Vulnerability scanner for Linux/FreeBSD, agentless, written in golang.
README in English
Slackチームはこちらから参加できます。(日本語でオッケーです)
- Vuls: VULnerability Scanner
- TOC
- Abstract
- Main Features
- What Vuls Doesn't Do
- Setup Vuls
- Tutorial: Local Scan Mode
- Tutorial: Remote Scan Mode
- Architecture
- Performance Considerations
- Use Cases
- Support OS
- Usage: Automatic Server Discovery
- Configuration
- Usage: Configtest
- Usage: Scan
- Usage: Report
- Usage: Scan vulnerability of non-OS package
- Usage: Integrate with OWASP Dependency Check to Automatic update when the libraries are updated (Experimental)
- Usage: TUI
- Display the previous scan results using peco
- Usage: go-cve-dictonary on different server
- Usage: Update NVD Data
- レポートの日本語化
- Update Vuls With Glide
- Misc
- Related Projects
- Data Source
- Authors
- Contribute
- Change Log
- License
毎日のように発見される脆弱性の調査やソフトウェアアップデート作業は、システム管理者にとって負荷の高いタスクである。 プロダクション環境ではサービス停止リスクを避けるために、パッケージマネージャの自動更新機能を使わずに手動更新で運用するケースも多い。 だが、手動更新での運用には以下の問題がある。
- システム管理者がNVDなどで新着の脆弱性をウォッチし続けなければならない
- サーバにインストールされているソフトウェアは膨大であり、システム管理者が全てを把握するのは困難
- 新着の脆弱性がどのサーバに該当するのかといった調査コストが大きく、漏れる可能性がある
Vulsは上に挙げた手動運用での課題を解決するツールであり、以下の特徴がある。
- システムに関係ある脆弱性のみ教えてくれる
- その脆弱性に該当するサーバを教えてくれる
- 自動スキャンのため脆弱性検知の漏れを防ぐことができる
- CRONなどで定期実行、レポートすることで脆弱性の放置を防ぐことできる
- Linuxサーバに存在する脆弱性をスキャン
- Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Amazon Linux, RHEL, Raspbianに対応
- クラウド、オンプレミス、Docker
- OSパッケージ管理対象外のミドルウェアをスキャン
- プログラミング言語のライブラリやフレームワーク、ミドルウェアの脆弱性スキャン
- CPEに登録されているソフトウェアが対象
- エージェントレスアーキテクチャ
- スキャン対象サーバにSSH接続可能なマシン1台にセットアップするだけで動作
- 非破壊スキャン(SSHでコマンド発行するだけ)
- AWSでの脆弱性/侵入テスト事前申請は必要なし
- 設定ファイルのテンプレート自動生成
- CIDRを指定してサーバを自動検出、設定ファイルのテンプレートを生成
- EmailやSlackで通知可能(日本語でのレポートも可能)
- 付属するTerminal-Based User Interfaceビューアでは、Vim風キーバインドでスキャン結果を参照可能
- Web UI(VulsRepo)を使えばピボットテーブルのように分析可能
- Vulsはソフトウェアアップデートは行わない
Vulsのセットアップは以下の2パターンがある
-
Dockerコンテナ上にセットアップ
see https://github.com/future-architect/vuls/tree/master/setup/docker -
手動でセットアップ
Hello Vulsチュートリアルでは手動でのセットアップ方法で説明する
本チュートリアルでは、Amazon EC2にVulsをセットアップし、自分に存在する脆弱性をスキャンする方法を説明する。 手順は以下の通り
- Amazon Linuxを新規作成
- 必要なソフトウェアをインストール
- go-cve-dictionaryをデプロイ
- Vulsをデプロイ
- 設定
- 設定ファイルと、スキャン対象サーバの設定のチェック
- Scan
- Reporting
- TUI(Terminal-Based User Interface)で結果を参照する
- Web UI(VulsRepo)で結果を参照する
-
今回は説明のために、脆弱性を含む古いAMIを使う (amzn-ami-hvm-2015.09.1.x86_64-gp2 - ami-383c1956)
-
EC2作成時に自動アップデートされるとVulsスキャン結果が0件になってしまうので、cloud-initに以下を指定してEC2を作成する。
#cloud-config repo_upgrade: none
Vulsセットアップに必要な以下のソフトウェアをインストールする。
- SQLite3 or MySQL
- git
- gcc
- GNU Make
- go v1.7.1 or later (The latest version is recommended)
$ ssh ec2-user@52.100.100.100 -i ~/.ssh/private.pem
$ sudo yum -y install sqlite git gcc make
$ wget https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.7.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.7.1.linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ mkdir $HOME/go/etc/profile.d/goenv.sh を作成し、下記を追加する。
export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin:$GOPATH/binカレントシェルに上記環境変数をセットする。
$ source /etc/profile.d/goenv.sh$ sudo mkdir /var/log/vuls
$ sudo chown ec2-user /var/log/vuls
$ sudo chmod 700 /var/log/vuls
$
$ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe
$ git clone https://github.com/kotakanbe/go-cve-dictionary.git
$ cd go-cve-dictionary
$ make installバイナリは、$GOPATH/bin以下に生成される
NVDから脆弱性データベースを取得する。
環境によって異なるが、AWS上では10分程度かかる。
$ cd $HOME
$ for i in `seq 2002 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchnvd -years $i; done
... snip ...
