diff --git a/leetcode/133. Clone Graph/README.md b/leetcode/133. Clone Graph/README.md
index 7e477517..27eb0c2f 100644
--- a/leetcode/133. Clone Graph/README.md
+++ b/leetcode/133. Clone Graph/README.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
# [133. Clone Graph (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/)
-Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
+Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
-Each node in the graph contains a val (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
+Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
@@ -16,15 +16,15 @@
Test case format:
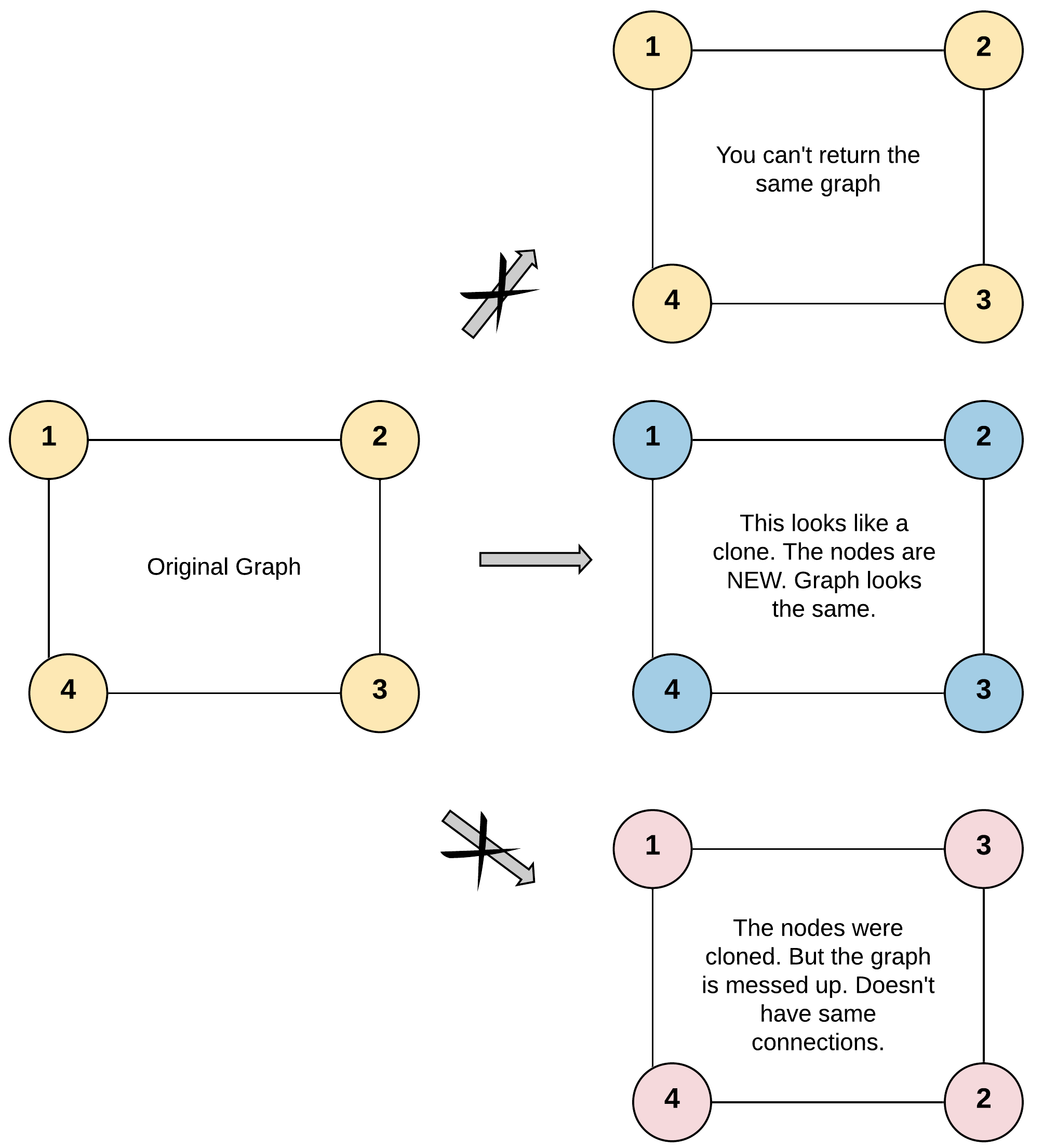
-For simplicity sake, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val = 1, the second node with val = 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
+For simplicity, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
-Adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
+An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
-The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
+The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
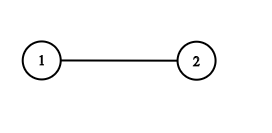
Example 1:
- +
+
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
@@ -48,26 +48,23 @@
Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
-Example 4:
- -
-Input: adjList = [[2],[1]]
-Output: [[2],[1]]
-
-
Constraints:
+ - The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100].
1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.val is unique for each node.- Number of Nodes will not exceed 100.
- - There is no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
+ - There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
+**Companies**:
+[Facebook](https://leetcode.com/company/facebook), [Amazon](https://leetcode.com/company/amazon), [Microsoft](https://leetcode.com/company/microsoft), [Google](https://leetcode.com/company/google), [Bloomberg](https://leetcode.com/company/bloomberg), [Salesforce](https://leetcode.com/company/salesforce), [Twitter](https://leetcode.com/company/twitter), [Oracle](https://leetcode.com/company/oracle)
+
**Related Topics**:
-[Depth-first Search](https://leetcode.com/tag/depth-first-search/), [Breadth-first Search](https://leetcode.com/tag/breadth-first-search/), [Graph](https://leetcode.com/tag/graph/)
+[Hash Table](https://leetcode.com/tag/hash-table/), [Depth-First Search](https://leetcode.com/tag/depth-first-search/), [Breadth-First Search](https://leetcode.com/tag/breadth-first-search/), [Graph](https://leetcode.com/tag/graph/)
**Similar Questions**:
* [Copy List with Random Pointer (Medium)](https://leetcode.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/)
@@ -87,13 +84,12 @@ class Solution {
unordered_map m;
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
- if (!node) return NULL;
- if (m.count(node) == 0) {
- auto copy = new Node(node->val);
- m[node] = copy;
- for (auto nei : node->neighbors) copy->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(nei));
- }
- return m[node];
+ if (!node) return nullptr;
+ if (m.count(node)) return m[node];
+ auto cpy = new Node(node->val);
+ m[node] = cpy;
+ for (auto &n : node->neighbors) cpy->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(n));
+ return cpy;
}
};
```
@@ -109,7 +105,7 @@ public:
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
- if (!node) return NULL;
+ if (!node) return nullptr;
queue q;
unordered_map m;
m[node] = new Node(node->val);
 +
+
 -
-