skewness: 0.1168 |
| 132 | +Kurtosis: 0.0662 |
| 133 | + |
| 134 | +Empirical Rule Verification: |
| 135 | +Data within 1 standard deviation: 68.60% (theoretical: 68%) |
| 136 | +Data within 2 standard deviations: 95.60% (theoretical: 95%) |
| 137 | +Data within 3 standard deviations: 99.70% (theoretical: 99.7%) |
| 138 | +``` |
| 139 | + |
| 140 | +The histogram with density curve shows the bell-shaped curve characteristic of normal distributions: |
| 141 | + |
| 142 | +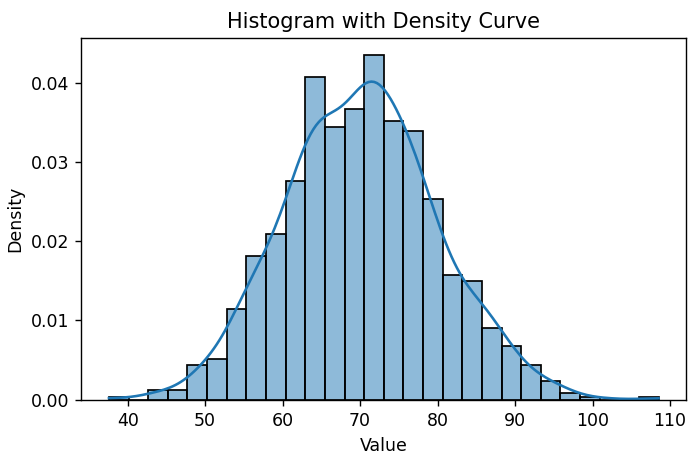 |
| 143 | + |
| 144 | +Q-Q plot compares the data quantiles against theoretical normal distribution quantiles to check if the data follows a normal distribution (points following the diagonal line indicate normality): |
| 145 | + |
| 146 | +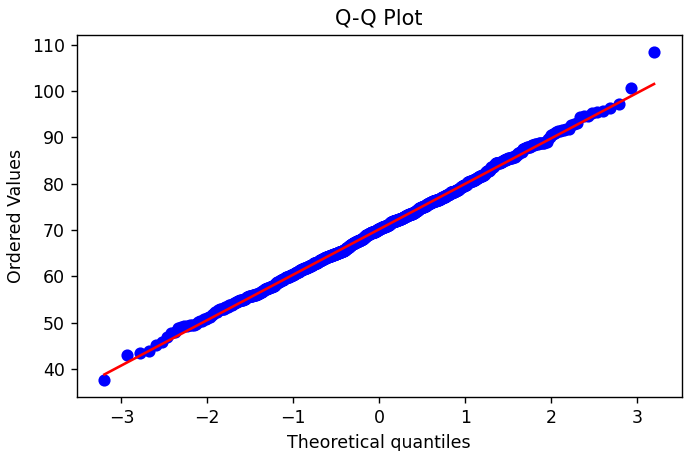 |
| 147 | + |
| 148 | +Box plot visualizes the central tendency and spread of the data: |
| 149 | + |
| 150 | +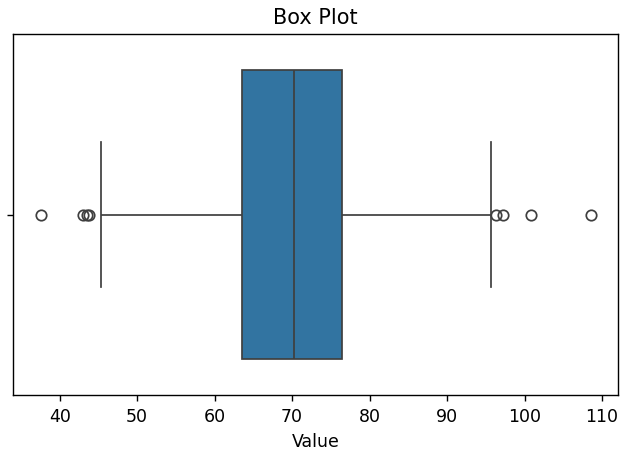 |
| 151 | + |
| 152 | +Bar chart tests whether the data follows the 68-95-99.7 rule by calculating the percentage of data points that fall within 1, 2, and 3 standard deviations: |
| 153 | + |
| 154 | +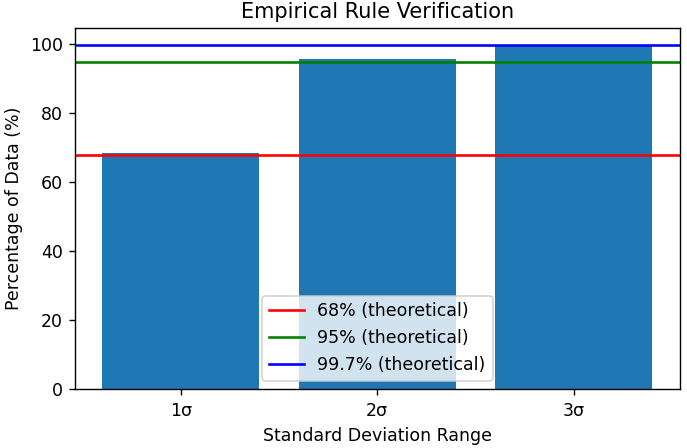 |
0 commit comments