$ ls -alh cve.sqlite3
-rw-r--r-- 1 ec2-user ec2-user 7.0M Mar 24 13:20 cve.sqlite3日本語化したい場合は、JVNから脆弱性データベースを取得する。
$ cd $HOME
$ for i in `seq 1998 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchjvn -years $i; done新規にターミナルを起動し、先ほど作成したEC2にSSH接続する。
$ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect
$ git clone https://github.com/future-architect/vuls.git
$ cd vuls
$ make install
Vulsの設定ファイルを作成する(TOMLフォーマット)
$ cd $HOME
$ cat config.toml
[servers]
[servers.localhost]
host = "localhost"
port = "local"
Root権限が必要なディストリビューションもあるので、スキャン対象サーバの/etc/sudoersを変更する。
パスワードありのsudoはセキュリティ上の理由からサポートしていないので、スキャンに必要なコマンドは、NOPASSAWORDとして、remote host上のetc/sudoersに定義しておく。
See Usage: Configtest#Check /etc/sudoers
$ vuls configtest
詳細は Usage: configtest を参照
$ vuls scan
... snip ...
Scan Summary
============
localhost amazon 2015.09 94 CVEs 103 updatable packages
View one-line summary
$ vuls report -format-one-line-text -cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3
One Line Summary
================
localhost Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14) 103 updatable packages
View short summary.
$ vuls report -format-short-text -cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 --lang=ja
localhost (amazon 2015.09)
===========================
Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14) 103 updatable packages
CVE-2016-5636 10.0 (High) CPython の zipimport.c の get_data 関数における整数オーバーフローの脆弱性
http://jvndb.jvn.jp/ja/contents/2016/JVNDB-2016-004528.html
https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2016-5636
python27-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-devel-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-devel-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-libs-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-libs-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
Confidence: 100 / YumUpdateSecurityMatch
... snip ...
View full report.
$ vuls report -format-full-text -cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 --lang=ja
localhost (amazon 2015.09)
============================
Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14) 103 updatable packages
CVE-2016-5636
-------------
Score 10.0 (High)
Vector (AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C)
Title CPython の zipimport.c の get_data 関数における整数オーバーフローの脆弱性
Description CPython (別名 Python) の zipimport.c の get_data
関数には、整数オーバーフローの脆弱性が存在します。
補足情報 : CWE による脆弱性タイプは、CWE-190: Integer Overflow or Wraparound
(整数オーバーフローまたはラップアラウンド) と識別されています。
http://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/190.html
CWE-190 https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/190.html
CWE-190(JVN) http://jvndb.jvn.jp/ja/cwe/CWE-190.html
JVN http://jvndb.jvn.jp/ja/contents/2016/JVNDB-2016-004528.html
NVD https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2016-5636
MITRE https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2016-5636
CVE Details http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-5636
CVSS Claculator https://nvd.nist.gov/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2016-5636&vector=(AV:N/AC:L/...
RHEL-CVE https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2016-5636
ALAS-2016-724 https://alas.aws.amazon.com/ALAS-2016-724.html
Package python27-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-devel-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-devel-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-libs-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-libs-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
Confidence 100 / YumUpdateSecurityMatch
... snip ...
Vulsにはスキャン結果の詳細を参照できるイカしたTUI(Terminal-Based User Interface)が付属している。
$ vuls tui
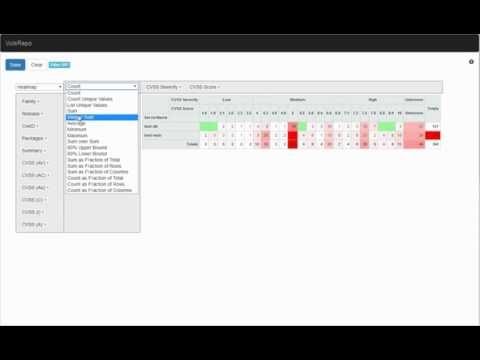
VulsRepoはスキャン結果をビボットテーブルのように分析可能にするWeb UIである。
Online Demoがあるので試してみて。
SSHを用いてリモートのホストをスキャンする方法を説明する。
- Amazon Linuxを新規に1台作成(スキャン対象)
- 必要なソフトウェアをインストール
- RemoteホストにlocalhostからSSH可能にする
- 設定
- 設定ファイルと、スキャン対象サーバの設定のチェック
- Scan
- Reporting
先程のチュートリアルで作成したVulsサーバ(以下localhostと記述)を用いる。
Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step1. Launch Amazon Linuxと同じ
新規にターミナルを開いて今作成したEC2にSSH接続する。
ディストリビューションによってはスキャンに必要な依存ソフトウェアをインストールする必要がある。
これらはリモートサーバ上に手動かAnsibleなどでインストールする。
依存ソフトウェアの詳細は Dependencies on Target Servers を参照。
VulsはSSHパスワード認証をサポートしてない。SSHの鍵認証の設定をしなければならない。
localhost上でkeypairを作成し、remote host上のauthorized_keysに追加する。
- Localhost
$ ssh-keygen -t rsaCopy ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to the clipboard.
