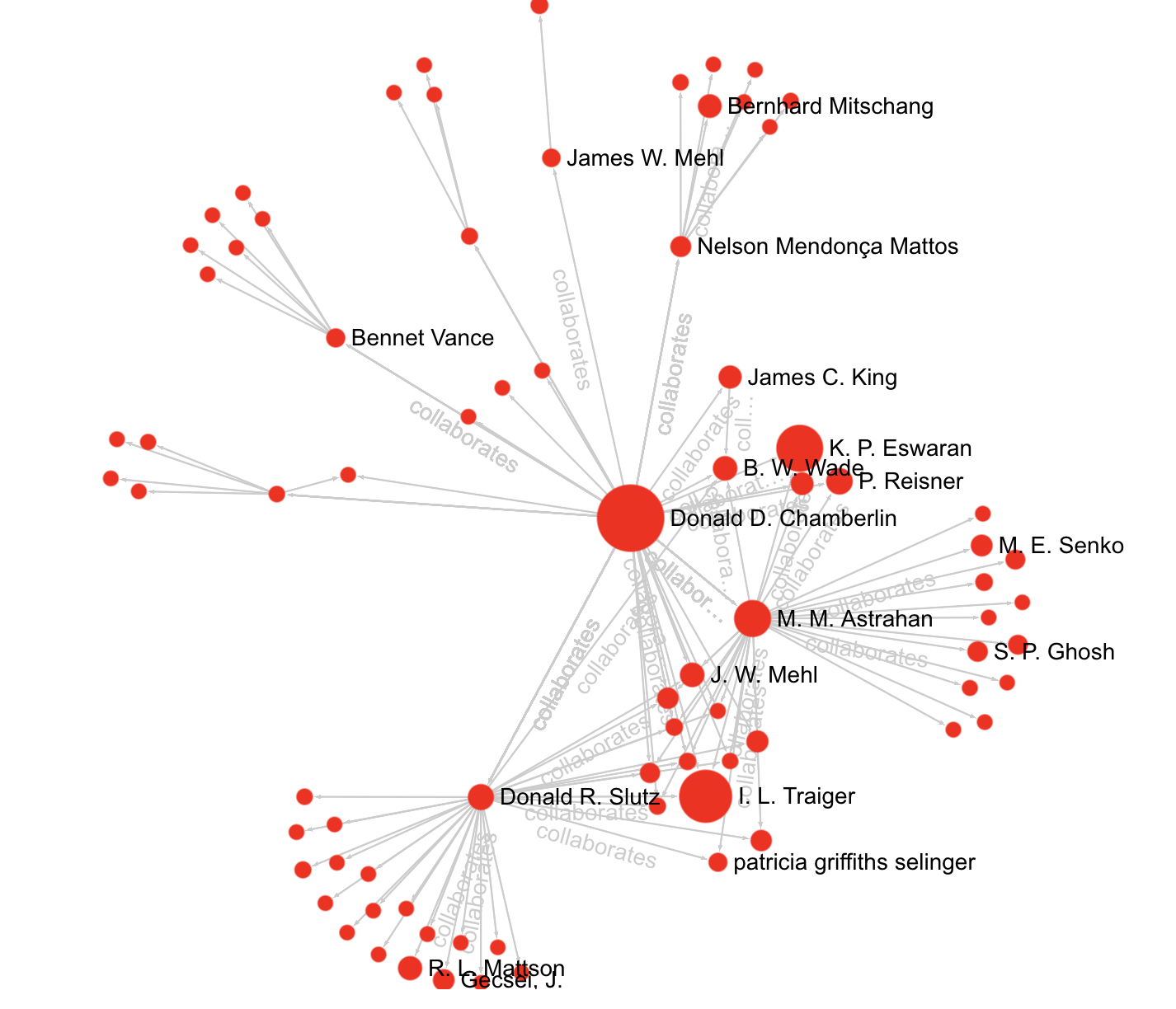
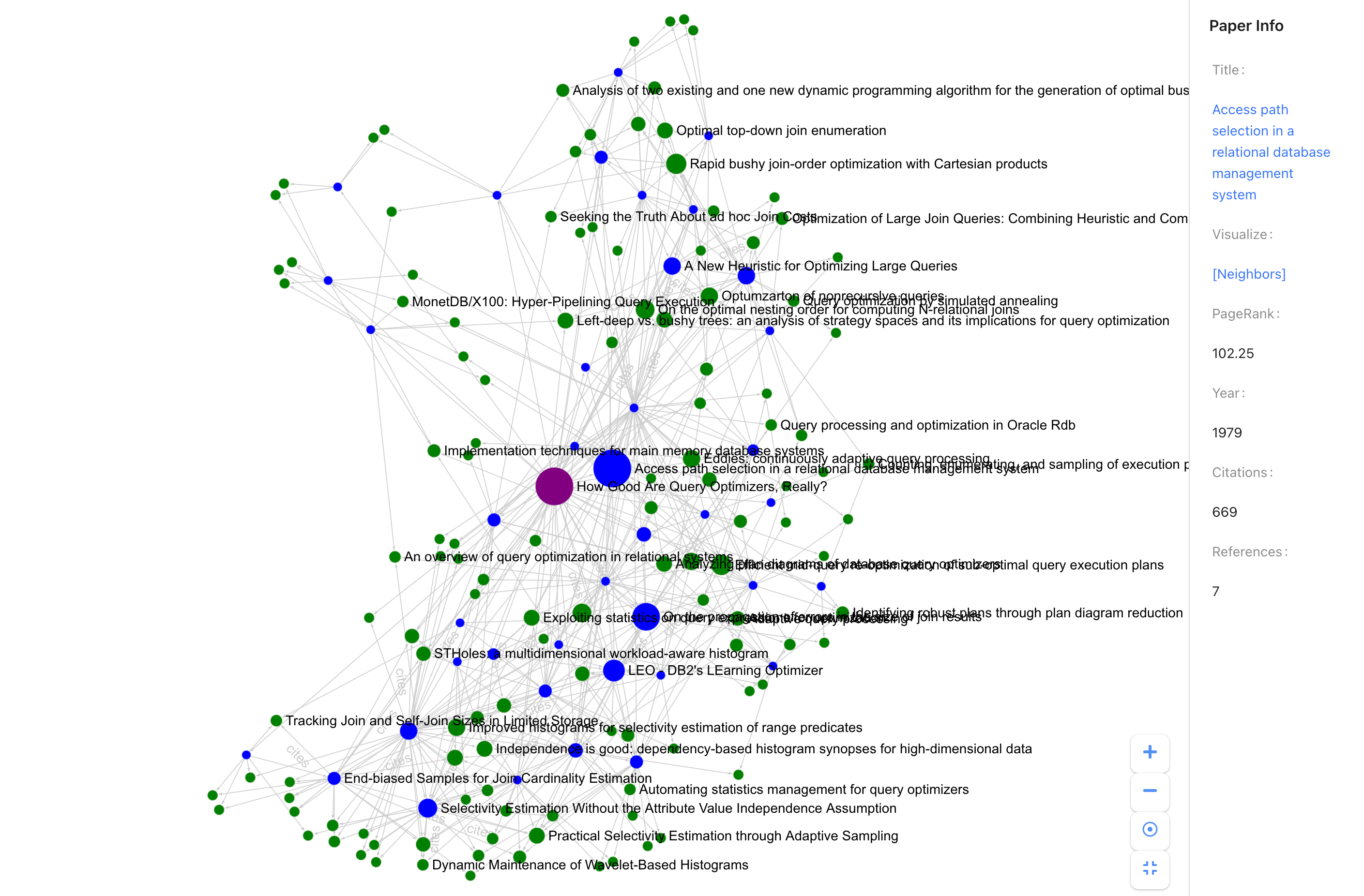
Citegraph is an open-source online visualizer of 5+ million papers, 4+ million authors, and various relationships. In total, Citegraph has 9.4 million vertices and 294 million edges. At the moment, Citegraph only has computer science bibliography.
Some interesting use cases:
- Find connected papers! What's the bedrock of this paper?
- How many degrees of separation are between researcher X and Y?
- What's researcher X's interests (cited papers, collaborators)?
- Who cites my works the most (and might write me a reference letter)?
- Which research community do I belong to? Who are my potential collaborators?
- What's the pagerank/influence of paper X or author Y?
CiteGraph is built on top of a few technologies. JanusGraph is the underlying graph database that stores the citation network. Other tech stacks include Spring Boot, Nginx, React, Remix (Server Side Rendering), Lucene, Cassandra, and Spark. The steps below are useful only if you want to launch CiteGraph on your own. Otherwise, just visit CiteGraph and have fun!
See README for steps.
JanusGraph requires a storage backend and optionally, an index backend. Here we only use a storage backend, Cassandra.
cd /datadrive/apache-cassandra-4.0.6
./bin/cassandra
Cassandra will be running in the background. Then we can start our JanusGraph server.
Enter the root directory of JanusGraph distribution, run the following command (please replace the absolute path accordingly, the config file is available here:
cd janusgraph/janusgraph-1.0.0/
JAVA_OPTIONS="-DJANUSGRAPH_RELATION_DELIMITER=@" ./bin/janusgraph-server.sh console /home/azureuser/gremlin-server-cql.yaml
Let's package the backend application to a JAR file first.
cd backend
mvn clean package