- Remote Host
$ mkdir ~/.ssh
$ chmod 700 ~/.ssh
$ touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ vim ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Paste from the clipboard to ~/.ssh/.authorized_keys
パスワードありのsudoはセキュリティ上の理由からサポートしていないので、スキャンに必要なコマンドは、NOPASSAWORDとして、remote host上のetc/sudoersに定義しておく。
See Usage: Configtest#Check /etc/sudoers
また、localhostのknown_hostsにremote hostのホストキーが登録されている必要があるので確認すること。
- Localhost
$ cd $HOME
$ cat config.toml
[servers]
[servers.172-31-4-82]
host = "172.31.4.82"
port = "22"
user = "ec2-user"
keyPath = "/home/ec2-user/.ssh/id_rsa"
$ vuls configtest
$ vuls scan
... snip ...
Scan Summary
============
172-31-4-82 amazon 2015.09 94 CVEs 103 updatable packages
See Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step8. Reporting
See Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step9. TUI
See Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step10. Web UI
Vulsをスキャン対象サーバにデプロイする。Vulsはローカルホストにコマンドを発行する(SSH経由ではない)。スキャン結果のJSONを別サーバに集約する。スキャン結果の詳細化のためにはCVEデータベースへのアクセスが必要なので、事前にgo-cve-dictionaryをserver modeで起動しておく。 その集約サーバ上で、あなたはWebUIやTUIを用いて各スキャン対象サーバのスキャン結果を参照することが可能。
- NVDとJVN(日本語)から脆弱性データベースを取得し、SQLite3に格納する。
- SSHでサーバに存在する脆弱性をスキャンし、CVE IDのリストを作成する
- Dockerコンテナのスキャンする場合、VulsはまずDockerホストにSSHで接続する。その後、Dockerホスト上で
docker exec経由でコマンドを実効する。Dockerコンテナ内にSSHデーモンを起動する必要はない
- Dockerコンテナのスキャンする場合、VulsはまずDockerホストにSSHで接続する。その後、Dockerホスト上で
- 検出されたCVEの詳細情報をgo-cve-dictionaryから取得する
- スキャン結果レポートを生成し、SlackやEmailなどで送信する
- スキャン結果をJSONファイルに出力すると詳細情報をターミナル上で参照可能
-
Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian
apt-get changelogでアップデート対象のパッケージのチェンジログを取得し、含まれるCVE IDをパースする。 アップデート対象のパッケージが沢山ある場合、チェンジログの取得に時間がかかるので、初回のスキャンは遅い。
ただ、2回目以降はキャッシュしたchangelogを使うので速くなる。 -
CentOS
アップデート対象すべてのchangelogを一度で取得しパースする。スキャンスピードは速い、サーバリソース消費量は小さい。 -
Amazon, RHEL and FreeBSD
高速にスキャンし、スキャン対象サーバのリソース消費量は小さい。
| Distribution | Scan Speed |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 初回は遅い / 2回目以降速い |
| Debian | 初回は遅い / 2回目以降速い |
| CentOS | 速い |
| Amazon | 速い |
| RHEL | 速い |
| FreeBSD | 速い |
| Raspbian | 初回は遅い / 2回目以降速い |
web/app server in the same configuration under the load balancer
| Distribution | Release |
|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 12, 14, 16 |
| Debian | 7, 8 |
| RHEL | 5, 6, 7 |
| CentOS | 6, 7 |
| Amazon Linux | All |
| FreeBSD | 10, 11 |
| Raspbian | Wheezy, Jessie |
Discoveryサブコマンドは指定されたCIDRレンジ内でpingが返ってくるサーバを発見して、ターミナル上にVulsの設定ファイルのテンプレートを出力する。
$ vuls discover -help
discover:
discover 192.168.0.0/24
$ vuls discover 172.31.4.0/24
# Create config.toml using below and then ./vuls --config=/path/to/config.toml
[slack]
hookURL = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/abc123/defghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
channel = "#channel-name"
#channel = "${servername}"
iconEmoji = ":ghost:"
authUser = "username"
notifyUsers = ["@username"]
[email]
smtpAddr = "smtp.gmail.com"
smtpPort = "587"
user = "username"
password = "password"
from = "from@address.com"
to = ["to@address.com"]
cc = ["cc@address.com"]
subjectPrefix = "[vuls]"
[default]
#port = "22"
#user = "username"
#keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
#cpeNames = [
# "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1",
#]
#optional = [
# ["key", "value"],
#]
[servers]
[servers.172-31-4-82]
host = "172.31.4.82"
#port = "22"
#user = "root"
#keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
#cpeNames = [
# "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1",
#]
#optional = [
# ["key", "value"],
#]
#[servers.172-31-4-82.containers]
#type = "lxd" # or "docker"
#includes = ["${running}"]
#excludes = ["container_name", "container_id"]
このテンプレート使ってVulsの設定ファイルを作ってもよい。
-
Slack section
[slack] hookURL = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/abc123/defghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" channel = "#channel-name" #channel = "${servername}" iconEmoji = ":ghost:" authUser = "username" notifyUsers = ["@username"]-
hookURL : Incoming webhook's URL
-
channel : channel name.
channelに${servername}を指定すると、結果レポートをサーバごとに別チャネルにすることが出来る。 以下のサンプルでは、#server1チャネルと#server2チャネルに送信される。スキャン前にチャネルを作成する必要がある。[slack] channel = "${servername}" ...snip... [servers] [servers.server1] host = "172.31.4.82" ...snip... [servers.server2] host = "172.31.4.83" ...snip... -
iconEmoji: emoji
-
authUser: username of the slack team
-
notifyUsers: ここにユーザ名を指定すると、Slackで通知を受け取ることができる。たとえば
["@foo", "@bar"]を指定すると、Slackのテキストに@fooと@barが含まれるのでスマホなどにPush通知が可能。
-
-
Mail section
[email] smtpAddr = "smtp.gmail.com" smtpPort = "587" user = "username" password = "password" from = "from@address.com" to = ["to@address.com"] cc = ["cc@address.com"] subjectPrefix = "[vuls]" -
Default section
[default] #port = "22" #user = "username" #keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" #cpeNames = [ # "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", #] #ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6313"] #optional = [ # ["key", "value"], #] #[servers.172-31-4-82.containers] #type = "lxd" # or "docker" #includes = ["${running}"] #excludes = ["container_name", "container_id"]下記serversセクションで値が指定されなかった場合のデフォルト値
-
servers section
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" #port = "22" #user = "root" #keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" #cpeNames = [ # "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", #] #ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6314"] #optional = [ # ["key", "value"], #] #containers = ["${running}"] #[servers.172-31-4-82.containers] #type = "lxd"serversセクションの値は、defaultセクションの値よりも優先される。 defaultセクションの値を使いたい場合は
#でコメントアウトする。- host: IP address or hostname of target server
- port: SSH Port number
- user: SSH username
- keyPath: SSH private key path
- cpeNames: see Usage: Scan vulnerability of non-OS package
- ignoreCves: CVE IDs that will not be reported. But output to JSON file.
- optional: JSONレポートに含めたい追加情報
- containers: see Usage: Scan Docker containers
Vulsは各サーバにSSHで接続するが、OSコマンドでの接続と、Goのネイティブ実装の2種類のSSH接続方法をサポートしている。 詳細は -ssh-native-insecure option を参照。
また、以下のSSH認証をサポートしている。
- SSH agent
- SSH public key authentication (with password, empty password) SSH Password認証はサポートしていない
$ vuls configtest --help
configtest:
configtest
[-config=/path/to/config.toml]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-ask-key-password]
[-ssh-native-insecure]
[-containers-only]
[-timeout=300]
[-http-proxy=http://192.168.0.1:8080]
[-debug]
[SERVER]...
-ask-key-password
Ask ssh privatekey password before scanning
-config string
/path/to/toml (default "/Users/kotakanbe/go/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls/config.toml")
-containers-only
Test containers only. Default: Test both of hosts and containers
-debug
debug mode
-http-proxy string
http://proxy-url:port (default: empty)
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-ssh-native-insecure
Use Native Go implementation of SSH. Default: Use the external command
-timeout int
Timeout(Sec) (default 300)
configtestサブコマンドは以下をチェックする
- config.tomlで定義されたサーバ/コンテナに対してSSH可能かどうか
- スキャン対象のサーバ上に依存パッケーがインストールされているか
- /etc/sudoers
スキャンするためには、下記のパッケージが必要なので、手動かまたはAnsibleなどのツールで事前にインストールする必要がある。
| Distribution | Release | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 12, 14, 16 | - |
| Debian | 7, 8 | aptitude |
| CentOS | 6, 7 | yum-plugin-changelog |
| Amazon | All | - |
| RHEL | 5 | yum-security |
| RHEL | 6, 7 | - |
| FreeBSD | 10 | - |
| Raspbian | Wheezy, Jessie | - |
スキャン対象サーバに対してパスワードなしでSUDO可能な状態か確認する。
また、requirettyも定義されているか確認する。(--ssh-native-insecureオプションでscanする場合はrequirettyは定義しなくても良い)
Defaults:vuls !requiretty
For details, see -ssh-native-insecure option
スキャン対象サーバ上の/etc/sudoersのサンプル
- CentOS
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/yum --changelog --assumeno update *
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- RHEL 5
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/yum --color=never repolist, /usr/bin/yum --color=never list-security --security, /usr/bin/yum --color=never check-update, /usr/bin/yum --color=never info-security
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- RHEL 6, 7
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/yum --color=never repolist, /usr/bin/yum --color=never --security updateinfo list updates, /usr/bin/yum --color=never check-update, /usr/bin/yum --color=never --security updateinfo updates
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- Debian
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/apt-get update
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- Ubuntu/Raspbian
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/apt-get update
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- Amazon Linux, FreeBSDは今のところRoot権限なしでスキャン可能
$ vuls scan -help
scan:
scan
[-config=/path/to/config.toml]
[-results-dir=/path/to/results]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-cachedb-path=/path/to/cache.db]
[-ssh-native-insecure]
[-containers-only]
[-skip-broken]
[-http-proxy=http://192.168.0.1:8080]
[-ask-key-password]
[-timeout=300]
[-timeout-scan=7200]
[-debug]
[-pipe]
[SERVER]...