# optional - upload the jar file to VM
scp -i citegraph_key.pem citegraph/backend/target/app-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar azureuser@20.253.223.140:~/We can then deploy the package to our preferred environment and run it. For example, we can upload it to Azure Virtual Machine and run the packaged jar file:
java -jar app-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarNow the web backend application runs on port 8080.
We use Remix for server-side rendering. Let's launch the web server that runs on 3000 port (tested using node.js v16):
cd frontend
npm install
npm run startIn production, you may want to set up a reverse proxy like Nginx to
help you serve the static files, handle SSL and 301 redirect. A complete
example that enables 301 redirect from non-www to www version, and http to https version,
looks like this (put it in a file under /etc/nginx/conf.d directory):
server {
listen 80;
server_name citegraph.io;
location / {
return 301 https://www.citegraph.io$request_uri;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.citegraph.io;
location / {
return 301 https://www.citegraph.io$request_uri;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name citegraph.io;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.citegraph.io/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.citegraph.io/privkey.pem;
location / {
return 301 https://www.citegraph.io$request_uri;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.citegraph.io;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.citegraph.io/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.citegraph.io/privkey.pem;
location /apis {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
}
}Note the above steps assumes you have an SSL certificate installed in /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.citegraph.io.
If you don't, you can follow this tutorial
to generate and install one in your VM.