-ask-key-password
Ask ssh privatekey password before scanning
-cachedb-path string
/path/to/cache.db (local cache of changelog for Ubuntu/Debian)
-config string
/path/to/toml
-containers-only
Scan containers only. Default: Scan both of hosts and containers
-debug
debug mode
-http-proxy string
http://proxy-url:port (default: empty)
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-pipe
Use stdin via PIPE
-results-dir string
/path/to/results
-skip-broken
[For CentOS] yum update changelog with --skip-broken option
-ssh-native-insecure
Use Native Go implementation of SSH. Default: Use the external command
-timeout int
Number of seconds for processing other than scan (default 300)
-timeout-scan int
Number of second for scaning vulnerabilities for all servers (default 7200)
Vulsは2種類のSSH接続方法をサポートしている。
デフォルトでは、外部SSHコマンドを使ってスキャンする。
SSH Configが使えるので、ProxyCommandを使った多段SSHなどが可能。
CentOSでは、スキャン対象サーバの/etc/sudoersに以下を追加する必要がある(user: vuls)
Defaults:vuls !requiretty
-ssh-native-insecureを指定すると、Goのネイティブ実装 (crypto/ssh) を使ってスキャンする。これは、SSHコマンドがインストールされていない環境でも動作する(Windowsなど)。-ssh-native-insecureは、ホストキーのチェックをしないことに注意すべき。
| SSH key password | -ask-key-password | |
|---|---|---|
| empty password | - | |
| with password | required | or use ssh-agent |
$ vuls scan -ask-key-password
この例では、
- SSH公開鍵認証(秘密鍵パスフレーズ)を指定
- configに定義された全サーバをスキャン
$ vuls scan server1 server2
この例では、
- SSH公開鍵認証(秘密鍵パスフレーズなし)
- ノーパスワードでsudoが実行可能
- configで定義されているサーバの中の、server1, server2のみスキャン
ローカルホストのスキャンする場合、SSHではなく直接コマンドの発行が可能。
config.tomlのhostにlocalhost または 127.0.0.1かつ、portにlocalを設定する必要がある。
For more details, see Architecture section
- config.toml
[servers] [servers.localhost] host = "localhost" # or "127.0.0.1" port = "local"
RHEL/CentOSの場合、スキャン対象サーバの/etc/sudoersに以下を追加する必要がある。(user: vuls)
Defaults:vuls !requiretty
コンテナはSSHデーモンを起動しないで運用するケースが一般的。
Docker Blog:Why you don't need to run SSHd in your Docker containers
Vulsは、DockerホストにSSHで接続し、docker execでDockerコンテナにコマンドを発行して脆弱性をスキャンする。
詳細は、Architecture sectionを参照
-
全ての起動中のDockerコンテナをスキャン
"${running}"をcontainersに指定する[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" [servers.172-31-4-82.containers] includes = ["${running}"] -
あるコンテナのみスキャン
コンテナID、または、コンテナ名を、containersに指定する。
以下の例では、container_name_aと、4aa37a8b63b9のコンテナのみスキャンする
スキャン実行前に、コンテナが起動中か確認すること。もし起動してない場合はエラーメッセージを出力してスキャンを中断する。[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" [servers.172-31-4-82.containers] includes = ["container_name_a", "4aa37a8b63b9"] -
あるコンテナ以外をスキャン
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" [servers.172-31-4-82.containers] includes = ["${running}"] excludes = ["container_name_a", "4aa37a8b63b9"] -
コンテナのみをスキャンする場合(ホストはスキャンしない)
--containers-onlyオプションを指定する
Vulsは、ホストにSSHで接続し、lxc execでLXDコンテナにコマンドを発行して脆弱性をスキャンする。
[servers]
[servers.172-31-4-82]
host = "172.31.4.82"
user = "ec2-user"
keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
[servers.172-31-4-82.containers]
type = "lxd"
includes = ["${running}"]
report:
report
[-lang=en|ja]
[-config=/path/to/config.toml]
[-results-dir=/path/to/results]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-refresh-cve]
[-cvedb-type=sqlite3|mysql]
[-cvedb-path=/path/to/cve.sqlite3]
[-cvedb-url=http://127.0.0.1:1323 or mysql connection string]
[-cvss-over=7]
[-diff]
[-ignore-unscored-cves]
[-to-email]
[-to-slack]
[-to-localfile]
[-to-s3]
[-to-azure-blob]
[-format-json]
[-format-xml]
[-format-one-email]
[-format-one-line-text]
[-format-short-text]
[-format-full-text]
[-gzip]
[-aws-profile=default]
[-aws-region=us-west-2]
[-aws-s3-bucket=bucket_name]
[-azure-account=accout]
[-azure-key=key]
[-azure-container=container]
[-http-proxy=http://192.168.0.1:8080]
[-debug]
[-debug-sql]
[-pipe]
[SERVER]...
-aws-profile string
AWS profile to use (default "default")
-aws-region string
AWS region to use (default "us-east-1")
-aws-s3-bucket string
S3 bucket name
-azure-account string
Azure account name to use. AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT environment variable is used if not specified
-azure-container string
Azure storage container name
-azure-key string
Azure account key to use. AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY environment variable is used if not specified
-config string
/path/to/toml
-cvedb-path string
/path/to/sqlite3 (For get cve detail from cve.sqlite3)
-cvedb-type string
DB type for fetching CVE dictionary (sqlite3 or mysql) (default "sqlite3")
-cvedb-url string
http://cve-dictionary.com:8080 or mysql connection string
-cvss-over float
-cvss-over=6.5 means reporting CVSS Score 6.5 and over (default: 0 (means report all))
-diff
Difference between previous result and current result
-debug
debug mode
-debug-sql
SQL debug mode
-format-full-text
Detail report in plain text
-format-json
JSON format
-format-one-email
Send all the host report via only one EMail (Specify with -to-email)
-format-one-line-text
One line summary in plain text
-format-short-text
Summary in plain text
-format-xml
XML format
-gzip
gzip compression
-http-proxy string
http://proxy-url:port (default: empty)
-ignore-unscored-cves
Don't report the unscored CVEs
-lang string
[en|ja] (default "en")
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-pipe
Use stdin via PIPE
-refresh-cve
Refresh CVE information in JSON file under results dir
-results-dir string
/path/to/results
-to-azure-blob
Write report to Azure Storage blob (container/yyyyMMdd_HHmm/servername.json/xml/txt)
-to-email
Send report via Email
-to-localfile
Write report to localfile
-to-s3
Write report to S3 (bucket/yyyyMMdd_HHmm/servername.json/xml/txt)
-to-slack
Send report via Slack
$ vuls report -format-full-text
172-31-4-82 (amazon 2015.09)
============================
Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14) 103 updatable packages
CVE-2016-5636
-------------
Score 10.0 (High)
Vector (AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C)
Summary Integer overflow in the get_data function in zipimport.c in CPython (aka Python)
before 2.7.12, 3.x before 3.4.5, and 3.5.x before 3.5.2 allows remote attackers
to have unspecified impact via a negative data size value, which triggers a
heap-based buffer overflow.
CWE https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/190.html
NVD https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2016-5636
MITRE https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2016-5636
CVE Details http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-5636
CVSS Claculator https://nvd.nist.gov/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2016-5636&vector=(AV:N/AC:L/...
RHEL-CVE https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2016-5636
ALAS-2016-724 https://alas.aws.amazon.com/ALAS-2016-724.html
Package python27-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-devel-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-devel-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-libs-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-libs-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
Confidence 100 / YumUpdateSecurityMatch
... snip ...
172-31-4-82 (amazon 2015.09)
============================
Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14) 103 updatable packages
172-31-4-82means that it is a scan report ofservers.172-31-4-82defined in cocnfig.toml.(amazon 2015.09)means that the version of the OS is Amazon Linux 2015.09.Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14)means that a total of 94 vulnerabilities exist, and the distribution of CVSS Severity is displayed.103 updatable packagesmeans that there are 103 updateable packages on the target server.
CVE-2016-5636
-------------
Score 10.0 (High)
Vector (AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C)
Summary Integer overflow in the get_data function in zipimport.c in CPython (aka Python)
before 2.7.12, 3.x before 3.4.5, and 3.5.x before 3.5.2 allows remote attackers
to have unspecified impact via a negative data size value, which triggers a
heap-based buffer overflow.
CWE https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/190.html
NVD https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2016-5636
MITRE https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2016-5636
CVE Details http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-5636
CVSS Claculator https://nvd.nist.gov/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2016-5636&vector=(AV:N/AC:L/...
RHEL-CVE https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2016-5636
ALAS-2016-724 https://alas.aws.amazon.com/ALAS-2016-724.html
Package python27-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-devel-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-devel-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-libs-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-libs-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
Confidence 100 / YumUpdateSecurityMatch
-
Scoremeans CVSS Score. -
Vectormeans CVSS Vector -
Summarymeans Summary of the CVE. -
CWEmeans CWE - Common Weakness Enumeration of the CVE. -
NVDMITRECVE DetailsCVSS Caluculator -
RHEL-CVEmeans the URL of OS distributor support. -
Packageshows the package version information including this vulnerability. -
Confidencemeans the reliability of detection.100is highly reliableYumUpdateSecurityMatchis the method of detecting this vulnerability.
-
Item list of
ConfidenceDetection Method Confidence OS Description YumUpdateSecurityMatch 100 RHEL, Amazon Linux Detection using yum-plugin-security ChangelogExactMatch 95 CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian Exact version match between changelog and package version ChangelogLenientMatch 50 Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian Lenient version match between changelog and package version PkgAuditMatch 100 FreeBSD Detection using pkg audit CpeNameMatch 100 All Search for NVD information with CPE name specified in config.toml
The scan results of Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian or CentOS are also output Changelog in TUI or report with -format-full-text. (RHEL, Amazon or FreeBSD will be available in the near future)
The output change log includes only the difference between the currently installed version and candidate version.
tar-1.28-2.1 -> tar-1.28-2.1ubuntu0.1
-------------------------------------
tar (1.28-2.1ubuntu0.1) xenial-security; urgency=medium
* SECURITY UPDATE: extract pathname bypass
- debian/patches/CVE-2016-6321.patch: skip members whose names contain
".." in src/extract.c.
- CVE-2016-6321
-- Marc Deslauriers <marc.deslauriers@ubuntu.com> Thu, 17 Nov 2016 11:06:07 -0500
$ vuls report \
-to-slack \
-cvss-over=7 \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3
With this sample command, it will ..
- Slack通知
- CVSS score が 7.0以上のもののみ通知
事前にAWS関連の設定を行う
- S3バケットを作成 Creating a Bucket
- いずれかの方法でS3リソースへアクセスする設定を行う
- 環境変数を設定 Configuring the AWS Command Line Interface
- Security Credentialsを設定 Configuring the AWS Command Line Interface
- サービス用のIAMロールを作成し、サービス(EC2, AWS Lambda)にアタッチ Creating a Role to Delegate Permissions to an AWS Service
- 環境変数、Security Credentialsを設定する場合はアクセスキーを作成する Managing Access Keys for IAM Users
IAMポリシーの例:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::vuls/*"
}
]
}
$ vuls scan \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 \
-to-s3 \
-format-json \
-aws-region=ap-northeast-1 \
-aws-s3-bucket=vuls \
-aws-profile=default
この例では、
- 結果をJSON形式でS3に格納する。
- バケット名 ... vuls
- リージョン ... ap-northeast-1
- 利用するProfile ... default
事前にAzure Blob関連の設定を行う
- Azure Blob Containerを作成
$ vuls scan \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 \
-to-azure-blob \
-format-xml \
-azure-container=vuls \
-azure-account=test \
-azure-key=access-key-string
この例では、
- 結果をXML形式でBlobに格納する。
- コンテナ名 ... vuls
- ストレージアカウント名 ... test
- アクセスキー ... access-key-string
また、アカウント名とアクセスキーは環境変数でも定義が可能
$ export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT=test
$ export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY=access-key-string
$ vuls scan \
-cve-dictionary-dbpath=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 \
-report-azure-blob \
-azure-container=vuls
Slack, EMail, テキスト出力しないくないCVE IDがある場合は、設定ファイルに定義することでレポートされなくなる。 ただ、JSONファイルには以下のように出力される。
- config.toml
[default]
ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6313"]
[servers.bsd]
host = "192.168.11.11"
user = "kanbe"
ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6314"]- bsd.json
[
{
"ServerName": "bsd",
"Family": "FreeBSD",
"Release": "10.3-RELEASE",
"IgnoredCves" : [
"CveDetail" : {
"CVE-2016-6313",
...
},
"CveDetail" : {
"CVE-2016-6314",
...
}
]
}
]追加情報をJSONに含めることができる。
デフォルトセクションのkey-valueはserversセクションのもので上書きされる。
使い方の例として、AzureリソースグループやVM名を指定しておくことで、結果のJSONをスクリプトでパースしてAzure VMの操作をする、などが可能。
- config.toml
[default]
optional = [
["key1", "default_value"],
["key3", "val3"],
]
[servers.bsd]
host = "192.168.11.11"
user = "kanbe"
optional = [
["key1", "val1"],
["key2", "val2"],
]- bsd.json
[
{
"ServerName": "bsd",
"Family": "FreeBSD",
"Release": "10.3-RELEASE",
.... snip ...
"Optional": [
[ "key1", "val1" ],
[ "key2", "val2" ],
[ "key3", "val3" ]
]
}
]$ vuls report \
-cvedb-type=mysql \
-cvedb-url="user:pass@tcp(localhost:3306)/dbname?parseTime=true"
Vulsは、CPEに登録されているソフトウェアであれば、OSパッケージ以外のソフトウェアの脆弱性もスキャン可能。
たとえば、自分でコンパイルしたものや、言語のライブラリ、フレームワークなど。
-
CPEの検索方法
-
NVD: Search Common Platform Enumerations (CPE)
Check CPE Naming Format: 2.2 -
go-cpe-dictionary is a good choice for geeks.
ターミナル上でCPEをインクリメンタル検索出来るツール
-
-
Configuration
例えば、Ruby on Rails v4.2.1の脆弱性を検知したい場合は、serversセクションに以下のように定義する。[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" cpeNames = [ "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", ]
Usage: Integrate with OWASP Dependency Check to Automatic update when the libraries are updated (Experimental)
OWASP Dependency check は、プログラミング言語のライブラリを特定し(CPEを推測)、公開済みの脆弱性を検知するツール。
VulsとDependency Checkを連携させる方法は以下
-
Dependency Checkを、--format=XMLをつけて実行する
-
そのXMLをconfig.toml内で以下のように定義する
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" dependencyCheckXMLPath = "/tmp/dependency-check-report.xml"
VulsとDependency Checkを連携すると以下の利点がある
- ライブラリを更新した場合に、config.tomlのCPEの定義を変更しなくても良い
- Vulsの機能でSlack, Emailで通知可能
- 日本語のレポートが可能
- Dependency Checkは日本語レポートに対応していない
tui:
tui
[-cvedb-type=sqlite3|mysql]
[-cvedb-path=/path/to/cve.sqlite3]
[-cvedb-url=http://127.0.0.1:1323 or mysql connection string]
[-refresh-cve]
[-results-dir=/path/to/results]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-debug]
[-debug-sql]
[-pipe]
-cvedb-path string
/path/to/sqlite3 (For get cve detail from cve.sqlite3)
-cvedb-type string
DB type for fetching CVE dictionary (sqlite3 or mysql) (default "sqlite3")
-cvedb-url string
http://cve-dictionary.com:8080 or mysql connection string
-debug
debug mode
-debug-sql
debug SQL
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-pipe
Use stdin via PIPE
-refresh-cve
Refresh CVE information in JSON file under results dir
-results-dir string
/path/to/results
Key binding is below.
| key | |
|---|---|
| TAB | move cursor among the panes |
| Arrow up/down | move cursor to up/down |
| Ctrl+j, Ctrl+k | move cursor to up/down |
| Ctrl+u, Ctrl+d | page up/down |
For details, see https://github.com/future-architect/vuls/blob/master/report/tui.go
- Display the list of scan results.
$ vuls history
20160524_1950 scanned 1 servers: amazon2
20160524_1940 scanned 2 servers: amazon1, romantic_goldberg
- Display the result of scan 20160524_1949
$ vuls tui 20160524_1950
- Display the result of scan 20160524_1948
$ vuls tui 20160524_1940
$ vuls history | peco | vuls tui -pipe
Run go-cve-dictionary as server mode before scanning on 192.168.10.1
$ go-cve-dictionary server -bind=192.168.10.1 -port=1323
Run Vuls with -cve-dictionary-url option.
$ vuls scan -cve-dictionary-url=http://192.168.0.1:1323
see go-cve-dictionary#usage-fetch-nvd-data
see go-cve-dictionary#usage-fetch-jvn-data
fetchjvn -> fetchnvdの順番だとすごく時間がかかる (2016年9月現在)
fetchnvd -> fetchjvnの順番で実行すること
$ for i in `seq 2002 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchnvd -years $i; done
$ for i in `seq 1998 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchjvn -years $i; done
の順でやった場合、最初のコマンドが15分程度、二つ目のコマンドが10分程度(環境依存)
$ for i in `seq 1998 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchjvn -years $i; done
$ for i in `seq 2002 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchnvd -years $i; done
の順で行うと、最初のコマンドは1時間くらいで終わるが二つ目のコマンドが21時間かかることもある(環境依存)。
$ vuls scan -lang=ja
Scan時にlang=jaを指定すると脆弱性レポートが日本語になる
slack, emailは日本語対応済み TUIは日本語表示未対応
- Update go-cve-dictionary
If the DB schema was changed, please specify new SQLite3 or MySQL DB file.
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe/go-cve-dictionary
$ git pull
$ mv vendor /tmp/foo
$ make install
- Update vuls
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls
$ git pull
$ mv vendor /tmp/bar
$ make install
- バイナリファイルは
$GOPATH/bin以下に作成される
-
go get時にエラーが出る
Gitをv2にアップデートしてお試しを
see https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/mgo-users/rO1-gUDFo_g -
HTTP Proxy サポート プロキシ環境下では、-http-proxyオプションを指定
-
go-cve-dictionaryのデーモン化
Use Systemd, Upstart or supervisord, daemontools... -
NVD, JVNの脆弱性データベースの自動更新
CRONなどを使えば可能 -
自動定期スキャン
CRONなどを使い、自動化のためにsudoと、秘密鍵のパスワードなしでも実行可能なようにする- スキャン対象サーバの /etc/sudoers に NOPASSWORD を設定する
- 秘密鍵パスフレーズなしの公開鍵認証か、ssh-agentを使う
-
スキャンが重く感じる
vulsのスキャン対象に脆弱性が溜まりすぎると実行時間が長くなります 脆弱性のある状態は溜めすぎないようにしましょう -
クロスコンパイル
$ cd /path/to/your/local-git-reporsitory/vuls $ GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o vuls.amd64 -
Logging
Log is under /var/log/vuls/ -
Debug
Run with --debug, --sql-debug option. -
Adjusting Open File Limit
Riak docs is awesome. -
Does Vuls accept ssh connections with fish-shell or old zsh as the login shell?
No, Vuls needs a user on the server for bash login. see also #8 -
Windows
Use Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer. MBSA
-
k1LoW/ssh_config_to_vuls_config
ssh_config to vuls config TOML format -
usiusi360/vulsrepo
VulsRepo is visualized based on the json report output in vuls.
Youtube
kotakanbe (@kotakanbe) created vuls and these fine people have contributed.
- fork a repository: github.com/future-architect/vuls to github.com/you/repo
- get original code: go get github.com/future-architect/vuls
- work on original code
- add remote to your repo: git remote add myfork https://github.com/you/repo.git
- push your changes: git push myfork
- create a new Pull Request
Please see CHANGELOG.
Please see LICENSE.